Abstract
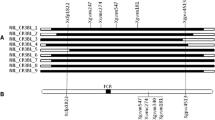
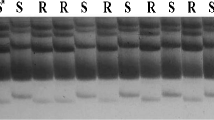
Downy mildew caused by the fungus Peronospora parisitica is a serious threat to members of the Brassicaceae family. Annually, a substantial loss of yield is caused by the widespread presence of this disease in warm and humid climates. The aim of this study was to localize the genetic factors affecting downy mildew resistance in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). To achieve this goal, we improved a preexisting genetic map of a doubled-haploid population derived from a cross between two diverse Chinese cabbage lines, 91-112 and T12-19, via microspore culture. Microsatellite simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers, isozyme markers, sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers, sequence-characterized amplified region markers and sequence-tagged-site markers were integrated into the previously published map to construct a composite Chinese cabbage map. In this way, the identities of linkage groups corresponding to the Brassica A genome reference map were established. The new map contains 519 markers and covers a total length of 1,070 cM, with an average distance between markers of 2.06 cM. All markers were designated as A1–A10 through alignment and orientation using 55 markers anchored to previously published B. rapa or B. napus reference maps. Of the 89 SSR markers mapped, 15 were newly developed from express sequence tags in Genbank. The phenotypic assay indicated that a single major gene controls seedling resistance to downy mildew, and that a major QTL was detected on linkage group A8 by both interval and MQM mapping methods. The RAPD marker K14-1030 and isozyme marker PGM flanked this major QTL in a region spanning 2.9 cM, and the SSR marker Ol12G04 was linked to this QTL by a distance of 4.36 cM. This study identified a potential chromosomal segment and tightly linked markers for use in marker-assisted selection to improve downy mildew resistance in Chinese cabbage.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnola B, Silue D, Boury S (2000) Identification of RAPD markers of downy mildew (Peronospora parasitica) resistance gene in broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica). In: King GJ (ed) Proceedings of the 3rd ISHS international symposium on Brassicas, Horticulture Research International, Wellesbourne, 5–9 September, p 64
Agrama HA, Moussa ME, Naser ME, Tarek MA, Ibrahim AH (1999) Mapping of QTL for downy mildew resistance in maize. Theor Appl Genet 99:519–523. doi:10.1007/s001220051265
Ajisaka H, Kuginuki Y, Yui S, Enomoto S, Hirai M (2001) Identification and mapping of a quantitative trait locus controlling extreme late bolting in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp pekinensis syn. campestris L.) using bulked segregant analysis—a QTL controlling extreme late bolting in Chinese cabbage. Euphytica 118:75–81. doi:10.1023/A:1004023532005
Beavis WD, Grant D (1991) A linkage map based on information from 4 F2 populations of maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 82:636–644. doi:10.1007/BF00226803
Beckmann JS, Soller M (1986) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms and genetic improvement of agriculture species. Euphytica 35:111–124. doi:10.1007/BF00028548
Choi SR, Teakle GR, Plaha P, Kim JH, Allender CJ, Beynon E, Piao ZY, Soengas P, Han TH, King GJ, Barker GC, Hand P, Lydiate DJ, Batley J, Edwards D, Koo DH, Bang JW, Park BS, Lim YP (2007) The reference genetic linkage map for the multinational Brassica rapa genome sequencing project. Theor Appl Genet 115:777–792. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0608-z
Chowdhury AK, Srinives P, Saksoong P, Tongpamnak P (2002) RAPD markers linked to resistance to downy mildew disease in soybean. Euphytica 128:55–60. doi:10.1023/A:1020635501050
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Chyi Y-S, Hoenecke ME, Sernyk JL (1992) A genetic linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci for Brassica rapa (syn. campestris). Genome 35:746–757
Cloutier S, Cappadocia M, Landry BS (1995) Study of microspore-culture responsiveness in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) by comparative mapping of a F2 population and two microspore-derived populations. Theor Appl Genet 91:841–847. doi:10.1007/BF00223890
Cui XM, Dong YX, Hou XL, Cheng Y, Zhang JY, Jin MF (2008) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis and transferability among related species. Agric Sci China 7:19–31. doi:10.1016/S1671-2927(08)60046-2
Farinhó M, Coelho P, Monteiro A, Leitão J (2007) SCAR and CAPS markers flanking the Brassica oleracea L. Pp523 downy mildew resistance locus demarcate a genomic region syntenic to the top arm end of Arabidopsis thaliana L. chromosome 1. Euphytica 157:215–221. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9414-6
Ferreira ME, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1994) RFLP mapping of Brassica napus using doubled haploid lines. Theor Appl Genet 89:615–621. doi:10.1007/BF00222456
Foisset N, Delourme R, Barret P, Hubert N, Landry BS, Renard M (1996) Molecular-mapping analysis in Brassica napus using isozyme, RAPD and RFLP markers on a doubled haploid progeny. Theor Appl Genet 93:1017–1025. doi:10.1007/BF00230119
George ML, Prasanna BM, Rathore RS, Setty TA, Kasim F, Azrai M, Vasal S, Balla O, Hautea D, Canama A, Regalado E, Vargas M, Khairallah M, Jeffers D, Hoisington D (2003) Identification of QTLs conferring resistance to downy mildews of maize in Asia. Theor Appl Genet 107:544–551. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1280-6
Gosselin I, Zhou Y, Bousquet J, Isabel N (2002) Megagametophyte-derived linkage maps of white spruce (Picea glauca) based on RAPD, SCAR and ESTP markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:987–997. doi:10.1007/s00122-001-0823-y
Hirai M, Harada T, Kubo N, Tsukada M (2004) A novel locus for clubroot resistance in Brassica rapa and its linkage markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:639–643. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1475-x
Kasha KJ, Kao KN (1970) High frequency haploid production in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Nature 225:874–876. doi:10.1038/225874a0
Kim JS, Chung TY, King GJ, Jin M, Yang TJ, Jin YM, Kim HI, Park BS (2006) A sequence-tagged linkage map of Brassica rapa. Genetics 174:29–39. doi:10.1534/genetics.106.060152
Kole C, Kole P, Vogelzang R, Osborn TC (1997) Genetic linkage map of a Brassica rapa recombinant inbred population. J Hered 88:553–557
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lim KB, de Jong H, Yang TJ, Park JY, Kwon SJ, Kim JS, Lim MH, Kim JA, Jin M, Jin YM, Kim SH, Lim YP, Bang JW, Kim HI, Park BS (2005) Characterization of rDNAs and tandem repeats in the heterochromatin of Brassica rapa. Mol Cells 19:436–444
Ling AE, Kaur J, Burgess B, Hand M, Hopkins CJ, Li X, Love CG, Vardy M, Walkiewicz M, Spangenberg G, Edwards D, Batley J (2007) Characterization of simple sequence repeat markers derived in silico from Brassica rapa bacterial artificial chromosome sequences and their application in Brassica napus. Mol Ecol Notes 7:273–277. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01578.x
Lowe AJ, Moule C, Trick M, Edwards KJ (2004) Efficient large scale development of microsatellites for marker and mapping applications in Brassica crop species. Theor Appl Genet 108:1103–1112. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1522-7
Lu G, Cao JS, Chen H (2002) Genetic linkage map of Brassica campestris L. using AFLP and RAPD markers. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 3:600–605. doi:10.1631/jzus.2002.0600
Lyttle TW (1991) Segregation distorters. Annu Rev Genet 25:511–557. doi:10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002455
Murray HG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of higher weight DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321. doi:10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Nair SK, Prasanna BM, Garg A, Rathore RS, Setty TA, Singh NN (2005) Identification and validation of QTLs conferring resistance to sorghum downy mildew (Peronosclerospora sorghi) and Rajasthan downy mildew (P. heteropogoni) in maize. Theor Appl Genet 110:1384–1392. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-1936-5
Nicolas A, Rossignol JL (1983) Gene conversion: point mutation heterozygosities lower heteroduplex formation. EMBO J 2:2265–2270
Nozaki T, Kumazaki A, Koba T, Ishikawa K, Ikehashi H (1997) Linkage analysis among loci for RAPDs, isozymes and some agronomic traits in Brassica campestris L. Euphytica 95:115–123. doi:10.1023/A:1002981208509
Piao ZY, Deng YQ, Choi SR, Park YJ, Lim YP (2004) SCAR and CAPS mapping of CRb, a gene conferring resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Theor Appl Genet 108:1458–1465. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1577-5
Piquemal J, Cinquin E, Couton F, Rondeau C, Seignoret E, Doucet I, Perret D, Villeger MJ, Vincourt P, Blanchard P (2005) Construction of an oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) genetic map with SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 111:1514–1523. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0080-6
Pradhan AK, Gupta V, Mukhopadhyay A, Arumugam N, Sodhi YS, Pental D (2003) A high-density linkage map in Brassica juncea (Indian mustard) using AFLP and RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:607–614
Qi X, Stam P, Lindhout P (1996) Comparison and integration of four barley genetic maps. Genome 39:379–394. doi:10.1139/g96-049
Saito M, Kubo N, Matsumoto S, Suwabe K, Tsukada M, Hirai M (2006) Fine mapping of the clubroot resistance gene, Crr3, in Brassica rapa. Theor Appl Genet 114:81–91. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0412-1
Soengas P, Hand P, Vicente JG, Pole JM, Pink DAC (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica rapa. Theor Appl Genet 114:637–645. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0464-2
Song KM, Suzuki JY, Slocum MK, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1991) A linkage map of Brassica rapa (syn. campestris) based on restriction fragment length polymorphism loci. Theor Appl Genet 82:296–304. doi:10.1007/BF02190615
Song K, Slocum MK, Osborn TC (1995) Molecular marker analysis of genes controlling morphological variation in Brassica rapa (syn. campestris). Theor Appl Genet 90:1–10
Suwabe K, Iketani H, Nunome T, Kage T, Hirai M (2002) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 104:1092–1098. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0875-7
Suwabe K, Tsukazaki H, Iketani H, Hatakeyama K, Fujimura M, Nunome T, Fukuoka H, Matsumoto S, Hirai M (2003) Identification of two loci for resistance to clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae Woronin) in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 107:997–1002
Suwabe K, Iketani H, Nunome T, Ohyama A, Hirai M, Fukuoka H (2004) Characteristics of microsatellites in Brassica rapa genome and their potential utilization for comparative genomics in cruciferae. Breed Sci 54:85–90. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.54.85
Suwabe K, Tsukazaki H, Iketani H, Hatakeyama K, Kondo M, Fujimura M, Nunome T, Fukuoka H, Hirai M, Matsumoto M (2006) SSR-based comparative genomics between Brassica rapa and Arabidopsis thaliana: the genetic origin of clubroot resistance. Genetics 173:309–319. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.038968
Szewc-McFadden AK, Kresovich S, Bliek SM, Mitchell SE, McFerson JR (1996) Identification of polymorphic, conserved simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in cultivated Brassica species. Theor Appl Genet 93:534–538. doi:10.1007/BF00417944
Tanhuanpää PK, Vilkki JP, Vikki HJ (1996) Mapping a QTL for oleic acid concentration in spring turnip rape (Brassica rapa ssp. oleifera). Theor Appl Genet 92:952–956. doi:10.1007/BF00224034
Tanksley SD, Young ND, Paterson AH, Bonierbale MW (1989) RFLP mapping in plant breeding: new tools for an old science. Biotechnology 7:257–264. doi:10.1038/nbt0389-257
Teutonico RA, Osborn TC (1994) Mapping of RFLP and qualitative trait loci in Brassica rapa and comparison to the linkage maps of B. napus, B. oleracea, and Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor Appl Genet 89:885–894. doi:10.1007/BF00224514
Uzunova M, Ecke W, Weissleder K, Röbbelen G (1995) Mapping the genome of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) I. Construction of an RFLP linkage map and localization of QTLs for seed glucosinolate content. Theor Appl Genet 90:194–204. doi:10.1007/BF00222202
Van Berloo R (2008) GGT 2.0: versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data. J Hered 99:232–236. doi:10.1093/jhered/esm109
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW, Boer MP, Jansen RC, Maliepaard C (2002) MapQTL Version® 4.0, software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wang ZR (1996) Plant allozyme analysis. Beijing Science, Beijing, pp 82–85, 91–102
Welter LJ, Göktürk-Baydar N, Akkurt M, Maul E, Eibach R, Töpfer R, Zyprian EM (2007) Genetic mapping and localization of quantitative trait loci affecting fungal disease resistance and leaf morphology in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L). Mol Breed 20:359–374. doi:10.1007/s11032-007-9097-7
Yang X, Yu YJ, Zhang FL, Zou ZR, Zhao XY, Zhang DS, Xu JB (2007) Linkage map construction and QTL analysis for bolting trait based on a DH population of Brassica rapa. J Integr Plant Biol 49:664–671. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00447.x
Young ND (1996) QTL mapping and quantitative disease resistance in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:479–501. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.34.1.479
Yu SC, Wang YJ, Zheng XY (2003) Mapping and analysis of QTL controlling some morphological traits in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis). Acta Genet Sin 30:1153–1160
Zamir D, Tadmor Y (1986) Unequal segregation of nuclear genes in plants. Bot Gaz 147:355–358. doi:10.1086/337602
Zhang FL, Wang GC, Wang M, Liu X, Zhao X, Yu YJ, Zhang D, Yu SC (2008a) Identification of SCAR markers linked to or, a gene inducing beta-carotene accumulation in Chinese cabbage. Euphytica 164:463–471. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9721-6
Zhang FL, Wang M, Liu XC, Zhao XY, Yang JP (2008b) Quantitative trait loci analysis for resistance against Turnip mosaic virus based on a doubled-haploid population in Chinese cabbage. Plant Breed 127:82–86
Zhou SW (1989) Biochemical experimental techniques. Beijing Agricultural University, Beijing, pp 100–200
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments regarding the manuscript. This work was supported in part by grants from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 program) (No. 2006AA10Z1C9), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation, China (No. 5062007 and 5083020), the Beijing Nova Programme, China (No. 2006B05) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30671422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, S., Zhang, F., Yu, R. et al. Genetic mapping and localization of a major QTL for seedling resistance to downy mildew in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol Breeding 23, 573–590 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9257-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9257-z