Abstract
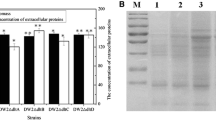
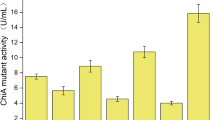
Cell surface engineering was proven as the efficient strategy for enhanced production of target metabolites. In this study, we want to improve the yield of target protein by engineering cell surface in Bacillus licheniformis. First, our results confirmed that deletions of d-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid synthetase gene dltD, cardiolipin synthase gene clsA and CDP-diacylglycerol-serine O-phosphatidyltransferase gene pssA were not conducive to cell growth, and the biomass of gene deletion strains were, respectively, decreased by 10.54 ± 1.43%, 14.17 ± 1.51%, and 17.55 ± 1.28%, while the concentrations of total extracellular proteins were improved, due to the increases of cell surface net negative charge and cell membrane permeability. In addition, the activities of target proteins, nattokinase, and α-amylase were also improved significantly in gene deletion strains. Furthermore, the triplicate gene (dltD, clsA, and pssA) deletion strain was constructed, which further led to the 45.71 ± 2.43% increase of cell surface net negative charge and 26.45 ± 2.31% increase of cell membrane permeability, and the activities of nattokinase and α-amylase reached 37.15 ± 0.89 FU/mL and 305.3 ± 8.4 U/mL, increased by 46.09 ± 3.51% and 96.34 ± 7.24%, respectively. Taken together, our results confirmed that cell surface engineering via deleting dltD, clsA, and pssA is an efficient strategy for enhanced production of target proteins, and this research provided a promising host strain of B. licheniformis for efficient protein expression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birrer GA, Cromwick AM, Gross RA (1994) Gamma-poly(glutamic acid) formation by Bacillus licheniformis 9945a: physiological and biochemical studies. Inter J Biol Macromol 16:265–275
Cai D, Chen Y, He P, Wang S, Mo F, Li X, Wang Q, Nomura CT, Wen Z, Ma X, Chen S (2018) Enhanced production of poly-gamma-glutamic acid by improving ATP supply in metabolically engineered Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:2541–2553
Cai D, He P, Lu X, Zhu C, Zhu J, Zhan Y, Wang Q, Wen Z, Chen S (2017) A novel approach to improve poly-γ-glutamic acid production by NADPH Regeneration in Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. Sci Rep 7:43404
Cai D, Rao Y, Zhan Y, Wang Q, Chen S (2019) Engineering Bacillus for efficient production of heterologous protein: current progress, challenge and prospect. J Appl Microbiol 126:1632–1642
Cai D, Wang H, He P, Zhu C, Wang Q, Wei X, Nomura CT, Chen S (2017) A novel strategy to improve protein secretion via overexpression of the SppA signal peptide peptidase in Bacillus licheniformis. Microb Cell Fact 16:70
Cai D, Wei X, Qiu Y, Chen Y, Chen J, Wen Z, Chen S (2016) High-level expression of nattokinase in Bacillus licheniformis by manipulating signal peptide and signal peptidase. J Appl Microbiol 121:704–712
Cai D, Zhu J, Zhu S, Lu Y, Zhang B, Lu K, Li J, Ma X, Chen S (2019) Metabolic engineering of main transcription factors in carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus metabolisms for enhanced production of bacitracin in Bacillus licheniformis. ACS Synth Biol 8:866–875
Cao H, van Heel AJ, Ahmed H, Mols M, Kuipers OP (2017) Cell surface engineering of Bacillus subtilis improves production yields of heterologously expressed alpha-amylases. Microb Cell Fact 16:56
Chen J, Fu G, Gai Y, Zheng P, Zhang D, Wen J (2015) Combinatorial Sec pathway analysis for improved heterologous protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis: identification of bottlenecks by systematic gene overexpression. Microb Cell Fact 14:92
Chen X, Gao C, Guo L, Hu G, Luo Q, Liu J, Nielsen J, Chen J, Liu L (2018) DCEO biotechnology: tools to design, construct, evaluate, and optimize the metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of chemicals. Chem Rev 118:4–72
Chen Y, Cai D, He P, Mo F, Zhang Q, Ma X, Chen S (2018) Enhanced production of heterologous proteins by Bacillus licheniformis with defective d-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:135
Craynest M, Jorgensen S, Sarvas M, Kontinen VP (2003) Enhanced secretion of heterologous cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase by a mutant of Bacillus licheniformis defective in the d-alanylation of teichoic acids. Lett Appl Microbiol 37:75–80
Cui W, Han L, Suo F, Liu Z, Zhou L, Zhou Z (2018) Exploitation of Bacillus subtilis as a robust workhorse for production of heterologous proteins and beyond. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:145
Degering C, Eggert T, Puls M, Bongaerts J, Evers S, Maurer KH, Jaeger KE (2010) Optimization of protease secretion in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis by screening of homologous and heterologous signal peptides. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6370–6376
Harwood CR, Cranenburgh R (2008) Bacillus protein secretion: an unfolding story. Trends Microbiol 16:73–79
He P, Wan N, Cai D, Hu S, Chen Y, Li S, Chen S (2019) (13)C-metabolic flux analysis reveals the metabolic flux redistribution for enhanced production of poly-gamma-glutamic acid in dlt over-expressed Bacillus licheniformis. Front Microbiol 10:105
Hoshida H, Kondo M, Kobayashi T, Yarimizu T, Akada R (2017) 5-UTR introns enhance protein expression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:241–251
Hyyrylainen HL, Pietiainen M, Lunden T, Ekman A, Gardemeister M, Murtomaki-Repo S, Antelmann H, Hecker M, Valmu L, Sarvas M, Kontinen VP (2007) The density of negative charge in the cell wall influences two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 153:2126–2136
Hyyrylainen HL, Vitikainen M, Thwaite J, Wu H, Sarvas M, Harwood CR, Kontinen VP, Stephenson K (2000) d-Alanine substitution of teichoic acids as a modulator of protein folding and stability at the cytoplasmic membrane/cell wall interface of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 275:26696–26703
Kang Z, Yang S, Du G, Chen J (2014) Molecular engineering of secretory machinery components for high-level secretion of proteins in Bacillus species. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:1599–1607
Kasahara J, Kiriyama Y, Miyashita M, Kondo T, Yamada T, Yazawa K, Yoshikawa R, Yamamoto H (2016) Teichoic acid polymers affect expression and localization of dl-endopeptidase LytE required for lateral cell wall hydrolysis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 198:1585–1594
Kawai F, Shoda M, Harashima R, Sadaie Y, Hara H, Matsumoto K (2004) Cardiolipin domains in Bacillus subtilis marburg membranes. J Bacteriol 186:1475–1483
Kiriukhin MY, Neuhaus FC (2001) d-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid: role of the d-alanyl carrier protein in acylation. J Bacteriol 183:2051–2058
Kovacs M, Halfmann A, Fedtke I, Heintz M, Peschel A, Vollmer W, Hakenbeck R, Bruckner R (2006) A functional dlt operon, encoding proteins required for incorporation of d-alanine in teichoic acids in gram-positive bacteria, confers resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 188:5797–5805
Lennen RM, Pfleger BF (2013) Modulating membrane composition alters free fatty acid tolerance in Escherichia coli. PLoS One 8:e54031
Ma RJ, Wang YH, Liu L, Bai LL, Ban R (2018) Production enhancement of the extracellular lipase LipA in Bacillus subtilis: effects of expression system and Sec pathway components. Protein Expr Purif 142:81–87
Neef J, Bongiorni C, Goosens VJ, Schmidt B, van Dijl JM (2017) Intramembrane protease RasP boosts protein production in Bacillus. Microb Cell Fact 16:57
Song Y, Fu G, Dong H, Li J, Du Y, Zhang D (2017) High-efficiency secretion of beta-mannanase in Bacillus subtilis through protein synthesis and secretion optimization. J Agric Food Chem 65:2540–2548
Su L, Jiang Q, Yu L, Wu J (2017) Enhanced extracellular production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by co-expression with Bacillus cereus phospholipase C. Microb Cell Fact 16:24
Su L, Woodard RW, Chen J, Wu J (2013) Extracellular location of Thermobifida fusca cutinase expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) without mediation of a signal peptide. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4192–4198
Tan Z, Khakbaz P, Chen Y, Lombardo J, Yoon JM, Shanks JV, Klauda JB, Jarboe LR (2017) Engineering Escherichia coli membrane phospholipid head distribution improves tolerance and production of biorenewables. Metab Eng 44:1–12
Ueda M (2016) Establishment of cell surface engineering and its development. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 80:1243–1253
Vitikainen M, Hyyrylainen HL, Kivimaki A, Kontinen VP, Sarvas M (2005) Secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis can be improved by engineering cell components affecting post-translocational protein folding and degradation. J Appl Microbiol 99:363–375
Vitikainen M, Lappalainen I, Seppala R, Antelmann H, Boer H, Taira S, Savilahti H, Hecker M, Vihinen M, Sarvas M, Kontinen VP (2004) Structure-function analysis of PrsA reveals roles for the parvulin-like and flanking N- and C-terminal domains in protein folding and secretion in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 279:19302–19314
Wang H, Wang Y, Yang R (2017) Recent progress in Bacillus subtilis spore-surface display: concept, progress, and future. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:933–949
Wecke J, Perego M, Fischer W (1996) d-alanine deprivation of Bacillus subtilis teichoic acids is without effect on cell growth and morphology but affects the autolytic activity. Microb Drug Resist 2:123–129
Wei X, Zhou Y, Chen J, Cai D, Wang D, Qi G, Chen S (2015) Efficient expression of nattokinase in Bacillus licheniformis: host strain construction and signal peptide optimization. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:287–295
Westbrook AW, Ren X, Moo-Young M, Chou CP (2018) Engineering of cell membrane to enhance heterologous production of hyaluronic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:216–231
Yang H, Lu X, Hu J, Chen Y, Shen W, Liu L (2018) Boosting secretion of extracellular protein by Escherichia coli via cell wall perturbation. Appl Environ Microbiol 84:e01382
Yang S, Du G, Chen J, Kang Z (2017) Characterization and application of endogenous phase-dependent promoters in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:4151–4161
Zhan Y, Sheng B, Wang H, Shi J, Cai D, Yi L, Yang S, Wen Z, Ma X, Chen S (2018) Rewiring glycerol metabolism for enhanced production of poly-gamma-glutamic acid in Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:306
Zhou S, Ding R, Chen J, Du G, Li H, Zhou J (2017) Obtaining a panel of cascade promoter-5′-UTR complexes in Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 6:1065–1075
Zhu S, Cai D, Liu Z, Zhang B, Li J, Chen S, Ma X (2019) Enhancement of bacitracin production by NADPH generation via overexpressing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Zwf in Bacillus licheniformis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187:1502–1514
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0900303, 2015CB150505), the Technical Innovation Special Fund of Hubei Province (No. 2018ACA149), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M642802), and the Science and Technology Project of Hubei Tobacco Company (027Y2019-018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XM and SC designed and supervised the study. FM, DC, PH, FY, and YC performed the experiments. FM, DC, PH, XM, and SC analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, F., Cai, D., He, P. et al. Enhanced production of heterologous proteins via engineering the cell surface of Bacillus licheniformis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46, 1745–1755 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02229-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02229-8