Abstract
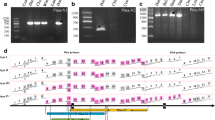
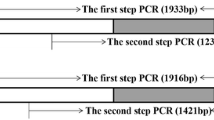
Kernel hardness is one of the most important factors determining the milling and processing quality of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). In the present study, 267 wheat cultivars and advanced lines from the Yellow and Huai Valley of China, CIMMYT, Russia and Ukraine were used for identification of SKCS (Single Kernel Characterization System) hardness and puroindoline alleles. Results indicated that Pinb-D1b is the most popular genotype in wheat cultivars from the Yellow and Huai Valley, Russia and Ukraine, whereas PINA null is a predominant genotype in wheat cultivars and advanced lines from CIMMYT. Molecular characterization of PINA-null alleles indicated that one Chinese landrace Chiyacao had the allele Pina-D1l with a single nucleotide C deletion at position 265 in Pina coding region based on sequencing results, and 35 of 39 PINA-null alleles belonged to Pina-D1b according to PCR amplification with the sequence-tagged site (STS) marker Pina-N developed previously. The remaining three cultivars (Jiangdongmen, Heshangtou and Hongquanmang from China) with PINA-null alleles were characterized at the DNA level by a primer walking strategy, and the results showed that all three cultivars with PINA-null alleles possessed a uniform 10,415-bp deletion from −5,117 bp to +5,298 bp (ATG codon references zero), designated as Pina-D1r. Correspondingly, an STS marker Pina-N2 with an expected fragment size of 436-bp spanning the 10,415-bp deletion was developed for detection of the Pina-D1r allele. This study provided a useful molecular marker for straightforward detection of one of the PINA-null alleles and would also be helpful to further understand the molecular and genetic basis of kernel hardness in bread wheat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behave M, Morris CF (2008a) Molecular genetics of puroindolines and related genes: allelic diversity in wheat and other grasses. Plant Mol Biol 66:205–219
Behave M, Morris CF (2008b) Molecular genetics of puroindolines and related genes: regulation of expression, membrane binding properties and applications. Plant Mol Biol 66:221–231
Bihan TL, Blochet JE, Desormeaux A, Marion D, Pezolet M (1996) Determination of the secondary structure and conformation of puroindolines by infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Biochem 35:12712–12722
Cane K, Spackman M, Eagles HA (2004) Puroindoline genes and their effects on grains quality traits in southern Australian wheat cultivars. Aust J Agric Res 55:89–95
Chang C, Zhang HP, Xu J, Li WH, Liu GT, You MS, Li BY (2006) Identification of allelic variations of puroindoline genes controlling grain hardness in wheat using a modified denaturing PAGE. Euphytica 152:225–234
Chantret N, Salse J, Sabot F, Rahman S, Bellec A, Laubin B, Dubois I, Dossat C, Sourdille P, Joudrier P, Gautier MF, Cattolico L, Bechert M, Aubourg S, Weissenbach J, Caboche M, Bernard M, Leroy P, Chalhoub B (2005) Molecular basis of evolutionary events that shaped the Hardness locus in diploid and polyploid wheat species (Triticum and Aegilops). Plant Cell 17:1033–1045
Chen F, He ZH, Xia XC, Lillemo M, Morris CF (2005) A new puroindoline b mutation presented in Chinese winter wheat cultivar Jingdong 11. J Cereal Sci 42:267–269
Chen F, He ZH, Xia XC, Xia LQ, Zhang XY, Lillemo M, Morris C (2006) Molecular and biochemical characterization of puroindoline a and b alleles in Chinese landraces and historical cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 112:400–409
Chen F, He ZH, Chen DS, Zhang CL, Xia XC (2007a) Influence of puroindoline allele on milling, steamed bread, noodles and pan bread in common spring wheat. J Cereal Sci 45:59–66
Chen F, He ZH, Chen DS, Zhang CL, Xia XC (2007b) Allelic variation of puroindoline gene in Chinese spring wheat. Sci Agri Sin 40:217–224 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen F, Yu YX, He ZH, Xia XC (2007c) Prevalence of a novel puroindoline allele in Yunnan endemic wheats (Triticum aestivum ssp Yunnanense King). Euphytica 156:39–46
Chen F, Beecher B, Morris CF (2010a) Physical mapping and a new variant of Puroindoline b-2 genes in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 120:745–751
Chen F, Zhang FY, Cheng XY, Morris CF, Xu HX, Dong ZD, Zhan KH, Cui DQ (2010b) Association of Puroindoline b-B2 variants with grain traits yield components and flag leaf size in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties of the Yellow and Huai Valleys of China. J Cereal Sci 52:247–253
Chen F, Xu HX, Zhang FY, Xia XC, He ZH, Wang DW, Dong ZD, Zhan KH, Cheng XY, Cui DQ (2010b) Physical mapping of puroindoline b-2 genes and molecular characterization of a novel variant in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L.). Mol Breed. doi: 10.1007/s11032-010-9469-2
Chen F, Zhang FY, Morris CF, He ZH, Xia XC, Cui DQ (2010d) Molecular characterization of the Puroindoline a-D1b allele and development of an STS marker in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Cereal Sci 52:80–82
Dubreil L, Méliande S, Chiron H, Compoint JP, Quillien L, Branlard G, Marion D (1998) Effect of puroindolines on the breadmaking properties of wheat flour. Cereal Chem 75:2222–2229
Giroux MJ, Morris CF (1997) A glycine to serine change in puroindoline b is associated with wheat grain hardness and low levels of starch-surface friabilin. Theor Appl Genet 95:857–864
Giroux MJ, Morris CF (1998) Wheat grain hardness results from highly conserved mutations in friabilin components puroindoline a and b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6262–6266
Giroux MJ, Talbert L, Debrrah K, Habernicht, Lanning S, Hemphill A, Martin JM (2000) Association of puroindolines sequence type and grain hardness in hard red spring wheat. Crop Sci 40:370–374
Greenwell P, Schofield JD (1986) A starch granule protein associated with endosperm softness in wheat. Cereal Chem 63:379–380
Ikeda TM, Ohnishi N, Nagamine T, Oda S, Hisatomi T, Yano H (2005) Identification of new puroindoline genotypes and their protein products among wheat cultivars. J Cereal Sci 41:1–6
Li GY, He ZH, Lillemo M, Sun QX, Xia XC (2008) Molecular characterization of allelic variations at Pina and Pinb loci in Shandong wheat landraces, historical and current cultivars. J Cereal Sci 47:510–517
Lillemo M, Chen F, Xia XC, William M, Peña RJ, Trethowan R, He ZH (2006) Puroindoline grain hardness alleles in CIMMYT bread wheat. J Cereal Sci 44:86–92
Ma DY, Zhang Y, Xia XC, Morris CF, He ZH (2009) Milling and Chinese raw white noodle qualities of common wheat near-isogenic lines differing in puroindoline b allele. J Cereal Sci 50:126–130
Martin JM, Frohberg RC, Morris CF, Talbert LE, Giroux MJ (2001) Milling and bread baking traits associated with puroindoline sequence type in hard red spring wheat. Crop Sci 41:228–234
McIntosh RA, Devos KM, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ, Morris CF, Appels R, Anderson OD (2007) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2007 supplement. Published online at: http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/wgc/2007upd.html
Morris CF (2002) Puroindolines: the molecular genetic basis of wheat grain hardness. Plant Mol Biol 48:633–647
Morris CF, Bhave M (2008) Reconciliation of D-genome puroindoline allele designations with current DNA sequence data. J Cereal Sci 48:277–287
Morris CF, Massa AN (2003) Puroindoline genotype of the US National Institute of Standards & Technology Reference Material 8441, wheat hardness. Cereal Chem 80:674–678
Morris CF, Lillemo M, Simeone MC, Giroux MJ, Babb SL, Kimberlee KK (2001) Prevalence of puroindoline grain hardness genotypes among historically significant North American spring and winter wheats. Crop Sci 41:218–228
Wang J, Sun JZ, Liu DC, Yang WL, Wang DW, Tong YP, Zhang AM (2008a) Analysis of Pina and Pinb alleles in the micro-core collections of Chinese wheat germplasm by Ecotilling and identification of a novel Pinb allele. J Cereal Sci 48:836–842
Wang L, Li GY, Xia XC, He ZH, Mu PY (2008b) Molecular characterization of Pina and Pinb allelic variations in Xinjiang landraces and commercial wheat cultivars. Euphytica 164:745–752
Wilkinson M, Wan Y, Tosi P, Leverington M, Snape J, Mitchel RAC, Shewry PR (2008) Identification and genetic mapping of variant forms of puroindoline b expressed in developing wheat grain. J Cereal Sci 48:722–728
Xia L, Chen F, He Z, Chen X, Morris CF (2005) Occurrence of puroindoline alleles in Chinese winter wheats. Cereal Chem 82:38–43
Zhuang QS (2003) Chinese wheat improvement and pedigree analysis. Chinese Agric Press, Beijing, pp 1–681 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation (31000708), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20104105120003) and National 948 project (2010-Z21) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Zhang, F.Y., Xia, XC. et al. Distribution of puroindoline alleles in bread wheat cultivars of the Yellow and Huai valley of China and discovery of a novel puroindoline a allele without PINA protein. Mol Breeding 29, 371–378 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9553-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9553-2