Abstract
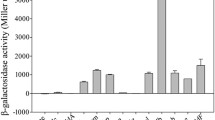
Bacillus subtilis as an important host has been widely used in synthetic biology, metabolic engineering, and production of industrial enzymes. To fully take advantage of this organism, 114 endogenous putative promoters were measured with a green fluorescent protein reporter and four classes of phase-dependent promoters (class I: exponential phase; class II: middle-log and early stationary phases; class III: lag-log and stationary phases; class IV: stationary phase) with different strengths were identified. The transcriptional strengths ranged from 0.03 to 2.03-fold of that of the commonly used strong promoter P43. On this basis, the temperature (for instance P bltD , P ydaD , and P gerBC ) and pH (such as P abrB , P ydjO , and P opuE ) inducible phase-dependent promoters were further identified and characterized. In comparison, P abrB (class I), P spoVG (class II), and P lytR (class III) achieved the highest expression levels of esterase, keratinase, and alkaline polygalacturonate lyase, respectively. The constructed phase-dependent promoter library should have great application potentials for enzyme production, metabolic engineering, and synthetic biology.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (1961) Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 81(5):741–746
Atalla A, Schumann W (2003) The pst operon of Bacillus subtilis is specifically induced by alkali stress. J Bacteriol 185(16):5019–5022
Bongers RS, Veening JW, Van Wieringen M, Kuipers OP, Kleerebezem M (2005) Development and characterization of a subtilin-regulated expression system in Bacillus subtilis: strict control of gene expression by addition of subtilin. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8818–8824
Dahl RH, Zhang F, Alonso-Gutierrez J, Baidoo E, Batth TS, Redding-Johanson AM, Petzold CJ, Mukhopadhyay A, Lee TS, Adams PD, Keasling JD (2013) Engineering dynamic pathway regulation using stress-response promoters. Nat Biotechnol 31(11):1039–1046
Daszczuk A, Dessalegne Y, Drenth I, Hendriks E, Jo E, van Lente T, Oldebesten A, Parrish J, Poljakova W, Purwanto AA, van Raaphorst R, Boonstra M, van Heel A, Herber M, van der Meulen S, Siebring J, Sorg RA, Heinemann M, Kuipers OP, Veening J-W (2014) Bacillus subtilis biosensor engineered to assess meat spoilage. ACS Synth Biol 3(12):999–1002
Fukuyama Y, Kiriyama Y, Kodama M, Iwaki H, Hosozawa S, Aki S, Matsui K (2001) DBTBS: a database of Bacillus subtilis promoters and transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 29(1):278–280
Geissendorfer M, Hillen W (1990) Regulated expression of heterologous genes in Bacillus subtilis using the Tn10 encoded tet regulatory elements. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33(6):657–663
Gerosa L, Kochanowski K, Heinemann M, Sauer U (2013) Dissecting specific and global transcriptional regulation of bacterial gene expression. Mol Syst Biol 9(1):395–408
Guan C, Cui W, Cheng J, Zhou L, Liu Z, Zhou Z (2016) Development of an efficient autoinducible expression system by promoter engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Microb Cell Factories 15(1):66
Hahne H, Mäder U, Otto A, Bonn F, Steil L, Bremer E, Hecker M, Becher D (2010) A comprehensive proteomics and transcriptomics analysis of Bacillus subtilis salt stress adaptation. J Bacteriol 192(3):870–882
Han MR, Shang LA, Chang HN, Han SJ, Kim YC, Lee JW (2006) Fermentation characteristics of a low-oxygen inducible hmp promoter system in Bacillus subtilis LAB1886. J Chem Technol Biot 81(6):1071–1074
Heimann JD (2002) The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Adv Microb Physiol 46(1):47–110
Huang W-Z, Wang J-J, Chen H-J, Chen J-T, Shaw G-C (2013) The heat-inducible essential response regulator WalR positively regulates transcription of sigI, mreBH and lytE in Bacillus subtilis under heat stress. Res Microbiol 164(10):998–1008
Jahn N, Preis H, Wiedemann C, Brantl S (2012) BsrG/SR4 from Bacillus subtilis the first temperature-dependent type I toxin-antitoxin system. Mol Microbiol 83(3):579–598
Jha RK, Kern TL, Fox DT, Strauss CEM (2014) Engineering an Acinetobacter regulon for biosensing and high-throughput enzyme screening in E. coli via flow cytometry. Nucleic Acids Res 42(12):8150–8160
Jin P, Kang Z, Zhang N, Du G, Chen J (2014) High-yield novel leech hyaluronidase to expedite the preparation of specific hyaluronan oligomers. Sci Rep 4:4471
Jin P, Kang Z, Yuan P, Du G, Chen J (2016) Production of specific-molecular-weight hyaluronan by metabolically engineered Bacillus subtilis 168. Metab Eng 35:21–30
Kang Z, Wang Q, Zhang H, Qi Q (2008) Construction of a stress-induced system in Escherichia coli for efficient polyhydroxyalkanoates production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(2):203–208
Kang Z, Yang S, Du GC, Chen J (2014a) Molecular engineering of secretory machinery components for high-level secretion of proteins in Bacillus species. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41(11):1599–1607
Kang Z, Zhang CZ, Zhang JL, Jin P, Zhang J, Du GC, Chen J (2014b) Small RNA regulators in bacteria: powerful tools for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3413–3424
Keggins KM, Lovett PS, Duvall EJ (1978) Molecular cloning of genetically active fragments of Bacillus DNA in Bacillus subtilis and properties of the vector plasmid pUB110. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 75(3):1423–1427
Keren L, Zackay O, Lotan-Pompan M, Barenholz U, Dekel E, Sasson V, Aidelberg G, Bren A, Zeevi D, Weinberger A (2013) Promoters maintain their relative activity levels under different growth conditions. Mol Syst Biol 9(1):2367–2367
Kim L, Mogk A, Schumann W (1996) A xylose-inducible Bacillus subtilis integration vector and its application. Gene 181(1–2):71–76
Lamsa A, Liu WT, Dorrestein PC, Pogliano K (2012) The Bacillus subtilis cannibalism toxin SDP collapses the proton motive force and induces autolysis. Mol Microbiol 84(3):486–500
Le ATT, Schumann W (2007) A novel cold-inducible expression system for Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr Purif 53(2):264–269
Lee JWK, Edwards CW, Hulett FM (1991) Bacillus licheniformis APase I gene promoter: a strong well-regulated promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol 137:1127–1133
Lee S-J, Pan J-G, Park S-H, Choi S-K (2010) Development of a stationary phase-specific autoinducible expression system in Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 149(1–2):16–20
Lesuisse E, Schanck K, Colson C (1993) Purification and preliminary characterization of the extracellular lipase of Bacillus subtilis 168, an extremely basic pH-tolerant enzyme. Eur J Biochem 216(1):155–160
Li W, Li H-X, Ji S-Y, Li S, Gong Y-S, Yang M-M, Chen Y-L (2007) Characterization of two temperature-inducible promoters newly isolated from B. subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358(4):1148–1153
Liu SL, Du K (2012) Enhanced expression of an endoglucanase in Bacillus subtilis by using the sucrose-inducible sacB promoter and improved properties of the recombinant enzyme. Protein Expr Purif 83(2):164–168
Liu BH, Zhang J, Fang Z, Du GC, Chen J, Liao XR (2014) Functional analysis of the C-terminal propeptide of keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis BBE11-1 and its effect on the production of keratinase in Bacillus subtilis. Process Biochem 49(9):1538–1542
MacLellan SR, Wecke T, Helmann JD (2008) A previously unidentified sigma factor and two accessory proteins regulate oxalate decarboxylase expression in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 69(4):954–967
Mahr R, von Boeselager RF, Wiechert J, Frunzke J (2016) Screening of an Escherichia coli promoter library for a phenylalanine biosensor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(15):6739–6753
Makita Y, Nakao M, Ogasawara N, Nakai K (2004) DBTBS: database of transcriptional regulation in Bacillus subtilis and its contribution to comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 32(Database issue):D75–D77
Ming-Ming Y, Wei-Wei Z, Xi-Feng Z, Pei-Lin C (2006) Construction and characterization of a novel maltose inducible expression vector in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Lett 28(21):1713–1718
Nguyen QA, Schumann W (2014) Use of IPTG-inducible promoters for anchoring recombinant proteins on the Bacillus subtilis spore surface. Protein Expr Purif 95:67–76
Nicolas P, Mader U, Dervyn E, Rochat T, Leduc A, Pigeonneau N, Bidnenko E, Marchadier E, Hoebeke M, Aymerich S, Becher D, Bisicchia P, Botella E, Delumeau O, Doherty G, Denham EL, Fogg MJ, Fromion V, Goelzer A, Hansen A, Hartig E, Harwood CR, Homuth G, Jarmer H, Jules M, Klipp E, Le Chat L, Lecointe F, Lewis P, Liebermeister W, March A, Mars RA, Nannapaneni P, Noone D, Pohl S, Rinn B, Rugheimer F, Sappa PK, Samson F, Schaffer M, Schwikowski B, Steil L, Stulke J, Wiegert T, Devine KM, Wilkinson AJ, van Dijl JM, Hecker M, Volker U, Bessieres P, Noirot P (2012) Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis. Science 335(6072):1103–1106
Panahi R, Vasheghani-Farahani E, Shojaosadati SA, Bambai B (2014) Auto-inducible expression system based on the SigB-dependent ohrB promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Biol 48(6):852–857
Phan TTP, Schumann W (2007) Development of a glycine-inducible expression system for Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 128(3):486–499
Ploss TN, Reilman E, Monteferrante CG, Denham EL, Piersma S, Lingner A, Vehmaanpera J, Lorenz P, van Dijl JM (2016) Homogeneity and heterogeneity in amylase production by Bacillus subtilis under different growth conditions. Microb Cell Fact 15
Promchai R, Promdonkoy B, Tanapongpipat S, Visessanguan W, Eurwilaichitr L, Luxananil P (2016) A novel salt-inducible vector for efficient expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 222:86–93
Rajkumar AS, Liu G, Bergenholm D, Arsovska D, Kristensen M, Nielsen J, Jensen MK, Keasling JD (2016) Engineering of synthetic, stress-responsive yeast promoters. Nucleic Acids Res
Schallmey M, Singh A, Ward OP (2004) Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can J Microbiol 50(1):1–17
Schumann W (2007) Production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Adv Appl Microbiol 62:137–189
Sierro N, Makita Y, de Hoon M, Nakai K (2008) DBTBS: a database of transcriptional regulation in Bacillus subtilis containing upstream intergenic conservation information. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D93–D96
Silbersack J, Juergen B, Hecker M, Schneidinger B, Schmuck R, Schweder T (2006) An acetoin-regulated expression system of Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(4):895–903
Song Y, Nikoloff JM, Fu G, Chen J, Li Q, Xie N, Zheng P, Sun J, Zhang D (2016) Promoter screening from Bacillus subtilis in various conditions hunting for synthetic biology and industrial applications. PLoS One 11(7):e0158447
Toymentseva AA, Schrecke K, Sharipova MR, Mascher T (2012) The LIKE system, a novel protein expression toolbox for Bacillus subtilis based on the liaI promoter. Microb Cell Factories 11(1):–13
van Dijl JM, Hecker M (2013) Bacillus subtilis: from soil bacterium to super-secreting cell factory. Microb Cell Factories 12:6
Wang PZ, Doi RH (1984) Overlapping promoters transcribed by Bacillus subtilis sigma 55 and sigma 37 RNA polymerase holoenzymes during growth and stationary phases. J Biol Chem 259(13):8619–8625
Westers L, Westers H, Quax WJ (2004) Bacillus subtilis as cell factory for pharmaceutical proteins: a biotechnological approach to optimize the host organism. Biochim Biophys Acta-Mol Cell Res 1694(1–3):299–310
Winkler UK, Stuckmann M (1979) Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol 138(3):663–670
Wu XC, Lee W, Tran L, Wong SL (1991) Engineering a Bacillus subtilis expression-secretion system with a strain deficient in 6 extracellular proteases. J Bacteriol 173(16):4952–4958
Yamamoto H, Murata M, Sekiguchi J (2000) The CitST two-component system regulates the expression of the Mg-citrate transporter in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 37(4):898–912
Yang CK, Tai PC, Lu CD (2014) Time-related transcriptome analysis of B. subtilis 168 during growth with glucose. Curr Microbiol 68(1):12–20
Yang S, Kang Z, Cao W, Du G, Chen J (2016) Construction of a novel, stable, food-grade expression system by engineering the endogenous toxin-antitoxin system in Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 219:40–47
Yansura DG, Henner DJ (1984) Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81(2):439–443
Zhang XZ, Cui ZL, Hong Q, Li SP (2005) High-level expression and secretion of methyl parathion hydrolase in Bacillus subtilis WB800. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(7):4101–4103
Zhang W-W, Gao Q-R, Yang M-M, Liu H, Wang D (2012) Assay and characterization of an osmolarity inducible promoter newly isolated from Bacillus subtilis. Mol Biol Rep 39(7):7347–7353
Zhang J, Kang Z, Ling Z, Cao W, Liu L, Wang M, Du G, Chen J (2013) High-level extracellular production of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase in Bacillus subtilis with optimized regulatory elements. Bioresour Technol 146:543–548
Zobel S, Kumpfmuller J, Sussmuth RD, Schweder T (2015) Bacillus subtilis as heterologous host for the secretory production of the non-ribosomal cyclodepsipeptide enniatin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(2):681–691
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670092), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20141107), a grant from the Key Technologies R&D Program of Jiangsu Province, China, (BE2014607), and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT_15R26).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 230 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Du, G., Chen, J. et al. Characterization and application of endogenous phase-dependent promoters in Bacillus subtilis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 4151–4161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8142-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8142-7