Abstract
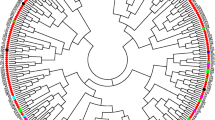
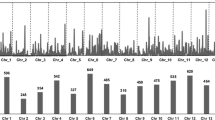
To better understand the genetic diversity of the cultivated Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and its structure at the molecular level, 193 Upland cotton cultivars collected from 26 countries were genotyped using 448 microsatellite markers. These markers were selected based on their mapping positions in the high density G. hirsutum TM-1 × G. barbadense 3-79 map, and they covered the whole genome. In addition, the physical locations of these markers were also partially identified based on the reference sequence of the diploid G. raimondii (D5) genome. The marker orders in the genetic map were largely in agreement with their orders in the physical map. These markers revealed 1,590 alleles belonging to 732 loci. Analysis of unique marker allele numbers indicated that the modern US Upland cotton had been losing its genetic diversity during the past century. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) between marker pairs was clearly un-even among chromosomes, and among regions within a chromosome. The average size of a LD block was 6.75 cM at r 2 = 0.10. A neighbor-joining phylogenic tree of these cultivars was generated using marker allele frequencies based on Nei’s genetic distance. The cultivars were grouped into 15 groups according to the phylogenic tree. Grouping results were largely congruent with the breeding history and pedigrees of the cultivars with a few exceptions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdurakhmonov IY, Kohel RJ, Yu JZ, Pepper AE, Abdullaev AA, Kushanov FN, Salakhutdinov IB, Buriev ZT, Saha S, Scheffler BE, Jenkins JN, Abdukarimov A (2008) Molecular diversity and association mapping of fiber quality traits in exotic G. hirsutum L. germplasm. Genomics 92:478–487
Ali S, Ijaz A, Zafar A, Ashraf A, Yunus M, Iqbal Z, Nadeem S, Rajoka MI (2011) Investigation of simple sequence repeats (SSR) marker-assisted genetic diversity among upland Bt- and non Bt-cotton varieties. African J Biotech 10:15222–15228
Bertini CHCM, Schuster I, Sediyama T, Barros EG, Moreira MA (2006) Characterization and genetic diversity analysis of cotton cultivars using microsatellites. Genet Mol Biol 29:321–329
Bezawada B, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Creech RG, McCarty JC (2003) SSR marker(s) associated with root knot nematode resistance gene(s) in cotton. J Cotton Sci 7:179–184
Blenda A, Fang DD, Rami JF, Garsmeur O, Luo F, Lacape JM (2012) A high density consensus genetic map of tetraploid cotton that integrates multiple component maps through molecular marker redundancy check. PLoS One 7:e45739
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bourland FM, Jones DC (2010) Registration of ‘UA48’ cotton cultivar. J Plant Regist 6:15–18
Bowman DT, Gutierrez OA, Percy RG, Calhoun DS, May OL (2007) Pedigrees of upland and pima cotton cultivars released between 1970 and 2005. Mississippi State Univ, Mississippi State, MS Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experimental Station Bulletin # 1155. http://msucares.com/pubs/bulletins/b1155.pdf. Accessed 16 Feb 2013
Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1994) Re-evaluating the origin of domesticated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum: Malvaceae) using nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). Am J Bot 81:1309–1326
Campbell BT, Williams VE, Park W (2009) Using molecular markers and field performance data to characterize the Pee Dee cotton germplasm resources. Euphytica 169:285–301
Cantrell RG, Davis DD (2000) Registration of NM24016, an interspecific-derived cotton genetic stock. Crop Sci 40:1208
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Duncan DR (2010) Cotton transformation. In: Zehr UB (ed) Cotton, biotechnology in agriculture and forestry 65. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 65–77
Fang DD, Yu JZ (2012) Addition of 455 microsatellite marker loci to the high density Gossypium hirsutum TM-1 × G. barbadense 3–79 genetic map. J Cotton Sci 16:229–248
Fang DD, Xiao J, Canci PC, Cantrell RG (2010) A new SNP haplotype associated with blue disease resistance gene in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 120:943–953
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP–Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Guitierrez OA, Basu S, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Shoemaker DB, Cheatham CL, McCarty JC (2002) Genetic distance among selected cotton genotypes and its relationship with F2 performance. Crop Sci 42:1841–1847
Hinze LL, Dever JK, Percy RG (2012) Molecular variation among and within improved cultivars in the US cotton germplasm collection. Crop Sci 52:222–230
Iqbal AE, Reddy OUK, El-Zik KM, Pepper AE (2001) A genetic bottleneck in the ‘evolution under domestication’ of upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. examined using DNA fingerprinting. Theor Appl Genet 103:547–554
Kalivas A, Xanthopoulos F, Kehagia O, Tsaftaaris AS (2011) Agronomic characterization, genetic diversity and association analysis of cotton cultivars using simple sequence repeat molecular markers. Genet Mol Res 10:208–217
Kohel RJ, Richmond TR, Lewis CF (1970) Texas Marker-1. Description of a genetic standard for Gossypium hirsutum. Crop Sci 10:670–671
Lacape JM, Dessauw D, Rajab M, Noyer JL, Hau B (2007) Microsatellite diversity in tetraploid Gossypium germplasm: assembling a highly informative genotyping set of cotton SSRs. Mol Breed 19:45–58
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Liu S, Cantrell RG, McCarty JC, Stewart JM (2000) Simple sequence repeat-based assessment of genetic diversity in cotton race stock accessions. Crop Sci 40:1459–1469
Lu HJ, Myers GO (2002) Genetic relationships and discrimination of ten influential upland cotton varieties using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:325–331
Mace ES, Rami JF, Bouchet S, Klein PE, Klein RR, Kilian A, Wenzl P, Xia L, Halloran K, Jordan DR (2009) A consensus genetic map of sorghum that integrates multiple component maps and high-throughput Diversity Array Technology (DArT) markers. BMC Plant Biol 9:13
May OL, Bowman DT, Calhoun DS (1995) Genetic diversity of US upland cotton cultivars released between 1980 and 1990. Crop Sci 35:1570–1574
Nei M, Tajima F, Tateno Y (1983) Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. II. Gene frequency data. J Mol Evol 19:153–170
Paterson AH, Wendel JF, Gundlach H, Guo H, J Jenkins et al (2012) Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature 492:423–427
Percival AE, Kohel RJ (1990) Distribution, collection, and evaluation of Gossypium. Adv Agron 44:225–256
Pillay M, Myers GO (1999) Genetic diversity in cotton assessed by variation in ribosomal RNA genes and AFLP markers. Crop Sci 39:1881–1886
Rahman M, Hussain D, Zafar Y (2002) Estimation of genetic divergence among elite cotton cultivars-genotypes by DNA fingerprinting technology. Crop Sci 42:2137–2144
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYSpc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.1. Exeter Software, Setauket
Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR (2005) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers reveal low levels of polymorphism between cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. Aust J Agric Res 56:301–307
Sargent DJ, Passey T, Surbanovski N, Lopez Girona E, Kuchta P, Davik J, Harrison R, Passey A, Whitehouse AB, Simpson DW (2012) A microsatellite linkage map for the cultivated strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa) suggests extensive regions of homozygosity in the genome that may have resulted from breeding and selection. Theor Appl Genet 124:1229–1240
Shen X, Van Becelaere G, Kumar P, Davis RF, May OL, Chee P (2006) QTL mapping for resistance to root-knot nematodes in the M-120 RNR Upland cotton line (Gossypium hirsutum L.) of the Auburn 623 RNR source. Theor Appl Genet 113:1539–1549
Sunilkumar G, Rathore KS (2001) Transgenic cotton: factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and regeneration. Mol Breed 8:37–52
Tatineni V, Cantrell RG, David DD (1996) Genetic diversity in elite cotton germplasm determined by morphological characteristics and RAPDs. Crop Sci 36:186–192
Van Becelaere G, Lubber EL, Paterson AH, Chee PW (2005) Pedigree- vs. DNA marker-based genetic similiarity estimates in cotton. Crop Sci 45:2281–2287
van Os H, Andrzejewski S, Bakker E, Barrena I, Bryan GJ, Caromel B, Ghareeb B, Isidore E, de Jong W, van Koert P, Lefebvre V, Milbourne D, Ritter E, van der Voort JN, Rousselle-Bourgeois F, van Vliet J, Waugh R, Visser RG, Bakker J, van Eck HJ (2006) Construction of a 10,000-marker ultradense genetic recombination map of potato: providing a framework for accelerated gene isolation and a genomewide physical map. Genetics 173:1075–1087
Wang K, Wang Z, Li F, Ye W, Wang J, Song G, Yue Z, Cong L, Shang H, Zhu S, Zou C, Li Q, Yuan Y, Lu C, Wei H, Gou C, Zheng Z, Yin Y, Zhang X, Liu K, Wang B, Song C, Shi N, Kohel RJ, Percy RG, Yu JZ, Zhu YX, Yu S (2012) The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. Nat Genet 44:1098–1103
Wendel JF, Cronn RC (2003) Polyploidy and the evolutionary history of cotton. Adv Agron 78:139–186
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Percival AE (1992) Genetic diversity in Gossypium hirsutum and the origin of Upland cotton. Am J Bot 79:1291–1310
Xiao J, Fang DD, Bhatti M, Hendrix B, Cantrell R (2010) A SNP haplotype associated with a gene resistant to Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. malvacearum in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed 25:593–602
Yu JZ, Fang DD, Kohel RJ, Ulloa M, Hinze LL, Percy RG, Zhang J, Chee P, Scheffler BE, Jones DC (2012a) Development of a core set of SSR markers for the characterization of Gossypium germplasm. Euphytica 187:203–213
Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Fang DD, Cho J, Van Deynze A, Ulloa M, Hoffman SM, Pepper AE, Stelly DM, Jenkins JN, Saha S, Kumpatla SP, Shah MR, Hugie WV, Percy RG (2012b) A high-density simple sequence repeat and single nucleotide polymorphism genetic map of the tetraploid cotton genome. G3 (Genes Genomes Genetics) 2:43–58
Zhang J, Lu Y, Cantrell RG, Hughs E (2005) Molecular markers diversity and field performance in commercial cotton cultivars evaluated in the Southwestern USA. Crop Sci 45:1483–1490
Zhong M, McCarty JC, Jenkins JN, Saha S (2002) Assessment of day-neutral backcross populations of cotton using AFLP markers. J Cotton Sci 6:97–103
Acknowledgments
This project was partially supported by Cotton Incorporated. We thank Dr. Linghe Zeng at USDA-ARS, Stoneville, MS for providing us seeds of some cultivars used in this study. Our great appreciation goes to Mrs. Sheron Simpson and Dr. Brian Scheffler at Genomic and Bioinformatic Research Unit at Stoneville, MS for their excellent support in SSR marker analysis. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U. S. Department of Agriculture that is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, D.D., Hinze, L.L., Percy, R.G. et al. A microsatellite-based genome-wide analysis of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars from major cotton-growing countries. Euphytica 191, 391–401 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0886-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0886-2