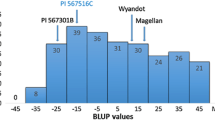
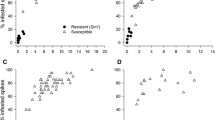
Abstract
Resistance to cotton blue disease (CBD) was evaluated in 364 F2.3 families of three populations derived from resistant variety ‘Delta Opal’. The CBD resistance in ‘Delta Opal’ was controlled by one single dominant gene designated Cbd. Two simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers were identified as linked to Cbd by bulked segregant analysis. Cbd resides at the telomere region of chromosome 10. SSR marker DC20027 was 0.75 cM away from Cbd. DC20027 marker fragments amplified from 3 diploid species and 13 cotton varieties whose CBD resistance was known were cloned and sequenced. One single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was identified at the 136th position by sequence alignment analysis. Screening SNP markers previously mapped on chromosome 10 identified an additional 3 SNP markers that were associated with Cbd. A strong association between a haplotype based on four SNP markers and Cbd was developed. This demonstrates one of the first examples in cotton where SNP markers were used to effectively tag a trait enabling marker-assisted selection for high levels of CBD resistance in breeding programs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Zhang T, Noor-Ul-Islam, Shaheen T, Mehboob-Ur-Rahman (2007) Identifying genetic variation in Gossypium based on single nucleotide polymorphism. Pak J Bot 39:1245–1250
Akhunov E, Nicolet C, Dvorak J (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping in polyploid wheat with the Illumina GoldenGate assay. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1059-5
Aslam M, Jiang C, Wright R, Paterson AH (2000) Identification of molecular markers linked to leaf curl virus disease resistance in cotton. J Sci I R Iran 11:277–280
Blenda A, Scheffler J, Scheffler B, Palmer M, Lacape J-M, Yu J, Jesudurai C, Jung S, Muthukumar S, Yellambalase P, Ficklin S, Staton M, Eshelman R, Ulloa M, Saha S, Burr B, Liu S, Zhang T, Fang D, Pepper A, Kumpatla S, Jacobs J, Tomkins J, Cantrell R, Main D (2006) CMD: a Cotton Microsatellite Database resource for Gossypium genomics. BMC Genomics 7:132
Bolek Y, El-Zik KM, Pepper AE, Bell AA, Magill CW, Thaxton PM, Reddy OUK (2005) Mapping of verticillium wilt resistance genes in cotton. Plant Sci 168:1581–1590
Brown JK (2001) Cotton blue disease. In: Kirkpatrick TL, Rothrock CS (eds) Compedium of cotton diseases, 2nd edn. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 50–51
Cauquil J (1977) Etudes sur une maladie d’origin virale du cotonnier: La maladie bleue. Coton Fibres Trop 32:259–278
Cauquil J, Vaissayre M (1971) La “maladie bleue” du cotonnier en Afrique: transmission de cotonnier à cotonnier par Aphis Gossypii Glover. Coton Fibres Trop 6:463–466
Choi IY, Hyten DL, Matukumalli LK, Song Q, Chaky JM, Quigley CV, Chase K, Lark KG, Reiter RS, Yoon MS, Hwang EY, Yi SI, Young ND, Shoemaker RC, van Tassell CP, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2007) A soybean transcript map: gene distribution, haplotype and single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Genetics 176:685–696
Correa RL, Silva TF, Simoes-Araujo JL, Barroso PAV, Vidal MS, Vaslin MFS (2005) Molecular characterization of a virus from the family Luteoviridae associated with cotton blue disease. Arch Virol 150:1357–1367
Eathington SR, Crosbie TM, Edwards MD, Reiter RS, Bull JK (2007) Molecular markers in a commercial breeding program. Crop Sci 47:S154–S163
Freire EC (1998) Doenca azul tem solucao. Cultivar, Pelotas 1:64–65
Guo WZ, Cai CP, Wang CB, Han ZG, Song XL, Wang K, Niu XW, Wang C, Lu KY, Shi B, Zhang TZ (2007) A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics 176:527–541
Haley SD, Miklas PN, Stavely JR, Byrum J, Kelly JD (1993) Identification of RAPD markers linked to a major rust resistance gene block in common bean. Theor Appl Genet 86:505–512
Hendrix B, Stewart JM (2005) Estimation of the nuclear DNA content of Gossypium species. Ann Bot (London) 95:789–797
Hsu CY, An C, Saha S, Ma DP, Jenkins JN, Scheffler B, Stelly DM (2008) Molecular and SNP characterization of two genome specific transcription factor genes GhMyb8 and GhMyb10 in cotton species. Euphytica 159:259–273
Innes NL (1983) Bacterial blight of cotton. Biol Rev 58:157–176
Iqbal MJ, Reddy OUK, El-Zik KM, Pepper AE (2001) A genetic bottleneck in the ‘evolution under domestication’ of upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. examined using DNA fingerprinting. Theor Appl Genet 103:547–554
Junior OP, Schuster I, Pinto RB, Pires E, Belot JL, Silvie P, Chitarra LG, Hoffmann LV, Barroso P (2008) Inheritance of resistance to cotton blue disease. Pesq Agropec Bras Brasilia 43(5):661–665
Kohel RJ (1973) Genetic nomenclature in cotton. J Hered 64:291–295
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) ClustalW and ClustalX version 2. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lin ZX, Zhang YX, Zhang XL, Guo XP (2009) A high-density integrative linkage map for Gossypium hirsutum. Euphytica 166:35–45
Liu HJ, Myers GO (2002) Genetic relationships and discrimination of ten influential Upland cotton varieties using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:325–331
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kessell RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes bybulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. PNAS 88:9828–9832
Nateshan H, Muniyappa V, Swanson MM, Harrison BD (1996) Host range, vector relations and serological relationships of cotton leaf curl virus from southern India. Ann Appl Biol 128:233–244
Nguyen TB, Giband M, Brottier P, Risterucci AM, Lacape JM (2004) Wide coverage of the tetraploid cotton genome using newly developed microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:167–175
Niu C, Lister HE, Nguyen B, Wheeler TA, Wright RJ (2008) Resistance to Thielaviopsis basicola in the cultivated A genome cotton. Theor Appl Genet 117:1313–1323
Paterson AH, Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Report 11:122–127
Rafalski JA (2002) Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:94–100
Romano GB, Sacks EJ, Stetina RS, Robinson AF, Fang DD, Gutierrez OA, Scheffler JA (2009) Identification and genomic location of a reniform nematode (Rotylenchulus reniformis) resistance locus (Ren ari) introgressed from Gossypium aridum into upland cotton (G. hirsutum). Theor Appl Genet 120:139–150
Royo OM, Erazzu L, Bonacic I, Poisson J, Montenegro A (2003) Screening of cotton germplasm for “blue disease” under natural field infestation. In: Swanepoel A (ed) Proceedings of the world cotton research conference-3, Cape Town, South Africa. Agricultural Research Council-Institute for Industrial Crops (Publisher), pp 305–316
Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR (2002) Investigation of the chromosomal location of the bacterial blight resistance gene present in an Australian cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivar. Aust J Agri Res 53:551–560
Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR (2005) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers reveal low levels of polymorphism between cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. Aust J Agric Res 56:301–307
Sedcole JR (1977) Number of plants necessary to recover a trait. Crop Sci 17:667–668
Shaheen T, Asif M, Zafar Y, Mehboob-Ur-Rahman (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of Mt-Shsp gene of Gossypium arboreum and its relationship with other diploid cotton genomes, G. hirsutum and Arabidopsis thaliana. Pak J Bot 41:177–183
Shen X, Van Becelaere G, Kumar P, Davis RF, May LO, Chee P (2006) QTL mapping for resistance to root-knot nematodes in the M-120 RNR Upland cotton line (Gossypium hirsutum L.) of the Auburn 623 RNR source. Theor Appl Genet 113:1539–1549
Silva TF, Correa RL, Castilho Y, Silvie P, Belot JL, Vaslin MFS (2008) Widespread distribution and a new recombinant species of Brazilian virus associated with cotton blue disease. Virol J 5:123–135
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Wang C, Ulloa M, Roberts PA (2006) Identification and mapping of microsatellite markers linked to a root-knot nematode resistancegene (rkn1) in Acala NemX cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:770–777
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Percival AE (1992) Genetic diversity in Gossypium hirsutum and the origin of upland cotton. Am J Bot 79:1291–1310
Xiao J, Wu K, Fang DD, Stelly DM, Yu J, Cantrell RG (2009) New SSR markers for use in cotton (Gossypium spp.) improvement. J Cotton Sci 13:75–157
Xiao J, Fang DD, Hendrix B, Bhatti M, Cantrell RG (2010) A SNP haplotype associated with a gene resistant to Xanthomonas campestris pv. malvacearum (Race 18) in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed (in press)
Ynturi P, Jenkins JN, McCarty JC Jr, Gutierrez OA, Saha S (2006) Association of root-knot nematode resistance genes with simple sequence repeat markers on two chromosomes in cotton. Crop Sci 46:2670–2674
Young RA, Kelly JD (1996) RAPD markers flanking the Are gene for anthracnose resistance in common bean. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 121:37–41
Zhang HB, Li Y, Wang B, Chee PW (2008) Recent advances in cotton genomics. Int J Plant Genomics. Hindawai Publishing Corporation, 20 pp. doi:10.115/2008/742304
Acknowledgment
We greatly thank two anonymous reviewers who made excellent suggestions for revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by I. Mackay.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, D.D., Xiao, J., Canci, P.C. et al. A new SNP haplotype associated with blue disease resistance gene in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 120, 943–953 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1223-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1223-y