Abstract
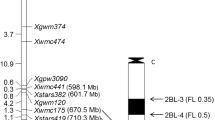
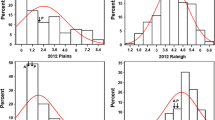
Powdery mildew significantly affects grain yield and end-use quality of winter wheat in the southern Great Plains. Employing resistance resources in locally adapted cultivars is the most effective means to control powdery mildew. Two types of powdery mildew resistance exist in wheat cultivars, i.e., qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative resistance is controlled by major genes, is race-specific, is not durable, and is effective in seedlings and in adult plants. Quantitative resistance is controlled by minor genes, is non-race-specific, is durable, and is predominantly effective in adult plants. In this study, we found that the segregation of powdery mildew resistance in a population of recombinant inbred lines developed from a cross between the susceptible cultivar Jagger and the resistant cultivar 2174 was controlled by a major QTL on the short arm of chromosome 1A and modified by four minor QTLs on chromosomes 1B, 3B, 4A, and 6D. The major QTL was mapped to the genomic region where the Pm3 gene resides. Using specific PCR markers for seven Pm3 alleles, 2174 was found to carry the Pm3a allele. Pm3a explained 61% of the total phenotypic variation in disease reaction observed among seedlings inoculated in the greenhouse and adult plants grown in the field and subjected to natural disease pressure. The resistant Pm3a allele was present among 4 of 31 cultivars currently being produced in the southern Great Plains. The genetic effects of several minor loci varied with different developmental stages and environments. Molecular markers associated with these genetic loci would facilitate incorporating genetic resistance to powdery mildew into improved winter wheat cultivars.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett AGA (1984) Resistance to powdery mildew in wheat: a review of its use in culture and breeding programs. Plant Pathol 33:279–300. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.1984.tb01324.x
Carver BF, Krenzer EG, Hunger RM, Porter DR, Smith EL, Klatt AR, Verchot-Lubicz J, Rayas-Duarte P, Guenzi AC, Bai G, Martin BC (2004) Registration of ‘Ok102’. Wheat Crop Sci 44:1468–1469
Carver BF, Hunger RM, Edwards JT, Porter DR, Peeper TF, Seabourn BW, Rayas-Duarte P, Klatt AR, Martin BC (2007) Registration of ‘Okfield’. Wheat J Plant Registrations 1:102–103. doi:10.3198/jpr2007.03.0132crc
Ceoloni C, Del Signore G, Ercoli L, Donini P (1992) Locating the alien chromatin segment in common wheat-Aegilops longissima mildew resistant transfers. Hereditas 116:239–245. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1992.tb00148.x
Chen Y, Carver BF, Wang S, Zhang F, Yan L (2009) Genetic loci associated with stem elongation and winter dormancy release in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 118:881–889. doi 10.1007/s00122-008-0946-5
Donini P, Koebner RMD, Ceoloni C (1995) Cytogenetic and molecular mapping of wheat—Aegilops longissima chromatin breakpoints in powdery mildew-resistant introgression lines. Plant J 91:738–743
Edwards JT, Carver BF, Payton ME (2007) Relationship of first hollow stem and heading in winter wheat. Crop Sci 47:2074–2077. doi:10.2135/cropsci2007.01.0057sc
Everts KL, Leath S, Finney PL (2001) Impact of powdery mildew and leaf rust on milling and baking quality of soft red winter wheat. Plant Dis 85(4):423–429. doi:10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.4.423
Feuillet C, Schachermayr G, Keller B (1997) Molecular cloning of a new receptor-like kinase gene encoded at the Lr10 disease resistance locus of wheat. Plant J 11:245–342. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11010045.x
Flor HH (1956) The complementary genic systems in flax and flax rust. Adv Genet 8:29–54. doi:10.1016/S0065-2660(08)60498-8
Griffey CA, Das MK (1994) Inheritance of adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Knox 62 and Massey winter wheats. Crop Sci 34:641–646
Griffey CA, Das MK, Stromberg EL (1993) Effectiveness of adult plant resistance in reducing loss to powdery mildew in winter wheat. Plant Dis 77:618–622
Hautea RA, Coffman WR, Sorrells ME, Bergstrom GC (1987) Inheritance of partial resistance to powdery mildew in spring wheat. Theor Appl Genet 73:609–615. doi:10.1007/BF00289202
Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ (2002) Breeding for powdery mildew resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). In: Belanger RR, Bushnell WR, Dik AJ, Carver TLW (eds) The powdery mildews, a comprehensive treatise. St. Paul, MN, pp 219–238
Hsam SLK, Huang XQ, Ernst F, Hartl L, Zeller FJ (1998) Chromosome location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). 5. Alleles at the Pm1 locus. Theor Appl Genet 96:1129–1134. doi:10.1007/s001220050848
Hsam SLK, Lapochkina IF, Zeller FJ (2003) Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). 8. Gene Pm32 in a wheat-Aegilops speltoides translocation line. Euphytica 133(3):367–370. doi:10.1023/A:1025738513638
Huang XQ, Röder M (2004) Molecular mapping of powdery mildew resistance genes in wheat: a review. Euphytica 137:203–223. doi:10.1023/B:EUPH.0000041576.74566.d7
Jia J, Devos KM, Chao S, Miller TE, Reader SM, Gale MD (1996) RFLP-based maps of the homoeologous group-6 chromosomes of wheat and their application in the tagging of Pm12, a powdery mildew resistance gene transferred from Aegilops speltoides to wheat. Theor Appl Genet 92(5):559–565
Johnson JW, Baenziger PS, Yamazaki WT, Smith RT (1979) Effects of powdery mildew on yield and quality of isogenic lines of ‘Chancellor’ wheat. Crop Sci 19:349–352
Kaur N, Street K, Mackay M, Yahiaoui N, Keller B (2008) Molecular approaches for characterization and use of natural disease resistance in wheat. Eur J Plant Pathol 121:387–397. doi:10.1007/s10658-007-9252-3
Keller M, Keller B, Schachermayr G, Winzeler M, Schmid JE, Stamp P, Messmer MM (1999) Quantitative trait loci for resistance against powdery mildew in a segregating wheat × spelt population. Theor Appl Genet 98:903–912. doi:10.1007/s001220051149
Leath S, Bowen KL (1989) Effects of powdery mildew, triadimenol seed treatment, and triadimefon foliar sprays on yield of winter wheat in North Carolina. Phytopathology 79(12):152–155. doi:10.1094/Phyto-79-152
Liu S, Anderson A (2003) Targeted molecular mapping of a major wheat QTL for Fusarium head blight resistance using wheat ESTs and synteny with rice. Genome 46:817–823. doi:10.1139/g03-066
Liu S, Griffey CA, Saghai Maroof MA (2001) Identification of molecular markers associated with adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat cultivar Massey. Crop Sci 141(4):1268
Lutz J, Hsam SLK, Limpert E, Zeller FJ (1995) Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance genes in Triticum aestivum L. (common wheat). 2. Genes Pm2 and Pm19 from Aegilops squarrosa L. Heredity 74:152–156. doi:10.1038/hdy.1995.22
Menzies JG, MacNeil BH (1986) Asexual recombination in Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici. Can J Plant Pathol 8:400–404
Mingeot D, Chantret N, Baret PV, Dekeyser A, Boukhatem N, Sourdill P, Doussinault G, Jacquemin JM (2002) Mapping QTL involved in adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in the winter wheat line RE714 in two susceptible genetic backgrounds. Plant Breed 121(2):133–140. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0523.2002.00679.x
Miranda LM, Murphy JP, Marshall D, Leath S (2006) Pm34: a new powdery mildew resistance gene transferred from Aegilops tauschii Coss. to common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113(8):1497–1504. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0397-9
Miranda LM, Murphy JP, Marshall D, Cowger C, Leath S (2007) Chromosomal location of Pm35, a novel Aegilops tauschii derived powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed into common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 114(8):1451–1456. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0530-4
Powers HR, Sando WJ (1960) Genetic control of the host-parasite relationship in wheat powdery mildew. Phytopathology 50:454–457
Qiu YC, Zhou RH, Kong XY, Zhang SS, Jia JZ (2005) Microsatellite mapping of a Triticum urartu Tum. derived powdery mildew resistance gene transferred to common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:1524–1531. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0081-5
Roberts JJ, Caldwell RM (1970) General resistance (slow mildewing) to Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici in Knox wheat. Phytopathology 60:1310
Shaner G (1973) Evaluation of slow-mildewing resistance of Knox wheat in the field. Phytopathology 63:867–872
Shi AN, Leath S, Murphy JP (1998) A major gene for powdery mildew resistance transferred to common wheat from wild Einkorn wheat. Phytopathology 88(2):144–147. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.1998.88.2.144
Srichumpa P, Brunner S, Keller B, Yahiaoui N (2005) Allelic series of four powdery mildew resistance genes at the Pm3 locus in hexaploid bread wheat. Plant Physiol 139:885–895. doi:10.1104/pp.105.062406
Tommasini L, Yahiaoui N, Srichumpa P, Keller B (2006) Development of functional markers specific for seven Pm3 resistant alleles and their validation in the bread wheat gene pool. Theor Appl Genet 114:165–175. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0420-1
Wolfe MS (1984) Trying to understand and control powdery mildew. Plant Pathol 33:451–466. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.1984.tb02868.x
Xu XY, Bai GH, Carver BF, Shaner GE, Hunger RM (2006) Molecular characterization of a powdery mildew resistance gene in wheat cultivar Suwon92. Phytopathology 96(5):496–500. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-96-0496
Yahiaoui N, Srichumpa P, Dudler R, Keller B (2004) Genome analysis at different ploidy levels allows cloning of the powdery mildew resistance gene Pm3b from hexaploid wheat. Plant J 37:528–538. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01977.x
Yahiaoui N, Brunner S, Keller B (2006) Rapid generation of new powdery mildew resistance genes after wheat domestication. Plant J 47:85–98. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02772.x
Zhu Z, Zhou R, Kong X, Dong Y, Jia J (2005) Microsatellite markers linked to 2 powdery mildew resistance genes introgressed from Triticum carthlicum accession PS5 into common wheat. Genome 48(4):585–590. doi:10.1139/g05-016
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Initiative of the USDA-Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CAP grant 2006-55606-16629), by the Oklahoma Wheat Research Foundation, and by the Oklahoma Center of Advanced Science and Technology (OCAST). This research project was partially funded by the Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Hunger, R.M., Carver, B.F. et al. Genetic characterization of powdery mildew resistance in U.S. hard winter wheat. Mol Breeding 24, 141–152 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9279-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9279-6