Abstract
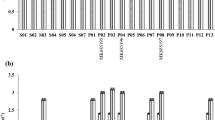
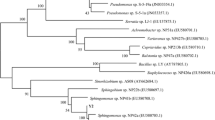
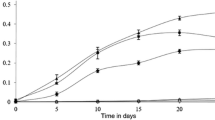
A novel epoxide hydrolase (EHase) from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading bacteria was identified and characterized. EHase activity was identified in four strains of PAH-degrading bacteria isolated from commercial gasoline and oil-contaminated sediment based on their growth on styrene oxide and its derivatives, such as 2,3- and 4-chlorostyrene oxides, as a sole carbon source. Gordonia sp. H37 exhibited high enantioselective hydrolysis activity for 4-chlorostyrene oxide with an enantiomeric ratio of 27. Gordonia sp. H37 preferentially hydrolyzed the (R)-enantiomer of styrene oxide derivatives resulting in the preparation of a (S)-enantiomer with enantiomeric excess greater than 99.9 %. The enantioselective EHase activity was identified and characterized in various PAH-degrading bacteria, and whole cell Gordonia sp. H37 was employed as a biocatalyst for preparing enantiopure (S)-styrene oxide derivatives.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archelas A, Furstoss R (1997) Synthesis of enantiopure epoxides through biocatalytic approaches. Annu Rev Microbiol 51:491–525
Archelas A, Furstoss R (2001) Synthetic applications of epoxide hydrolases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:112–119
Besse P, Veschambre H (1994) Chemical and biological synthesis of chiral epoxides. Tetrahedron 50:8885–8892
Chen C-S, Fujimoto Y, Girdaukas G, Sih CJ (1982) Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers. J Am Chem Soc 104:7294–7299
Choi SH, Kim HS, Lee EY (2009) Comparative homology modeling-inspired protein engineering for improvement of catalytic activity of Mugil cephalus epoxide hydrolase. Biotechnol Lett 31:1617–1624
de Vries EJ, Janssen DB (2003) Biocatalytic conversion of epoxides. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:414–420
Grogan G, Roberts SM, Willetts AJ (1996) Novel aliphatic epoxide hydrolase activities from dematiaceous fungi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 141:239–243
Hwang Y-O, Kang SG, Woo J-H, Kwon KK, Sato T, Lee EY, Han MS, Kim S-J (2008) Screening enantioselective epoxide hydrolase activities from marine microorganisms: detection of activities in Erythrobacter spp. Marine Biotechnol 10:366–373
Hwang S, Choi CY, Lee EY (2010) Bio- and chemo-catalytic preparation of chiral epoxides. J Ind Eng Chem 16:1–6
Jia X, Wang Z, Li Z (2008) Preparation of (S)-2-, 3-, and 4-chlorostyrene oxides with the epoxide hydrolase from Sphingomonas sp. HXN-200. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 19:407–415
Karboune S, Archelas A, Baratti JC (2010) Free and immobilized Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolase-catalyzed hydrolytic kinetic resolution of racemic p-chlorostyrene oxide in a neat organic solvent medium. Process Biochem 45:210–215
Kasai N, Suzuki T, Furukawa Y (1998) Chiral C3 epoxides and halohydrins: their preparation and synthetic application. J Mol Catal B Enzym 4:237–252
Kim HS, Lee OK, Hwang S, Kim BJ, Lee EY (2008) Biosynthesis of (R)-phenyl-1,2-ethanediol from racemic styrene oxide by using bacterial and marine fish epoxide hydrolases. Biotechnol Lett 30:127–133
Kloosterman M, Elferink VHM, van Iersel J, Roskam JH, Meijer EM, Hulshof LA, Sheldon RA (1988) Lipase in the preparation of β-blockers. Trends Biotechnol 6:251–256
Kwon T-H, Kim J-T, Kim J-S (2010) Application of a modified sublimation method to screen for PAH-degrading microorganisms. Korean J Microbiol 46:109–111
Lee EY (2008) Epoxide hydrolase-mediated enantioconvergent bioconversions to prepare chiral epoxides and alcohols. Biotechnol Lett 30:1509–1514
Orru RV, Faber K (1999) Stereoselectivities of microbial epoxide hydrolases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 3:16–21
Straathof AJJ, Jongejan JA (1997) The enantiomeric ratio: origin, determination and prediction. Enzym Microb Technol 21:559–571
Tokunaga M, Larrow JF, Kakiuchi F, Jacobsen EN (1997) Asymmetric catalysis with water: efficient kinetic resolution of terminal epoxides by means of catalytic hydrolysis. Science 277:936–938
van Loo B, Kingma J, Arand M, Wubbolts MG, Janssen DB (2006) Diversity and biocatalytic potential of epoxide hydrolases identified by genome analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2905–2917
Weijers CAGM, de Bont JAM (1999) Epoxide hydrolases from yeasts and other sources: versatile tools in biocatalysis. J Mol Catal B Enzym 6:199–214
Woo J-H, Hwang O-K, Kang SG, Lee HS, Cho J, Kim S-J (2007) Cloning and characterization of three novel epoxide hydrolases from a marine bacterium, Erythrobacter litoralis HTCC2594. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:365–375
Woo J-H, Kang JH, Kang SG, Hwang O-K, Kim S-J (2009) Cloning and characterization of an epoxide hydrolase from Novosphingovium aromaticivorans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:873–881
Woo J-H, Hwang O-K, Kang JH, Kim S-J, Kang SG (2010a) Enantioselective hydrolysis of racemic epichlorohydrin using an epoxide hydrolase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans. J Biosci Bioeng 110:295–297
Woo J-H, Kang JH, Hwang O-K, Cho J, Kim S-J, Kang SG (2010b) Biocatalytic resolution of glycidyl phenyl ether using a novel epoxide hydrolase from a marine bacterium, Rhodobacterales bacterium HTCC2654. J Biosci Bioeng 109:539–544
Yeate CA, Krie HM, Breytenbac JC (2007) Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin induced complexation for the biocatalytic resolution of a poorly soluble epoxide. Enzym Microb Technol 40:228–235
Acknowledgments
This work supported by GIMB in-House R&D Program and the Marine and Extreme Genome Research Centre Program, Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, JH., Kwon, TH., Kim, JT. et al. Identification and characterization of epoxide hydrolase activity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria for biocatalytic resolution of racemic styrene oxide and styrene oxide derivatives. Biotechnol Lett 35, 599–606 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1114-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1114-1