Abstract
Interest in gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease has blossomed over the past 30 years and has generated a wealth of investigation into this non-motor aspect of the disorder, research that has encompassed its pathophysiology, its clinical features, and its impact on quality of life. The question of gastrointestinal dysfunction in the other synucleinopathies has not received nearly as much attention, but information and knowledge are growing. In this review, the current knowledge, controversies, and gaps in our understanding of the pathophysiology of gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease and the other synucleinopathies will be addressed, and extended focus will be directed toward the clinical problems involving saliva management, swallowing, gastric emptying, small intestinal function, and bowel function that are so problematic in these disorders.

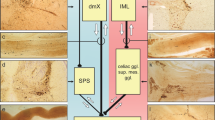
Modified from Pfeiffer RF. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 2020 [269]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qualman SJ, Haupt HM, Yang P, Hamilton SR (1984) Esophageal Lewy bodies associated with ganglion cell loss in achalasia. Gastroenterology 87(4):848–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(84)90079-9
Spillantini M, Schmidt M, Lee V, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Braak H, de Vos R, Bohl J, Del Tredici K (2006) Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett 396:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2005.11.012
Lebouvier T, Chaumette T, Damier P, Coron E, Touchefeu Y, Vrignaud S, Naveilhan P, Galmiche J-P, des BruleyVarannes S, Derkinderen P, Neunlist M (2008) Pathological lesions in colonic biopsies during Parkinson’s disease. Gut 57:1741–1743. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.162503
Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Mutlu E, Dodiya HB, Daian D, Jaglin JA, Kordower JH (2012) Alpha-synuclein in colonic submucosa in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27:709–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23838
Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Dodiya HB, Jakate S, Kordower JH (2012) Is alpha-synuclein in the colon a biomarker for premotor Parkinson’s Disease? Evidence from 3 cases. Mov Disord 27:716–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25020
Hilton D, Stephens M, Kirk L, Edwards P, Potter R, Zajicek J, Broughton E, Hagan H, Carroll C (2014) Accumulation of α-synuclein in the bowel of patients in the pre-clinical phase of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 127:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1214-6
Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, White LR, Masaki KH, Tanner CM, Curb JD, Grandinetti A, Blanchette PL, Popper JS, Ross GW (2001) Frequency of bowel movements and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 57:456–462. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.57.3.456
Ueki A, Otsuka M (2004) Life style risks of Parkinson’s disease: association between decreased water intake and constipation. J Neurol 251:vii18–vii23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-1706-3
Svensson E, Horváth-Puhó E, Thomsen RW, Djurhuus JC, Pedersen L, Borghammer P, Sørensen HT (2015) Vagotomy and subsequent risk of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 78:522–529. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24448
Liu S-Y, Chan P, Stoessl AJ (2017) The underlying mechanism of prodromal PD: insights from the parasympathetic nervous system and the olfactory system. Transl Neurodegener 6:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-017-0074-8
Killinger BA, Madaj Z, Sikora JW, Rey N, Haas AJ, Vepa Y, Lindqvist D, Chen H, Thomas PM, Brundin P, Brundin L, Labrie V (2018) The vermiform appendix impacts the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med 10:eaar5280. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aar5280
Liu B, Fang F, Ye W, Wirdefeldt K (2020) Appendectomy, tonsillectomy and Parkinson’s disease risk: a Swedish register-based study. Front Neurol 11:510. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00510
Mendes A, Gonçalves A, Vila-Chã N, Moreira I, Fernandes J, Damásio J, Teixeira-Pinto A, Taipa R, Lima AB, Cavaco S (2015) Appendectomy may delay Parkinson’s disease Onset. Mov Disord 30:1404–1407. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26311
Marras C, Lang AE, Austin PC, Lau C, Urbach DR (2016) Appendectomy in mid and later life and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a population-based study. Mov Disord 31:1243–1247. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26670
Svensson E, Horváth-Puhó E, Stokholm MG, Sørensen HT, Henderson VW, Borghammer P (2016) Appendectomy and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a nationwide cohort study with more than 10 years of follow-up. Mov Disord 31:1918–1922. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26761
Palacios N, Hughes KC, Cereda E, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2018) Appendectomy and risk of Parkinson’s disease in two large prospective cohorts of men and women. Mov Disord 33:1492–1496. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.109
Forsyth CB, Shannon KM, Kordower JH, Voigt RM, Shaikh M, Jaglin JA, Estes JD, Dodiya HB, Keshavarzian A (2011) Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 6:e28032. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028032
Clairembault T, Leclair-Visonneau L, Coron E, Bourreille A, Le Dily S, Vavasseur F, Heymann M-F, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2015) Structural alterations of the intestinal epithelial barrier in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 3:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-015-0196-0
Drolet RE, Cannon JR, Montero L, Greenamyre JT (2009) Chronic rotenone exposure reproduces Parkinson’s disease gastrointestinal neuropathology. Neurobiol Dis 36:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.06.017
Holmqvist S, Chutna O, Bousset L, Aldrin-Kirk P, Li W, Björklund T, Wang Z-Y, Roybon L, Melki R, Li J-Y (2014) Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathol 128:805–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1343-6
Uemura N, Yagi H, Uemura MT, Hatanaka Y, Yamakado H, Takahashi R (2018) Inoculation of α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces Lewy body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Mol Neurodegener 13:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-018-0257-5
Barbut D, Stolzenberg E, Zasloff M (2019) Gastrointestinal immunity and alpha-synuclein. J Parkinsons Dis 9:S313–S322. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191702
Lin J-C, Lin C-S, Hsu C-W, Lin C-L, Kao C-H (2016) Association between Parkinson’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease: a nationwide Taiwanese retrospective cohort study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 22:1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000000735
Villumsen M, Aznar S, Pakkenberg B, Jess T, Brudek T (2019) Inflammatory bowel disease increases the risk of Parkinson’s disease: a Danish nationwide cohort study 1977–2014. Gut 68:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315666
Weimers P, Halfvarson J, Sachs MC, Saunders-Pullman R, Ludvigsson JF, Peter I, Burisch J, Olén O (2018) Inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease: a nationwide Swedish cohort study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 25:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izy190
Camacho-Soto A, Gross A, Searles Nielsen S, Dey N, Racette BA (2018) Inflammatory bowel disease and risk of Parkinson’s disease in Medicare beneficiaries. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 50:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.02.008
Fujioka S, Curry SE, Kennelly KD, Tacik P, Heckman MG, Tsuboi Y, Strongosky AJ, van Gerpen JA, Uitti RJ, Ross OA, Ikezu T, Wszolek ZK (2017) Occurrence of Crohn’s disease with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 37:116–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.01.013
Killinger BA, Kordower JH (2019) Spreading of alpha-synuclein – relevant or epiphenomenon? J Neurochem 150:605–611. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14779
Leclair-Visonneau L, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P, Lebouvier T (2020) The gut in Parkinson’s disease: bottom-up, top-down, or neither? Neurogastroenterol Motil 32:e13777. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13777
Lionnet A, Leclair-Visonneau L, Neunlist M, Murayama S, Takao M, Adler CH, Derkinderen P, Beach TG (2018) Does Parkinson’s disease start in the gut? Acta Neuropathol 135:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1777-8
Adler CH, Beach TG (2016) Neuropathological basis of nonmotor manifestations of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 31:1114–1119. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26605
Zheng L-F, Song J, Fan R-F, Chen C-L, Ren Q-Z, Zhang X-L, Feng X-Y, Zhang Y, Li L-S, Zhu J-X (2014) The role of the vagal pathway and gastric dopamine in the gastroparesis of rats after a 6-hydroxydopamine microinjection in the substantia nigra. Acta Physiol 211:434–446. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12229
Ulusoy A, Phillips RJ, Helwig M, Klinkenberg M, Powley TL, Di Monte DA (2017) Brain-to-stomach transfer of α-synuclein via vagal preganglionic projections. Acta Neuropathol 133:381–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1661-y
O’Donovan SM, Crowley EK, Brown JR-M, O’Sullivan O, O’Leary OF, Timmons S, Nolan YM, Clarke DJ, Hyland NP, Joyce SA, Sullivan AM, O’Neill C (2020) Nigral overexpression of α-synuclein in a rat Parkinson’s disease model indicates alterations in the enteric nervous system and the gut microbiome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 32:e13726. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13726
Hinkle JT, Perepezko K, Mills KA, Mari Z, Butala A, Dawson TM, Pantelyat A, Rosenthal LS, Pontone GM (2018) Dopamine transporter availability reflects gastrointestinal dysautonomia in early Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 55:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.08.010
Elfil M, Kamel S, Kandil M, Koo BB, Schaefer SM (2020) Implications of the gut microbiome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 35:921–933. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28004
Keshavarzian A, Green SJ, Engen PA, Voigt RM, Naqib A, Forsyth CB, Mutlu E, Shannon KM (2015) Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30:1351–1360. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26307
Scheperjans F, Aho V, Pereira PAB, Koskinen K, Paulin L, Pekkonen E, Haapaniemi E, Kaakkola S, Eerola-Rautio J, Pohja M, Kinnunen E, Murros K, Auvinen P (2015) Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson’s disease and clinical phenotype. Mov Disord 30:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26069
Unger MM, Spiegel J, Dillmann K-U, Grundmann D, Philippeit H, Bürmann J, Faßbender K, Schwiertz A, Schäfer K-H (2016) Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ between patients with Parkinson’s disease and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 32:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.08.019
Hill-Burns EM, Debelius JW, Morton JT, Wissemann WT, Lewis MR, Wallen ZD, Peddada SD, Factor SA, Molho E, Zabetian CP, Knight R, Payami H (2017) Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease medications have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Mov Disord 32:739–749. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26942
Bedarf JR, Hildebrand F, Coelho LP, Sunagawa S, Bahram M, Goeser F, Bork P, Wüllner U (2017) Functional implications of microbial and viral gut metagenome changes in early stage l-DOPA-naïve Parkinson’s disease patients. Genome Med 9:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-017-0428-y
Hopfner F, Künstner A, Müller SH, Künzel S, Zeuner KE, Margraf NG, Deuschl G, Baines JF, Kuhlenbäumer G (2017) Gut microbiota in Parkinson disease in a northern German cohort. Brain Res 1667:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.04.019
Lin C-H, Chen C-C, Chiang H-L, Liou J-M, Chang C-M, Lu T-P, Chuang EY, Tai Y-C, Cheng C, Lin H-Y, Wu M-S (2019) Altered gut microbiota and inflammatory cytokine responses in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 16:129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1528-y
Boertien JM, Pereira PAB, Aho VTE, Scheperjans F (2019) Increasing comparability and utility of gut microbiome studies in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. J Parkinsons Dis 9:S297–S312. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191711
Lubomski M, Tan AH, Lim S-Y, Holmes AJ, Davis RL, Sue CM (2020) Parkinson’s disease and the gastrointestinal microbiome. J Neurol 267:2507–2523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09320-1
Sun MF, Shen YQ (2018) Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and microbial metabolites in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 45:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.04.004
Quigley EMM (2017) Microbiota-brain-gut axis and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 17:94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-017-0802-6
Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, Challis C, Schretter CE, Rocha S, Gradinaru V, Chesselet M-F, Keshavarzian A, Shannon KM, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Wittung-Stafshede P, Knight R, Mazmanian SK (2016) Gut Microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167:1469–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018
Edwards LL, Pfeiffer RF, Quigley EMM, Hofman R, Balluff M (1991) Gastrointestinal symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 6:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870060211
Edwards LL, Quigley EMM, Pfeiffer RF (1992) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s' disease. Neurology 42(4):726–32. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.42.4.726
Martinez-Martin P, Schapira AHV, Stocchi F, Sethi K, Odin P, MacPhee G, Brown RG, Naidu Y, Clayton L, Abe K, Tsuboi Y, MacMahon D, Barone P, Rabey M, Bonuccelli U, Forbes A, Breen K, Tluk S, Olanow CW, Thomas S, Rye D, Hand A, Williams AJ, Ondo W, Chaudhuri KR (2007) Prevalence of nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease in an international setting; Study using nonmotor symptoms questionnaire in 545 patients. Mov Disord 22:1623–1629. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21586
Cersosimo MG, Raina GB, Pecci C, Pellene A, Calandra CR, Gutiérrez C, Micheli FE, Benarroch EE (2013) Gastrointestinal manifestations in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence and occurrence before motor symptoms. J Neurol 260:1332–1338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6801-2
Khoo TK, Yarnall AJ, Duncan GW, Coleman S, O’Brien JT, Brooks DJ, Barker RA, Burn DJ (2013) The spectrum of nonmotor symptoms in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 80:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31827deb74
Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LWC, Lang AE, Pfeiffer RF (2015) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14:625–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00007-1
van Wamelen DJ, Leta V, Johnson J, Ocampo CL, Podlewska AM, Rukavina K, Rizos A, Martinez-Martin P, Chaudhuri KR (2020) Drooling in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence and progression from the non-motor international longitudinal study. Dysphagia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10102-5
Bagheri H, Damase-Michel C, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Cismondo S, O’Connell D, Senard JM, Rascol O, Montastruc JL (1999) A study of salivary secretion in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 22:213–215
Karakoc M, Yon MI, Cakmakli GY, Ulusoy EK, Gulunay A, Oztekin N, Ak F (2016) Pathophysiology underlying drooling in Parkinson’s disease: oropharyngeal bradykinesia. Neurol Sci 37:1987–1991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2708-5
Rajiah K, Maharajan MK, Yeen SJ, Lew S (2017) Quality of life and caregivers’ burden of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroepidemiology 48(3–4):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479031
Hyson HC, Johnson AM, Jog MS (2002) Sublingual Atropine for sialorrhea secondary to Parkinsonism: a pilot study. Mov Disord 17:1318–1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10276
Isaacson SH, Ondo W, Jackson CE, Trosch RM, Molho E, Pagan F, Lew M, Dashtipour K, Clinch T, Espay AJ, Group for the MS (2020) Safety and efficacy of rimabotulinumtoxinB for treatment of sialorrhea in adults: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol 77:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4565
Jost WH, Friedman A, Michel O, Oehlwein C, Slawek J, Bogucki A, Ochudlo S, Banach M, Pagan F, Flatau-Baqué B, Dorsch U, Csikós J, Blitzer A (2020) Long-term incobotulinumtoxinA treatment for chronic sialorrhea: efficacy and safety over 64 weeks. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 70:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.11.024
Ondo WG, Hunter C, Moore W (2004) A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of botulinum toxin B for sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 62:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000101713.81253.4C
Narayanaswami P, Geisbush T, Tarulli A, Raynor E, Gautam S, Tarsy D, Gronseth G (2016) Drooling in Parkinson’s disease: a randomized controlled trial of incobotulinum toxin A and meta-analysis of botulinum toxins. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 30:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.07.001
Hawkey NM, Zaorsky NG, Galloway TJ (2016) The role of radiation therapy in the management of sialorrhea: a systematic review. Laryngoscope 126(1):80–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25444
Pfeiffer RF (2011) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.08.003
Takizawa C, Gemmell E, Kenworthy J, Speyer R (2016) A systematic review of the prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, head injury, and pneumonia. Dysphagia 31:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9695-9
Kalf JG, de Swart BJM, Bloem BR, Munneke M (2012) Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:311–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.006
Pflug C, Bihler M, Emich K, Niessen A, Nienstedt JC, Flügel T, Koseki J-C, Plaetke R, Hidding U, Gerloff C, Buhmann C (2018) Critical dysphagia is common in Parkinson disease and occurs even in early stages: a prospective cohort study. Dysphagia 33:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-017-9831-1
Jones CA, Ciucci MR (2016) Multimodal swallowing evaluation with high-resolution manometry reveals subtle swallowing changes in early and mid-stage Parkinson disease. J Parkinsons Dis 6:197–208. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-150687
Coelho M, Marti MJ, Tolosa E, Ferreira JJ, Valldeoriola F, Rosa M, Sampaio C (2010) Late-stage Parkinson’s disease: the Barcelona and Lisbon cohort. J Neurol 257:1524–1532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5566-8
Paul B, Singh T, Paul G, Singh G, Kaushal S et al (2019) Prevalence of malnutrition in Parkinson’s disease and correlation with gastrointestinal symptoms. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 22(4):447–452. https://doi.org/10.4103/aian.AIAN_349_18
Fabbri M, Coelho M, Abreu D, Guedes LC, Rosa MM, Godinho C, Cardoso R, Guimaraes I, Antonini A, Zibetti M, Lopiano L, Ferreira JJ (2019) Dysphagia predicts poor outcome in late-stage Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 64:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.02.043
Mu L, Sobotka S, Chen J, Su H, Sanders I, Adler CH, Shill HA, Caviness JN, Samanta JE, Beach TG, Consortium APD (2012) Altered pharyngeal muscles in Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:520–530. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e318258381b
Mu L, Sobotka S, Chen J, Su H, Sanders I, Nyirenda T, Adler CH, Shill HA, Caviness JN, Samanta JE, Sue LI, Beach TG, Consortium APD (2013) Parkinson disease affects peripheral sensory nerves in the pharynx. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72:614–623. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182965886
Mu L, Sobotka S, Chen J, Su H, Sanders I, Adler CH, Shill HA, Caviness JN, Samanta JE, Beach TG, Consortium APD (2013) Alpha-synuclein pathology and axonal degeneration of the peripheral motor nerves innervating pharyngeal muscles in Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182801cde
Suntrup S, Teismann I, Bejer J, Suttrup I, Winkels M, Mehler D, Pantev C, Dziewas R, Warnecke T (2013) Evidence for adaptive cortical changes in swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 136:726–738. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt004
Labeit B, Claus I, Muhle P, Lapa S (2020) Oropharyngeal freezing and its relation to dysphagia: an analogy to freezing of gait. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 75:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.05.002
Byrne KG, Pfeiffer R, Quigley EMM (1994) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: a report of clinical experience at a single center. J Clin Gastroenterol 19(1):11–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-199407000-00004
Born LJ, Harned RH, Rikkers LF, Pfeiffer RF, Quigley EMM (1996) Cricopharyngeal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: role in dysphagia and response to myotomy. Mov Disord 11:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870110110
Su A, Gandhy R, Barlow C, Triadafilopoulos G (2017a) A practical review of gastrointestinal manifestations in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 39:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.02.029
Pfeiffer RF (2003) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 2:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00307-7
Stroudley J, Walsh M (1991) Radiological assessment of dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Br J Radiol 64:890–893. https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-64-766-890
Nagaya M, Kachi T, Yamada T, Igata A (1998) Videofluorographic study of swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 13:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009562
Lin C-W, Chang Y-C, Chen W-S, Chang K, Chang H-Y, Wang T-G (2012) Prolonged swallowing time in dysphagic Parkinsonism patients with aspiration pneumonia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 93:2080–2084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.07.010
Bird MR, MiC W, Gibson EM, Phyland DJ, Fonda D (1994) Asymptomatic swallowing disorders in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease: a description of findings on clinical examination and video fluoroscopy in sixteen patients. Age Ageing 23:251–254. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/23.3.251
Gross RD, Atwood CW, Ross SB, Eichhorn KA, Olszewski JW, Doyle PJ (2008) The coordination of breathing and swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 23:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9113-4
Suttrup I, Warnecke T (2016) Dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 31:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9671-9
Curtis JA, Troche MS (2020) Handheld cough testing: a novel tool for cough assessment and dysphagia screening. Dysphagia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10097-z
Melo A, Monteiro L (2013) Swallowing improvement after levodopa treatment in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: lack of evidence. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:279–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.11.017
Sutton JP (2013) Dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease is responsive to levodopa. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:282–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.11.007
Warnecke T, Suttrup I, Schröder JB, Osada N, Oelenberg S, Hamacher C, Suntrup S, Dziewas R (2016) Levodopa responsiveness of dysphagia in advanced Parkinson’s disease and reliability testing of the FEES-Levodopa-test. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 28:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.04.034
Labeit B, Claus I, Muhle P, Suntrup-Krueger S, Dziewas R, Warnecke T (2020) Effect of intestinal levodopa-carbidopa infusion on pharyngeal dysphagia: results from a retrospective pilot study in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2020:4260501. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4260501
Hirano M, Isono C, Fukuda K, Ueno S, Nakamura Y, Kusunoki S (2019) Effects of the rotigotine transdermal patch versus oral levodopa on swallowing in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 404:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2019.07.003
Tison F, Wiart L, Guatterie M, Fouillet N, Lozano V, Henry P, Barat M (1996) Effects of central dopaminergic stimulation by apomorphine on swallowing disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 11:729–732. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870110622
Curtis JA, Avery D, Michelle T (2020) Respiratory-swallow coordination training and voluntary cough skill training: a single-subject treatment study in a person with Parkinson’s disease. J Speech Lang Hear Res 63:472–486. https://doi.org/10.1044/2019_JSLHR-19-00207
Troche MS, Okun MS, Rosenbek JC, Musson N, Fernandez HH, Rodriguez R, Romrell J, Pitts T, Wheeler-Hegland KM, Sapienza CM (2010) Aspiration and swallowing in Parkinson disease and rehabilitation with EMST. Neurology 75:1912–1919. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181fef115
Byeon H (2016) Effect of simultaneous application of postural techniques and expiratory muscle strength training on the enhancement of the swallowing function of patients with dysphagia caused by Parkinson’s disease. J Phys Ther Sci 28:1840–1843. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.1840
Miles A, Jardine M, Johnston F, de Lisle M, Friary P, Allen J (2017) Effect of Lee Silverman voice treatment (LSVT LOUD®) on swallowing and cough in Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. J Neurol Sci 383:180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2017.11.015
Kawaguchi M, Samura K, Miyagi Y, Okamoto T, Yamasaki R, Sakae N, Yoshida F, Iihara K (2020) The effects of chronic subthalamic stimulation on nonmotor symptoms in advanced Parkinson’s disease, revealed by an online questionnaire program. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 162:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04182-y
Fabbri M, Zibetti M, Rizzone MG, Giannini G, Borellini L, Stefani A, Bove F, Bruno A, Calandra-Buonaura G, Modugno N, Piano C, Peppe A, Ardolino G, Romagnolo A, Artusi CA, Berchialla P, Montanaro E, Cortelli P, Luigi R, Eleopra R, Minafra B, Pacchetti C, Tufo T, Cogiamanian F, Lopiano L (2020) Should we consider deep brain stimulation discontinuation in late-stage Parkinson’s disease? Mov Disord 35(8):1379–1387. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28091
Xie T, Bloom L, Padmanaban M, Bertacchi B, Kang W, MacCracken E, Dachman A, Vigil J, Satzer D, Zadikoff C, Markopoulou K, Warnke P, Kang UJ (2018) Long-term effect of low frequency stimulation of STN on dysphagia, freezing of gait and other motor symptoms in PD. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89:989–994. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-318060
Yin Z, Cao Y, Zheng S, Duan J, Zhou D, Xu R, Hong T, Lu G (2018) Persistent adverse effects following different targets and periods after bilateral deep brain stimulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 393:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2018.08.016
Restivo DA, Palmeri A, Marchese-Ragona R (2002) Botulinum toxin for cricopharyngeal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 346:1174–1175. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200204113461517
Heetun ZS, Quigley EMM (2012) Gastroparesis and Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.12.004
Heimrich KG, Jacob VYP, Schaller D, Stallmach A, Witte OW, Prell T (2019) Gastric dysmotility in Parkinson’s disease is not caused by alterations of the gastric pacemaker cells. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 5:15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-019-0087-3
Goetze O, Wieczorek J, Mueller T, Przuntek H, Schmidt WE, Woitalla D (2005) Impaired gastric emptying of a solid test meal in patients with Parkinson’s disease using 13C-sodium octanoate breath test. Neurosci Lett 375:170–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.007
Tanaka Y, Kato T, Nishida H, Yamada M, Koumura A, Sakurai T, Hayashi Y, Kimura A, Hozumi I, Araki H, Murase M, Nagaki M, Moriwaki H, Inuzuka T (2012) Is there delayed gastric emptying in patients with multiple system atrophy? An analysis using the 13C-acetate breath test. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6372-7
Fosso CL, Quigley EMM (2018) A critical review of the current clinical landscape of gastroparesis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 14:140–145
Camilleri M, Parkman HP, Shafi MA, Abell TL, Gerson L (2013) Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 108(1):18–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.373
Pfeiffer RF, Isaacson SH, Pahwa R (2020) Clinical implications of gastric complications on levodopa treatment in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 76:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.05.001
Miyaue N, Yabe H, Nagai M, Nomoto M (2020) Abnormal upper gastrointestinal structures underlying levodopa malabsorption. J Neurol Sci 414:116855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2020.116855
Bestetti A, Capozza A, Lacerenza M, Manfredi L, Mancini F (2017) Delayed gastric emptying in advanced Parkinson disease: correlation with therapeutic doses. Clin Nucl Med 42(2):83–87. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000001470
Berkowitz DM, McCallum RW (1980) Interaction of levodopa and metoclopramide on gastric emptying. Clin Pharmacol Ther 27:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1980.55
Parkman HP, Trate DM, Knight LC, Brown KL, Maurer AH, Fisher RS (1999) Cholinergic effects on human gastric motility. Gut 45:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.45.3.346
Knudsen K, Szwebs M, Hansen AK, Borghammer P (2018) Gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease: a mini-review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 55:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.06.003
Camps G, Mars M, Witteman BJM, de Graaf C, Smeets PAM (2018) Indirect vs direct assessment of gastric emptying: a randomized crossover trial comparing C-isotope breath analysis and MRI. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30(7):e13317. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13317
Su A, Gandhy R, Barlow C, Triadafilopoulos G (2017b) Utility of the wireless motility capsule and lactulose breath testing in the evaluation of patients with Parkinson’s disease who present with functional gastrointestinal symptoms. BMJ Open Gastroenterol 4:e000132. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000132
Hasler WL, May KP, Wilson LA, Van Natta M, Parkman HP, Pasricha PJ, Koch KL, Abell TL, McCallum RW, Nguyen LA, Snape WJ, Sarosiek I, Clarke JO, Farrugia G, Calles-Escandon J, Grover M, Tonascia J, Lee LA, Miriel L, Hamilton FA, (GpCRC) the NGCRC, (2018) Relating gastric scintigraphy and symptoms to motility capsule transit and pressure findings in suspected gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30:e13196. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13196
Keller J, Bassotti G, Clarke J, Dinning P, Fox M, Grover M, Hellström PM, Ke M, Layer P, Malagelada C, Parkman HP, Scott SM, Tack J, Simren M, Törnblom H, Camilleri M, International Working Group for Disorders of Gastrointestinal Motility and Function (2018) Expert consensus document: Advances in the diagnosis and classification of gastric and intestinal motility disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(5):291–308. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2018.7
Nyholm D, Lennernäs H (2008) Irregular gastrointestinal drug absorption in Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.4.2.193
Müller T, Erdmann C, Bremen D, Schmidt WE, Muhlack S, Woitalla D, Goetze O (2006) Impact of gastric emptying on levodopa pharmacokinetics in Parkinson disease patients. Clin Neuropharmacol 29(2):61–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002826-200603000-00001.
Fukae J, Fujioka S, Umemoto G, Arahata H, Yanamoto S, Mishima T, Tsuboi Y (2020) Impact of residual drug in the pharynx on the delayed-on phenomenon in Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord Clin Pract 7:273–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12908
Fasano A, Bove F, Gabrielli M, Petracca M, Zocco MA, Ragazzoni E, Barbaro F, Piano C, Fortuna S, Tortora A, Di Giacopo R, Campanale M, Gigante G, Lauritano EC, Navarra P, Marconi S, Gasbarrini A, Bentivoglio AR (2013) The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 28:1241–1249. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25522
Sato H, Yamamoto T, Sato M, Furusawa Y, Murata M (2018) Dysphagia causes symptom fluctuations after oral l-DOPA treatment in a patient with Parkinson disease. Case Rep Neurol 10:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488138
Staisch J, Bakis G, Nutt J (2018) A wrinkle in ON-time: a GI structural abnormality confounding levodopa therapy with Duodopa rescue; a case study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 50:130–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.02.021
Brüssow H (2020) Parkinson disease, levodopa and the gut microbiota—when microbiology meets pharmacology. Environ Microbiol 22:808–812. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14919
Maini Rekdal V, Bess EN, Bisanz JE, Turnbaugh PJ, Balskus EP (2019) Discovery and inhibition of an interspecies gut bacterial pathway for Levodopa metabolism. Science 14:364(6445):eaau6323. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6323
Leelakanok N, Holcombe A, Schweizer ML (2016) Domperidone and risk of ventricular arrhythmia and cardiac death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Drug Investig 36:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0360-0
Buffery P, Strother R (2015) Domperidone safety: a mini-review of the science of QT prolongation and clinical implications of recent global regulatory recommendations. N Z Med J 128(1416):66–74
Omer A, Quigley EMM (2017) An update on prucalopride in the treatment of chronic constipation. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 10:877–887. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756283X17734809
Quigley EMM (2015) Prokinetics in the management of functional gastrointestinal disorders. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:330–336. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm15094
Asai H, Udaka F, Hirano M, Minami T, Oda M, Kubori T, Nishinaka K, Kameyama M, Ueno S (2005) Increased gastric motility during 5-HT4 agonist therapy reduces response fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11:499–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2005.06.007
Pinyopornpanish K, Soontornpun A, Kijdamrongthum P, Teeyasoontranon W, Angkurawaranon C, Thongsawat S (2017) The effect of prucalopride on gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease patients, a pilot randomized, open-label study. Dig Sys 1:1–6
Doi H, Sakakibara R, Sato M, Hirai S, Masaka T, Kishi M, Tsuyusaki Y, Tateno A, Tateno F, Takahashi O, Ogata T (2014) Nizatidine ameliorates gastroparesis in Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. Mov Disord 29:562–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25777
Chedid V, Camilleri M (2017) Relamorelin for the treatment of gastrointestinal motility disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 26:1189–1197. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2017.1373088
Lembo A, Camilleri M, McCallum R, Sastre R, Breton C, Spence S, White J, Currie M, Gottesdiener K, Stoner E (2016) Relamorelin reduces vomiting frequency and severity and accelerates gastric emptying in adults with diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 151:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.038
Camilleri M, McCallum RW, Tack J, Spence SC, Gottesdiener K, Fiedorek FT (2017) Efficacy and safety of relamorelin in diabetics with symptoms of gastroparesis: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Gastroenterology 153:1240–1250. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.035
Gil RA, Hwynn N, Fabian T, Joseph S, Fernandez HH (2011) Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of gastroparesis in Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17:285–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.01.007
Triadafilopoulos G, Gandhy R, Barlow C (2017) Pilot cohort study of endoscopic botulinum neurotoxin injection in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 44:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.08.020
Shada A, Nielsen A, Marowski S, Helm M, Funk LM, Kastenmeier A, Lidor A, Gould JC (2018) Wisconsin’s Enterra Therapy experience: a multi-institutional review of gastric electrical stimulation for medically refractory gastroparesis. Surgery 164:760–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.04.043
Arai E, Arai M, Uchiyama T, Higuchi Y, Aoyagi K, Yamanaka Y, Yamamoto T, Nagano O, Shiina A, Maruoka D, Matsumura T, Nakagawa T, Katsuno T, Imazeki F, Saeki N, Kuwabara S, Yokosuka O (2012) Subthalamic deep brain stimulation can improve gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 135:1478–1485. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws086
Cloud LJ, Greene JG (2011) Gastrointestinal Features of Parkinson’s Disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 11:379–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-011-0204-0
Legge J, Fleming N, Cloud LJ (2020) Gastrointestinal care of the Parkinson patient. Clin Geriatr Med 36:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2019.09.003
Bracco F, Malesani R, Saladini M, Battistin L (1991) Protein redistribution diet and antiparkinsonian response to levodopa. Eur Neurol 31:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1159/000116649
Pincus JH, Barry K (1988) Protein redistribution diet restores motor function in patients with dopa-resistant “off” periods. Neurology 38(3):481–483. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.38.3.481
Riley D, Lang AE (1988) Practical application of a low-protein diet for Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 38:1026–1026. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.38.7.1026
Tan AH, Hew YC, Lim S-Y, Ramli NM, Kamaruzzaman SB, Tan MP, Grossmann M, Ang BH, Tan JY, Manap MAAA, Tay TK, Tan SL, New RP, Fadzli F, Yee EJ, Moy FM, Mahadeva S, Lang AE (2018) Altered body composition, sarcopenia, frailty, and their clinico-biological correlates, in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 56:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.06.020
Davies KN, King D, Billington D, Barrett JA (1996) Intestinal permeability and orocaecal transit time in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease. Postgrad Med J 72:164–167. https://doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.72.845.164
Dutkiewicz J, Szlufik S, Nieciecki M, Charzyńska I, Królicki L, Smektała P, Friedman A (2015) Small intestine dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 122:1659–1661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-015-1442-0
Knudsen K, Haase A-M, Fedorova TD, Bekker AC, Østergaard K, Krogh K, Borghammer P (2017) Gastrointestinal transit time in Parkinson’s disease using a magnetic tracking system. J Parkinsons Dis 7:471–479. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-171131
Tan AH, Mahadeva S, Thalha AM, Gibson PR, Kiew CK, Yeat CM, Ng SW, Ang SP, Chow SK, Tan CT, Sen YH, Marras C, Fox SH, Lim S-Y (2014) Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20:535–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.02.019
Niu X-L, Liu L, Song Z-X, Li Q, Wang Z-H, Zhang J-L, Li H-H (2016) Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 123:1381–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1612-8
Gabrielli M, Bonazzi P, Scarpellini E, Bendia E, Lauritano EC, Fasano A, Ceravolo MG, Capecci M, Rita Bentivoglio A, Provinciali L, Tonali PA, Gasbarrini A (2011) Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26:889–892. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23566
Vizcarra JA, Wilson-Perez HE, Fasano A, Espay AJ (2018) Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease: tribulations of a trial. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 54:110–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.04.003
Quigley EMM, Murray JA, Pimentel M (2020) AGA clinical practice update on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: expert review. Gastroenterology 159(4):1526–1532. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.090
Shah ED (2020) Breath test or duodenal aspirate for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: still no breath of fresh air. Dig Dis Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06556-0
van Kessel SP, Frye AK, El-Gendy AO, Castejon M, Keshavarzian A, van Dijk G, El Aidy S (2019) Gut bacterial tyrosine decarboxylases restrict levels of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun 10:310. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08294-y
Alsahafi M, Cramer P, Chatur N, Donnellan F (2017) The effect of prucalopride on small bowel transit time in hospitalized patients undergoing capsule endoscopy. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017:2696947. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2696947
Freitas ME, Alqaraawi A, Lang AE, Liu LWC (2018) Linaclotide and prucalopride for management of constipation in patients with Parkinsonism. Mov Disord Clin Pract 5:218–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12577
Jost WH, Schimrigk K (1991) Constipation in Parkinson’s disease. Klin Wochenschr 69:906–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01798536
Edwards LL, Quigley EM, Harned RK, Hofman R, Pfeiffer RF (1994) Characterization of swallowing and defecation in Parkinson’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 89:15–25
Ashraf W, Pfeiffer RF, Park F, Lof J, Quigley EMM (1997) Constipation in parkinson’s disease: objective assessment and response to psyllium. Mov Disord 12:946–951. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870120617
Knudsen K, Fedorova TD, Bekker AC, Iversen P, Østergaard K, Krogh K, Borghammer P (2017) Objective colonic dysfunction is far more prevalent than subjective constipation in Parkinson’s disease: a colon transit and volume study. J Parkinsons Dis 7:359–367. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-161050
Knudsen K, Krogh K, Østergaard K, Borghammer P (2017) Constipation in Parkinson’s disease: subjective symptoms, objective markers, and new perspectives. Mov Disord 32:94–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26866
Pfeiffer R (2017) Management of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Semin Neurol 37(2):176–185. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1601568
De Pablo-Fernández E, Passananti V, Zárate-López N, Emmanuel A, Warner T (2019) Colonic transit, high-resolution anorectal manometry and MRI defecography study of constipation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 66:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.08.016
Savica R, Carlin JM, Grossardt BR, Bower JH, Ahlskog JE, Maraganore DM, Bharucha AE, Rocca WA (2009) Medical records documentation of constipation preceding Parkinson disease. Neurology 73:1752–1758. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c34af5
Berg D, Postuma RB, Adler CH, Bloem BR, Chan P, Dubois B, Gasser T, Goetz CG, Halliday G, Joseph L, Lang AE, Liepelt-Scarfone I, Litvan I, Marek K, Obeso J, Oertel W, Olanow CW, Poewe W, Stern M, Deuschl G (2015) MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30:1600–1611. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26431
Armstrong MJ, Okun MS (2020) Diagnosis and treatment of parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 323:548–560. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.22360
Parkinson Study Group (2017) A randomized trial of relamorelin for constipation in Parkinson’s disease (MOVE-PD): trial results and lessons learned. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 37:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.02.003
Toebosch S, Tudyka V, Masclee A, Koek G (2012) Treatment of recurrent sigmoid volvulus in Parkinson’s disease by percutaneous endoscopic colostomy. World J Gastroenterol 18:5812–5815. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5812
Blackley S, Maguire C, Daniels T (2016) Seven cases of sigmoid volvulus in Parkinson’s disease. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 46(3):157–159. https://doi.org/10.4997/JRCPE.2016.303
Van Laar T, Boertien JM, Herranz AH (2019) Faecal transplantation, pro- and prebiotics in Parkinson’s disease; hope or hype? J Parkinsons Dis 9:S371–S379. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191802
Barichella M, Pacchetti C, Bolliri C, Cassani E, Iorio L, Pusani C, Pinelli G, Privitera G, Cesari I, Faierman SA, Caccialanza R, Pezzoli G, Cereda E (2016) Probiotics and prebiotic fiber for constipation associated with Parkinson disease. Neurology 87:1274–1280. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003127
Zesiewicz TA, Sullivan KL, Arnulf I, Chaudhuri KR, Morgan JC, Gronseth GS, Miyasaki J, Iverson DJ, Weiner WJ (2010) Practice parameter: treatment of nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson disease. Neurology 74:924–931. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0b013e3181d55f24
Ondo WG, Kenney C, Sullivan K, Davidson A, Hunter C, Jahan I, McCombs A, Miller A, Zesiewicz TA (2012) Placebo-controlled trial of lubiprostone for constipation associated with Parkinson disease. Neurology 78:1650–1654. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182574f28
Sadjadpour K (1983) Pyridostigmine bromide and constipation in Parkinson’s disease. JAMA 249:1148
Pagano G, Tan EE, Haider JM, Bautista A, Tagliati M (2015) Constipation is reduced by beta-blockers and increased by dopaminergic medications in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21:120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.11.015
Sakakibara R, Doi H, Sato M, Hirai S, Masaka T, Kishi M, Tsuyusaki Y, Tateno A, Tateno F, Aiba Y, Ogata T, Suzuki Y (2015) Nizatidine ameliorates slow transit constipation in Parkinson’s disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 63:399–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.13279
Sharman SK, Islam BN, Hou Y, Usry M, Bridges A, Singh N, Sridhar S, Rao S, Browning DD (2017) Sildenafil normalizes bowel transit in preclinical models of constipation. PLoS ONE 12:e0176673. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176673
Coletto E, Dolan JS, Pritchard S, Gant A, Hikima A, Jackson MJ, Benham CD, Chaudhuri KR, Rose S, Jenner P, Iravani MM (2019) Contractile dysfunction and nitrergic dysregulation in small intestine of a primate model of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 5:10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-019-0081-9
Perni M, Galvagnion C, Maltsev A, Meisl G, Müller MBD, Challa PK, Kirkegaard JB, Flagmeier P, Cohen SIA, Cascella R, Chen SW, Limbocker R, Sormanni P, Heller GT, Aprile FA, Cremades N, Cecchi C, Chiti F, Nollen EAA, Knowles TPJ, Vendruscolo M, Bax A, Zasloff M, Dobson CM (2017) A natural product inhibits the initiation of α-synuclein aggregation and suppresses its toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:E1009–E1017. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1610586114
Hauser RA, Sutherland D, Madrid JA, Rol MA, Frucht S, Isaacson S, Pagan F, Maddux BN, Li G, Tse W, Walter BL, Kumar R, Kremens D, Lew MF, Ellenbogen A, Oguh O, Vasquez A, Kinney W, Lowery M, Resnick M, Huff N, Posner J, Ballman KV, Harvey BE, Camilleri M, Zasloff M, Barbut D (2019) Targeting neurons in the gastrointestinal tract to treat Parkinson’s disease. Clin Park Relat Disord 1:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prdoa.2019.06.001
Chiu C-M, Wang C-P, Sung W-H, Huang S-F, Chiang S-C, Tsai P-Y (2009) Functional magnetic stimulation in constipation associated with Parkinson’s disease. J Rehabil Med 41:1085–1089. https://doi.org/10.2340/16501977-0456
Mcclurg D, Walker K, Aitchison P, Jamieson K, Dickinson L, Paul L, Hagen S, Cunnington A-L (2016) Abdominal massage for the relief of constipation in people with Parkinson’s: a qualitative study. Parkinsons Dis 2016:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4842090
Ron Y, Halpern Z, Safadi R, Dickman R, Dekel R, Sperber AD (2015) Safety and efficacy of the vibrating capsule, an innovative non-pharmacological treatment modality for chronic constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12485
Dutta SK, Verma S, Jain V, Surapaneni BK, Vinayek R, Phillips L, Nair PP (2019) Parkinson’s disease: the emerging role of gut dysbiosis, antibiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:363–376. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm19044.
Vendrik KEW, Ooijevaar RE, de Jong PRC, Laman JD, van Oosten BW, van Hilten JJ, Ducarmon QR, Keller JJ, Kuijper EJ, Contarino MF (2020) Fecal microbiota transplantation in neurological disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:98. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00098
Bassotti G, Maggio D, Battaglia E, Giulietti O, Spinozzi F, Reboldi G, Serra AM, Emanuelli G, Chiarioni G (2000) Manometric investigation of anorectal function in early and late stage Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 68:768–770. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.68.6.768
Sun WM, Rao SSC (2001) Manometric assessment of anorectal function. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 30:15–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-8553(05)70165-5
Mathers SE, Kempster PA, Law PJ, Frankel JP, Bartram CI, Lees AJ, Stern GM, Swash M (1989) Anal sphincter dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 46:1061–1064. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1989.00520460037010
Edwards LL, Quigley EMM, Harned RK, Hofman R, Pfeiffer RF (1993) Defecatory function in Parkinson’s disease: response to apomorphine. Ann Neurol 33:490–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410330512
Ashraf W, Pfeiffer RF, Quigley EMM (1994) Anorectal manometry in the assessment of anorectal function in Parkinson’s disease: a comparison with chronic idiopathic constipation. Mov Disord 9:655–663. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870090612
Mathers SE, Kempster PA, Swash M, Lees AJ (1988) Constipation and paradoxical puborectalis contraction in anismus and Parkinson’s disease: a dystonic phenomenon? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:1503–1507. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.51.12.1503
Tateno F, Sakakibara R, Yokoi Y, Kishi M, Ogawa E, Uchiyama T, Yamamoto T, Yamanishi T, Takahashi O (2011) Levodopa ameliorated anorectal constipation in de novo Parkinson’s disease: the QL-GAT study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17:662–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.06.002
Bassotti G, Chistolini F, Sietchiping-Nzepa F, de Roberto G, Morelli A, Chiarioni G (2004) Biofeedback for pelvic floor dysfunction in constipation. BMJ 328:393–396. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7436.393
Rao SSC, Valestin JA, Xiang X, Hamdy S, Bradley CS, Zimmerman MB (2018) Home-based versus office-based biofeedback therapy for constipation with dyssynergic defecation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:768–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30266-8
Ashraf W, Wszolek ZK, Pfeiffer RF, Normand M, Maurer K, Srb F, Edwards LL, Quigley EMM (1995) Anorectal function in fluctuating (on-off) Parkinson’s disease: evaluation by combined anorectal manometry and electromyography. Mov Disord 10:650–657. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870100519
Albanese A, Maria G, Bentivoglio AR, Brisinda G, Cassetta E, Tonali P (1997) Severe constipation in parkinson’s disease relieved by botulinum toxin. Mov Disord 12:764–766. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870120524
Albanese A, Brisinda G, Bentivoglio A, Maria G (2003) Treatment of outlet obstruction constipation in Parkinson’s disease with botulinum neurotoxin A. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1439–1440. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07514.x
Jellinger KA (2014) Neuropathology of multiple system atrophy: new thoughts about pathogenesis. Mov Disord 29(14):1720–1741. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26052
Papp MI, Lantos PL (1994) The distribution of oligodendroglial inclusions in multiple system atrophy and its relevance to clinical symptomatology. Brain 117(Pt 2):235–243. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/117.2.235
Ozawa T, Paviour D, Quinn NP, Josephs KA, Sangha H, Kilford L, Healy DG, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Holton JL, Revesz T (2004) The spectrum of pathological involvement of the striatonigral and olivopontocerebellar systems in multiple system atrophy: clinicopathological correlations. Brain 127(Pt 12):2657–71. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh303
Yabe I, Soma H, Takei A, Fujiki N, Yanagihara T, Sasaki H (2006) MSA-C is the predominant clinical phenotype of MSA in Japan: analysis of 142 patients with probable MSA. J Neurol Sci 249(2):115–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2006.05.064
Schrag A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Quinn NP (1999) Prevalence of progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 354(9192):1771–1775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)04137-9
Ben-Shlomo Y, Wenning GK, Tison F, Quinn NP (1997) Survival of patients with pathologically proven multiple system atrophy: a meta-analysis. Neurology 48(2):384–93. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.48.2.384
Wenning GK, Geser F, Krismer F, Seppi K, Duerr S, Boesch S, Köllensperger M, Goebel G, Pfeiffer KP, Barone P, Pellecchia MT, Quinn NP, Koukouni V, Fowler CJ, Schrag A, Mathias CJ, Giladi N, Gurevich T, Dupont E, Ostergaard K, Nilsson CF, Widner H, Oertel W, Eggert KM, Albanese A, Del Sorbo F, Tolosa E, Cardozo A, Deuschl G, Hellriegel H, Klockgether T, Dodel R, Sampaio C, Coelho M, Djaldetti R, Melamed E, Gasser T, Kamm C, Meco G, Colosimo C, Rascol O, Meissner WG, Tison F, Poewe W, European Multiple System Atrophy Study Group (2013) The natural history of multiple system atrophy: a prospective European cohort study. Lancet Neurol 12(3):264–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70327-7
Wenning GK, Ben SY, Magalhães M, Danie SE, Quinn NP (1994) Clinical features and natural history of multiple system atrophy: an analysis of 100 cases. Brain 117(Pt 4):835–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/117.4.835
Magari T, Fukabori Y, Ogura H, Suzuki K (2013) Lower urinary tract symptoms of neurological origin in urological practice. Clin Auton Res 23(2):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-012-0183-5
Ikeda T, Ikenoshita S, Sakamoto F, Shiraishi S, Nakahara K, Masuda T, Yamashita S (2019) Is 123I-MIBG scintigraphy beneficial or excessive for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease in the early phase? Neurodegener Dis 19(2):88–95. https://doi.org/10.1159/000504006
Sakakibara R, Tateno F, Aiba Y, Ogata T, Kishi M, Terada H, Inaoka T, Nakatsuka T, Matsuoka K (2019) MIBG myocardial scintigraphy identifies premotor PD/DLB during a negative DAT scan period: second report. Mov Disord Clin Pract 6(1):46–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12697
Sakakibara R, Doi H, Fukudo S (2019) Lewy body constipation. J Anus Rectum Colon 3(1):10–17.https://doi.org/10.23922/jarc.2018-022
Akbar U, Stopa E, Anthony D, Donahue J, Friedman J (2015) Alpha-synuclein pathology in colonic biopsy of a suspected multiple system atrophy patient-a case report. Neurology 84(14 Supplement):177
Ozawa T, Shimizu H, Matsui H, Onodera O, Kakita A (2019) Shrinkage of the myenteric neurons of the small intestine in patients with multiple system atrophy. Auton Neurosci 221:102583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2019.102583
Pouclet H, Lebouvier T, Coron E, Rouaud T, Flamant M, Toulgoat F, Roy M, Vavasseur F, Bruley des Varannes S, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2012) Analysis of colonic alpha-synuclein pathology in multiple system atrophy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(7):893–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.04.020
Hague K, Lento P, Morgello S, Caro S, Kaufmann H (1997) The distribution of Lewy bodies in pure autonomic failure: autopsy findings and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol 94:192–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050693
Arai K, Kato N, Kashiwado KI, Hattori T (2000) Pure autonomic failure in association with human α-synucleinopathy. Neurosci Lett 296(2–3):171–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01623-2
Kaufmann H, Biaggioni I (2003) Autonomic failure in neurodegenerative disorders. Semin Neurol 23(4):351–363. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-817719
Bradbury S, Eggleston C (1925) Postural hypotension. A report of three cases. Am Heart J 1(1):73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-8703(25)90007-5
The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology (1996) Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy. Neurology 46(5):1470. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.46.5.1470
Quinn N (2020) Multiple system atrophy: The nature of the beast revisited. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 91(1):3–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-318187
Kaufmann H, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Palma JA, Biaggioni I, Low PA, Singer W, Goldstein DS, Peltier AC, Shibao CA, Gibbons CH, Freeman R, Robertson D, Autonomic Disorders Consortium (2017) Natural history of pure autonomic failure: a United States prospective cohort. Ann Neurol 81(2):287–297. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24877
Ito S, Takao M, Hatsuta H, Kanemaru K, Arai T, Saito Y, Fukayama M, Murayama S (2014) Alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry of gastrointestinal and biliary surgical specimens for diagnosis of Lewy body disease. Int. J Clin Exp Pathol 15;7(4):1714–1723
Jellinger KA (2018) Dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease-dementia: current concepts and controversies. J Neural Transm 125:615–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1821-9
Chiba Y, Fujishiro H, Iseki E, Ota K, Kasanuki K, Hirayasu Y, Satoa K (2012) Retrospective survey of prodromal symptoms in dementia with lewy bodies: Comparison with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 33(4):273–281. https://doi.org/10.1159/000339363
Stubendorff K, Aarsland D, Minthon L, Londos E (2012) The impact of autonomic dysfunction on survival in patients with dementia with lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease with dementia. PLoS ONE 7(10):e45451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045451
Benarroch EE, Schmeichel AM, Sandroni P, Low PA, Parisi JE (2006) Involvement of vagal autonomic nuclei in multiple system atrophy and Lewy body disease. Neurology 66(3):378–383. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000196638.98781.bb
Nishe M, Mori F, Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Yoshimoto M, Iwatsubo T, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2004) Accumulation of phosphorylated α-synuclein in the brain and peripheral ganglia of patients with multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol 107(4):292–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0811-1
Wan L, Zhou X, Wang C, Chen Z, Peng H, Hou X, Peng Y, Wang P, Li T, Yuan H, Shi Y, Hou X, Xu K, Xie Y, He L, Xia K, Tang B, Jiang H (2019) Alterations of the gut microbiota in multiple system atrophy patients. Front Neurosci 13:1102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01102
Tan AH, Chong CW, Song SL, Teh CSJ, Yap IKS, Loke MF, Tan YQ, Sen Yong H, Mahadeva S, Lang AE, Lim SY (2018) Altered gut microbiome and metabolome in patients with multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 33(1):174–176. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27203
Du J, Huang P, Qian Y, Yang X, Cui S, Lin Y, Gao C, Zhang P, He Y, Xiao Q, Chen S (2019) Fecal and blood microbial 16s rRNA gene alterations in chinese patients with multiple system atrophy and its subtypes. J Parkinsons Dis 9(4):711–721. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191612
Chen Y, Huang H, Ning P, Zhao Q, Wang H, Shen Q, Xu Y (2019) Frequency and factors related to drooling in Chinese patients with multiple system atrophy: a cross-sectional study. Clin Auton Res 29(6):595–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-019-00602-2
Ducla-Soares JL, Guerreiro AS, Póvoa P, Alvares E, Guerreiro L, Carrilho F, Santos M, Figueirinhas J, Carvalho M (1993) Pure autonomic failure. Acta Médica Port 6:11. https://doi.org/10.20344/amp.3154
Klein CM, Vernino S, Lennon VA, Sandroni P, Fealey RD, Benrud-Larson L, Sletten D, Low PA (2003) The spectrum of autoimmune autonomic neuropathies. Ann Neurol 53:752–758. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10556
Do HJ, Seo HG, Lee HH, Oh BM, Kim Y, Kim A, Kim HJ, Jeon B, Han TR (2020) Progression of oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with multiple system atrophy. Dysphagia 35(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-09990-z
Müller J, Wenning GK, Verny M, McKee A, Chaudhuri KR, Jellinger K, Poewe W, Litvan I (2001) Progression of dysarthria and dysphagia in postmortem-confirmed parkinsonian disorders. Arch Neurol 58(2):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.58.2.259
Alfonsi E, Versino M, Merlo IM, Pacchetti C, Martignoni E, Bertino G, Moglia A, Tassorelli C, Nappi G (2007) Electrophysiologic patterns of oral-pharyngeal swallowing in parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology 68(8):583–589. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000254478.46278.67
Merlo IM, Occhini A, Pacchetti C, Alfonsi E (2002) Not paralysis, but dystonia causes stridor in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 58(4):649–652. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.58.4.649
Higo R, Tayama N, Watanabe T, Nitou T, Takeuchi S (2003) Vocal fold motion impairment in patients with multiple system atrophy: evaluation of its relationship with swallowing function. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74(7):982–984. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.74.7.982
Taniguchi H, Nakayama H, Hori K, Nishizawa M, Inoue M, Shimohata T (2015) Esophageal Involvement in Multiple System Atrophy. Dysphagia 30(6):669–673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9641-2
Aubert M, Ohanessian J, Perret J, Micoud MJ, Barrie J (1980) Shy-Drager syndrome and megaesophagus (author’s transl). J Chir (Paris) 117(3):195–197
Londos E, Hanxsson O, Alm Hirsch I, Janneskog A, Bülow M, Palmqvist S (2013) Dysphagia in Lewy body dementia - a clinical observational study of swallowing function by videofluoroscopic examination. BMC Neurol 13:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-13-140
Thomaides T, Karapanayiotides T, Zoukos Y, Haeropoulos C, Kerezoudi E, Demacopoulos N, Floodas G, Papageorgiou E, Armakola F, Thomopoulos Y, Zaloni I (2005) Gastric emptying after semi-solid food in multiple system atrophy and Parkinson disease. J Neurol 252(9):1055–1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0815-y
Ozawa T, Tokunaga J, Arakawa M, Ishikawa A, Takeuchi R, Mezaki N, Miura T, Sakai N, Hokari M, Takeshima A, Utsumi K, Kondo T, Yokoseki A, Nishizawa M (2013) Abnormal ghrelin secretion contributes to gastrointestinal symptoms in multiple system atrophy patients. J Neurol 260(8):2073–2077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6944-9
Sakakibara Y, Asahina M, Suzuki A, Hattori T (2009) Gastric myoelectrical differences between Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 24(11):1579–1586. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22265
Maule S, Lombardo L, Rossi C, Crocellà L, Masoero G, Della Monica P, Catalfamo E, Calvo C, Mecca F, Quadri R (2002) Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric function in primary autonomic neuropathy. Clin Auton Res 12(3):193–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-002-0030-1
Köllensperger M, Geser F, Ndayisaba JP, Boesch S, Seppi K, Ostergaard K, Dupont E, Cardozo A, Tolosa E, Abele M, Klockgether T, Yekhlef F, Tison F, Daniels C, Deuschl G, Coelho M, Sampaio C, Bozi M, Quinn N, Schrag A, Mathias CJ, Fowler C, Nilsson CF, Widner H, Schimke N, Oertel W, Del Sorbo F, Albanese A, Pellecchia MT, Barone P, Djaldetti R, Colosimo C, Meco G, Gonzalez-Mandly A, Berciano J, Gurevich T, Giladi N, Galitzky M, Rascol O, Kamm C, Gasser T, Siebert U, Poewe W, Wenning GK, EMSA-SG (2010) Presentation, diagnosis, and management of multiple system atrophy in Europe: final analysis of the European multiple system atrophy registry. Mov Disord 25(15):2604–2612. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23192
Jung YJ, Kim HJ, Yoo D, Choi JH, Im JH, Yang HJ, Jeon B (2020) Various motor and non-motor symptoms in early multiple system atrophy. Neurodegener Dis 19(5–6):238–243. https://doi.org/10.1159/000507292
Sakakibara R, Odaka T, Uchiyama T, Liu R, Asahina M, Yamaguchi K, Yamaguchi T, Yamanishi T, Hattori T (2004) Colonic transit time, sphincter EMG, and rectoanal videomanometry in multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 19(8):924–929. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20165
Zhang LY, Cao B, Ou RW, Wei QQ, Zhao B, Yang J, Wu Y, Shang HF (2017) Non-motor symptoms and the quality of life in multiple system atrophy with different subtypes. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 35:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.12.007
Schmidt C, Herting B, Prieur S, Junghanns S, Schweitzer K, Globas C, Schöls L, Reichmann H, Berg D, Ziemssen T (2008) Autonomic dysfunction in different subtypes of multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 23(12):1766–1772. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22187
Coon EA, Mandrekar JN, Berini SE, Benarroch EE, Sandroni P, Low PA, Singer W (2020) Predicting phenoconversion in pure autonomic failure. Neurology 95(7):e889–e897. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000010002
Mabuchi N, Hirayama M, Koike Y, Watanabe H, Ito H, Kobayashi R, Hamada K, Sobue G (2005) Progression and prognosis in pure autonomic failure (PAF): Comparison with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(7):947–952. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2004.049023
Yamanaka Y, Sakakibara R, Asahina M, Uchiyama T, Liu Z, Yamamoto T, Ito T, Suenaga T, Odaka T, Yamaguchi T, Uehara K, Hattori T (2006) Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction as the initial feature of pure autonomic failure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77(6):800. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2005.079905
Pramstaller PP, Wenning GK, Smith SJM, Beck RO, Quinn NP, Fowler CJ (1995) Nerve conduction studies, skeletal muscle EMG, and sphincter EMG in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58(5):618–621. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.58.5.618
Giladi N, Simon ES, Korczyn AD, Groozman GB, Orlov Y, Shabtai H, Drory VE (2000) Anal sphincter EMG does not distinguish between multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease. Muscle Nerve 23(5):731–734. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(200005)23:5<731::aid-mus10>3.0.co;2-#
Libelius R, Johansson F (2000) Quantitative electromyography of the external anal sphincter in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Muscle Nerve 23(8):1250–1256. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4598(200008)23:8<1250::aid-mus14>3.0.co;2-w
Winge K, Jennum P, Lokkegaard A, Werdelin L (2010) Anal sphincter EMG in the diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndromes. Acta Neurol Scand 121(3):198–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2009.01169.x
Racette BA, Good L, Sagitto S, Perlmuter JS (2003) Botulinum toxin B reduces sialorrhea in Parkinsonism. Mov Disord 18(9):1059–1061. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10484
Thobois S, Broussolle E, Toureille L, Vial C (2001) Severe dysphagia after botulinum toxin injection for cervical dystonia in multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 16(4):764–765. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.1101
Postma AG, Heesters MAAM, Van Laar T (2007) Radiotherapy to the salivary glands as treatment of sialorrhea in patients with parkinsonism. Mov Disord 22(16):2430–2435. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21752
Larsson V, Torisson G, Bülow M, Londos E (2017) Effects of carbonated liquid on swallowing dysfunction in dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Clin Interv Aging 12:1215–1222. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S140389
Ueha R, Nito T, Sakamoto T, Yamauchi A, Tsunoda K, Yamasoba T (2016) Post-operative swallowing in multiple system atrophy. Eur J Neurol 23(2):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12880
Eichhorn TE, Oertel WH (2001) Macrogol 3350/electrolyte improves constipation in parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 16(6):1176–1177. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.1211
Sakakibara R, Odaka T, Lui Z, Uchiyama T, Yamaguchi K, Yamaguchi T, Asahina M, Yamamoto T, Ito T, Hattori T (2005) Dietary herb extract dai-kenchu-to ameliorates constipation in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 20(2):261–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20352
Kii Y, Ito T (1997) Effects of 5-HT4-receptor agonists, cisapride, mosapride citrate, and zacopride, on cardiac action potentials in guinea pig isolated papillary muscles. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 29(5):670–675. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-199705000-00016
Liu Z, Sakakibara R, Odaka T, Uchiyama T, Yamamoto T, Ito T, Asahina M, Yamaguchi K, Yamaguchi T, Hattori T (2005) Mosapride citrate, a novel 5-HT4 agonist and partial 5-HT3 antagonist, amerliorates constipation in Parkinsonian patients. Mov Disord 20(6):680–686. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20387
Pfeiffer RF (2020) Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-020-00897-4. Online ahead of print
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Kathryn A. Chung, MD: none. Ronald F. Pfeiffer, MD: consulting honoraria—Acadia, Acorda; lecture honoraria—Acadia; royalties for book editing—CRC Press, Humana Press; legal consulting fees—Henry and Beaver LLP.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, K.A., Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in the synucleinopathies. Clin Auton Res 31, 77–99 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-020-00745-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-020-00745-7