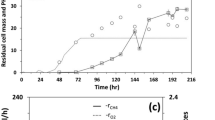
Abstract
Mixotrophic cultivation of three microalgae species, Chlorella sorokiniana, Scenedesmus obliquus and Scenedesmus abundans, was carried out with a mixed substrate containing glucose and acetate (1:1) under indoor and outdoor conditions. For indoor cultivation, the highest biomass productivities for C. sorokiniana, S. obliquus and C. abundans were 331 ± 11.5, 317 ± 3.5, and 130.7 ± 3.1 mg L−1 day−1, respectively. The key result showed that the highest lipid productivities (29.8–36.2 mg L−1 day−1) were obtained for C. sorokiniana for the cases in which acetate was added on day 1 in glucose-mediated cultures. Lipid accumulation was higher (27–36% of dry weight) for S. obliquus and S. abundans. The highest amount of lipid was accumulated for the strategies in which acetate was added on day 1 in glucose-mediated culture. C. sorokiniana showed the highest biomass yields of 0.39 g g−1 as compared to the other two species. For outdoor cultivation, the biomass and lipid productivity values for C. sorokiniana and S. obliquus were 172.8 ± 4.2 and 183.9 ± 6.8 mg L−1 day−1 and 30.5 ± 2.2 and 26.9 ± 3.1 mg L−1 day−1, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anahas AMP, Muralitharan G (2015) Isolation and screening of heterocystous cyanobacterial strains for biodiesel production by evaluating the fuel properties from fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) profiles. Bioresour Technol 184:9–17
Andruleviciute V, Makareviciene V, Skorupskaite V, Gumbyte M (2014) Biomass and oil content of Chlorella sp., Haematococcus sp., Nannochloris sp. and Scenedesmus sp. under mixotrophic growth conditions in the presence of technical glycerol. J Appl Phycol 26:83–90
Barros A, Guerra LT, Simoes M, Santos E, Fonseca D, Silva J, Costa L, Navalho J (2017) Mass balance analysis of carbon and nitrogen in industrial scale mixotrophic microalgae cultures. Algal Res 21:35–41
Bartley ML, Boeing WJ, Dungan BN, Holguin FO, Schaub T (2014) pH effects on growth and lipid accumulation of the biofuel microalgae Nannochloropsis salina and invading organisms. J Appl Phycol 26:1431–1437
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algal species. Phycological Studies, University of Texas 4:1–95
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 37:911–917
Bouarab L, Dauta A, Loudiki M (2004) Heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth of Micractinium pusillum Fresenius in the presence of acetate and glucose: effect of light and acetate gradient concentration. Water Res 38:2706–2712
Choi YY, Joun JM, Lee J, Hong ME, Pham HM, Chang WS, Sim SJ (2017) Development of large-scale and economic pH control system for outdoor cultivation of microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis using industrial flue gas. Bioresour Technol 244:1235–1244
Darpito C, Shin WS, Jeon S, Lee H, Nam K, Kwon JH, Yang JW (2015) Cultivation of Chlorella protothecoides in anaerobically treated brewery wastewater for cost-effective biodiesel production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:523–530
Dvořáková-Hladká J (1966) Utilization of organic substrates during mixotrophic and heterotrophic cultivation of algae. Biol Plant 8:354–361
Dvořáková-Hladká J (1967) The role of sugars in the respiration of differently cultivated green algae. Biol Plant 9:340–353
Fett JP, Coleman JR (1994) Regulation of periplasmic carbonic anhydrase expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by acetate and pH. Plant Physiol 106:103–108
Gardner R, Peters P, Peyton B, Cooksey KE (2011) Medium pH and nitrate concentration effects on accumulation of triacylglycerol in two members of the Chlorophyta. J Appl Phycol 23:1005–1016
Gupta S, Pawar SB (2018) Mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae to enhance the quality of lipid for biodiesel application: effects of scale of cultivation and light spectrum on reduction of α-linolenic acid. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41:531–542
Gupta PL, Choi HJ, Pawar RR, Jung SP, Lee SM (2016a) Enhanced biomass production through optimization of carbon source and utilization of wastewater as a nutrient source. J Environ Manag 184:585–595
Gupta S, Pandey R, Pawar S (2016b) Microalgal bioremediation of food-processing industrial wastewater under mixotrophic conditions. Front Chem Sci Eng 10:499–508
Gupta S, Pandey RA, Pawar SB (2017) Bioremediation of synthetic high strength COD wastewater using microalgae sp. Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bioremediat J 21:38–51
Hegewald E (2000) New combinations in the genus Desmodesmus (Chlorophyceae, Scenedesmaceae). Algol Stud 96:1–18
Heifetz PB, Förster B, Osmond CB, Giles LJ, Boynton JE (2000) Effects of acetate on facultative autotrophy in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii assessed by photosynthetic measurements and stable isotope analyses. Plant Physiol 122:1439–1445
Huang A, Sun L, Wu S, Liu C, Zhao P, Xie X, Wang G (2017) Utilization of glucose and acetate by Chlorella and the effect of multiple factors on cell composition. J Appl Phycol 29:23–33
Lee Y-K, Ding S-Y, Hoe C-H, Low C-S (1996) Mixotrophic growth of Chlorella sorokiniana in outdoor enclosed photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 8:163–169
Li Y, Zhou W, Hu B, Min M, Chen P, Ruan RR (2012) Effect of light intensity on algal biomass accumulation and biodiesel production for mixotrophic strains Chlorella kessleri and Chlorella protothecoide cultivated in highly concentrated municipal wastewater. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:2222–2229
Li T, Zheng Y, Yu L, Chen S (2014) Mixotrophic cultivation of a Chlorella sorokiniana strain for enhanced biomass and lipid production. Biomass Bioenergy 66:204–213
Liu X, Duan S, Li A, Xu N, Cai Z, Hu Z (2009) Effects of organic carbon sources on growth, photosynthesis, and respiration of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Appl Phycol 21:239–246
Martínez ME, Camacho F, Jiménez JM, Espínola JB (1997) Influence of light intensity on the kinetic and yield parameters of Chlorella pyrenoidosa mixotrophic growth. Process Biochem 32:93–98
Miller AG, Colman G (1980) Evidence for HCO3 − transport by the blue green alga (cyanobacterium) Coccochloris peniocystis. Plant Physiol 65:397–402
Moheimani NR (2013) Inorganic carbon and pH effect on growth and lipid productivity of Tetraselmis suecica and Chlorella sp (Chlorophyta) grown outdoors in bag photobioreactors. J Appl Phycol 25:387–398
Moon M, Kim CW, Park WK, Yoo G, Choi YE, Yang JW (2013) Mixotrophic growth with acetate or volatile fatty acids maximizes growth and lipid production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Algal Res 2:352–357
Najafabadi HA, Malekzadeh M, Jalilian F, Vossoughi M, Pazuki G (2015) Effect of various carbon sources on biomass and lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris during nutrient sufficient and nitrogen starvation conditions. Bioresour Technol 180:311–317
Neilson AH, Lewin RA (1974) The uptake and utilization of organic carbon by algae: an essay in comparative biochemistry. Phycologia 13:227–264
Pagnanelli F, Altimari P, Trabucco F, Toro L (2014) Mixotrophic growth of Chlorella vulgaris and Nannochloropsis oculata: interaction between glucose and nitrate. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:652–661
Pawar S (2016) Effectiveness mapping of open raceway pond and tubular photobioreactors for sustainable production of microalgae biofuel. Renew Sust Energ Rev 62:640–653
Pawar S, Gupta S (2018) Mass production of microalgae in photobioreactors for biodiesel application: selection, limitations, and optimization. In: Purohit H, Kalia V, Vaidya A, Khardenavis A (eds) Optimization and applicability of bioprocesses. Springer, Singapore, pp 211–232
Sharma AK, Sahoo PK, Singhal S, Patel A (2016) Impact of various media and organic carbon sources on biofuel production potential from Chlorella spp. 3 Biotech 6:116
Silva HR, Prete CEC, Zambrano F, de Mello VH, Tischer CA, Andrade DS (2016) Combining glucose and sodium acetate improves the growth of Neochloris oleoabundans under mixotrophic conditions. AMB Expr 6:10
Tan XB, Zhao XC, Zhang YL, Zhou YY, Yang LB, Zhang WW (2018) Enhanced lipid and biomass production using alcohol wastewater as carbon source for Chlorella pyrenoidosa cultivation in anaerobically digested starch wastewater in outdoors. Bioresour Technol 247:784–793
Wan M, Liu P, Xia J, Rosenberg JN, Oyler GA, Betenbaugh MJ, Nie Z, Qiu G (2011) The effect of mixotrophy on microalgal growth, lipid content, and expression levels of three pathway genes in Chlorella sorokiniana. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:835–844
Wang Y, Chiu SY, Ho SH, Liu Z, Hasunuma T, Chang TT, Chang KF, Chang JS, Ren NQ, Kondo A (2016) Improving carbohydrate production of Chlorella sorokiniana NIES-2168 through semi-continuous process coupled with mixotrophic cultivation. Biotechnol J 11:1072–1081
Wynne MJ, Hallan JK (2016) Reinstatement of Tetradesmus G.M.Smith (Sphaeropleales, Chlorophyta). Feddes Rep 126:83–86
Zili F, Bouzidi N, Ammar J, Zakhama W, Ghoul M, Sayadi S, Ben Ouada H (2017) Mixotrophic cultivation promotes growth, lipid productivity, and PUFA production of a thermophilic Chlorophyta strain related to the genus Graesiella. J Appl Phycol 29:35–43
Acknowledgments
Ms. Suvidha Gupta is thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for providing Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) for her Ph.D. work.
Funding
The corresponding author was financially supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, under the scheme of DST INSPIRE Faculty Award (IFA13–ENG63).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Pawar, S.B. Strategic mixed substrate cultivation of microalgae: productivity, respiration, yield, and lipid quality. J Appl Phycol 31, 1573–1588 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1688-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1688-7