Abstract
Background and Objective
Domperidone is a drug used globally for relieving nausea and vomiting and stimulating breast milk production. Several case reports and studies linked domperidone usage with major cardiovascular adverse events (cardiac arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death). However, multiple randomized controlled efficacy studies failed to detect such adverse events. Our objectives were to systematically review and meta-analyze the association between current domperidone exposure and cardiovascular adverse events.
Methods
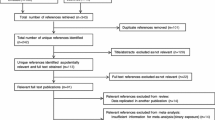
The first author performed EMBASE, PubMed and Scopus searches to identify human studies assessing the association between current domperidone exposure and cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Thirteen related articles were identified and the first and second authors independently reviewed the articles. Six studies were included in the final analysis. Meta-analysis was performed with a random effect model using the inverse variance approach. Heterogeneity was evaluated using the Q statistic and I 2 test.
Results
Five case-control studies and one case-crossover study were included in this meta-analysis. Pooled risk estimates demonstrated that the current use of domperidone increased the risk of ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death (pooled adjusted odds ratio = 1.70; 95 % confidence interval 1.47–1.97; I 2 = 0 %). The I 2 test showed that the underlying population was homogeneous.
Conclusions
Evidence from this meta-analysis suggests that current domperidone use increases the risk of cardiac arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death by 70 %. Domperidone usage in older populations should be discouraged. Larger observational studies or randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm the findings of this analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barone JA. Domperidone: a peripherally acting dopamine2-receptor antagonist. Ann Pharmacother. 1999;33(4):429–40.
Patterson D, Abell T, Rothstein R, Koch K, Barnett J. A double-blind multicenter comparison of domperidone and metoclopramide in the treatment of diabetic patients with symptoms of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(5):1230–4.
Dumitrascu DL, Weinbeck M. Domperidone versus metoclopramide in the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(1):316–7.
Franzese A, Borrelli O, Corrado G, Rea P, Di Nardo G, Grandinetti AL, et al. Domperidone is more effective than cisapride in children with diabetic gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16(5):951–7.
Sugumar A, Singh A, Pasricha PJ. A systematic review of the efficacy of domperidone for the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6(7):726–33.
Vandenplas Y, Salvatore S, Hauser B. The diagnosis and management of gastro-oesophageal reflux in infants. Early Hum Dev. 2005;81(12):1011–24.
Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJO, Jones MJ, Verlinden M, Talley NJ. Efficacy of cisapride and domperidone in functional (nonulcer) dyspepsia: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(3):689–96.
Doggrell SA, Hancox JC. Cardiac safety concerns for domperidone, an antiemetic and prokinetic, and galactogogue medicine. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(1):131–8.
Alvarez A, Ortiz AM, McCallum R, Sarosiek I. Cardiovascular safety profile of domperidone in a limited access program in the usa motility center. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(5):S845–6.
Di Lorenzo CY, Nader N. Diagnosis and management of intestinal motility disorders. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010;19(1):50–8.
Osadchy A, Moretti ME, Koren G. Effect of domperidone on insufficient lactation in puerperal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2012;2012:642893.
da Silva OP, Knoppert DC, Angelini MM, Forret PA. Effect of domperidone on milk production in mothers of premature newborns: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CMAJ. 2001;164(1):17–21.
Ingram J, Taylor H, Churchill C, Pike A, Greenwood R. Metoclopramide or domperidone for increasing maternal breast milk output: a randomised controlled trial. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012;97(4):F241–5.
Jantarasaengaram S, Sreewapa P. Effects of domperidone on augmentation of lactation following cesarean delivery at full term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2012;116(3):240–3.
Wan EW, Davey K, Page-Sharp M, Hartmann PE, Simmer K, Ilett KF. Dose-effect study of domperidone as a galactagogue in preterm mothers with insufficient milk supply, and its transfer into milk. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;66(2):283–9.
Stork D, Timin EN, Berjukow S, Huber C, Hohaus A, Auer M, et al. State dependent dissociation of HERG channel inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;151(8):1368–76.
Rocha CM, Barbosa MM. QT interval prolongation associated with the oral use of domperidone in an infant. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005;26(5):720–3.
Boyce MJ, Baisley KJ, Warrington SJ. Pharmacokinetic interaction between domperidone and ketoconazole leads to QT prolongation in healthy volunteers: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;73(3):411–21.
Djeddi D, Kongolo G, Lefaix C, Mounard J, Leke A. Effect of domperidone on QT interval in neonates. J Pediatr. 2008;153(5):663–6.
Rossi M, Giorgi G. Domperidone and long QT syndrome. Curr Drug Saf. 2010;5(3):257–62.
Giaccone G, Bertetto O, Calciati A. Two sudden deaths during prophylactic antiemetic treatment with high doses of domperidone and methylprednisolone. Lancet. 1984;2(8415):1336–7.
Joss RA, Goldhirsch A, Brunner KW, Galeazzi RL. Sudden death in cancer patient on high-dose domperidone. Lancet. 1982;1(8279):1019.
Roussak JB, Carey P, Parry H. Cardiac arrest after treatment with intravenous domperidone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1984;289(6458):1579.
Bozzo P, Koren G, Ito S. Health Canada advisory on domperidone should I avoid prescribing domperidone to women to increase milk production? Can Fam Physician. 2012;58(9):952–3.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA cautions breast-feeding moms. FDA Consum. 2004;38(5):6. Available at: http://permanent.access.gpo.gov/lps1609/www.fda.gov/fdac/departs/2004/504_upd.html#moms .
Ortiz A, Cooper CJ, Alvarez A, Gomez Y, Sarosiek I, McCallum RW. Cardiovascular safety profile and clinical experience with high-dose domperidone therapy for nausea and vomiting. Am J Med Sci. 2015;349(5):421–4.
Czinn SJ, Blanchard S. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in neonates and infants: when and how to treat. Paediatr Drugs. 2013;15(1):19–27.
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. 2014 [cited June, 2015 4]; Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Woolf B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955;19(4):251–3.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Straus SM, Sturkenboom MC, Bleumink GS, Dieleman JP, Van Der Lei J, De Graeff PA, et al. Non-cardiac QTc-prolonging drugs and the risk of sudden cardiac death. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(19):2007–12.
De Bruin ML, Langendijk PN, Koopmans RP, Wilde AA, Leufkens HG, Hoes AW. In-hospital cardiac arrest is associated with use of non-antiarrhythmic QTc-prolonging drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;63(2):216–23.
Jolly K, Gammage MD, Cheng KK, Bradburn P, Banting MV, Langman MJS. Sudden death in patients receiving drugs tending to prolong the QT interval. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;68(5):743–51.
van Noord C, Dieleman JP, Verhamme K, Sturkenboom MC. Ventricular arrhythmia and sudden unexpected death and domperidone. Pharmacoepidememiol Drug Saf. 2009;18(S1):S155.
van Noord C, Dieleman JP, van Herpen G, Verhamme K, Sturkenboom MC. Domperidone and ventricular arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death: a population-based case-control study in the Netherlands. Drug Saf. 2010;33(11):1003–14.
Johannes CB, Varas-Lorenzo C, McQuay LJ, Midkiff KD, Fife D. Risk of serious ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in a cohort of users of domperidone: a nested case-control study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010;19(9):881–8.
Arana A, Johannes C, Varas C, Rothman KJ, McQuay LJ, Yang Q, et al. Risk of out-of-hospital sudden cardiac death with use of domperidone, proton pump inhibitors, and metoclopramide. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2014;23:189.
Arana A, Johannes CB, McQuay LJ, Varas-Lorenzo C, Fife D, Rothman KJ. Risk of out-of-hospital sudden cardiac death in users of domperidone, proton pump inhibitors, or metoclopramide: a population-based nested case-control study. Drug Saf. 2015;38(12):1187–99.
Chen HL, Hsiao FY. Domperidone, cytochrome P450 3A4 isoenzyme inhibitors and ventricular arrhythmia: a nationwide case-crossover study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015;24(8):841–8.
Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. In: Higgins JPT GS, editor. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011; 2011.
Marzi M, Weitz D, Avila A, Molina G, Caraballo L, Piskulic L. Cardiac adverse effects of domperidone in adult patients: a systematic review. Rev Med Chil. 2015;143(1):14–21.
Paul C, Zenut M, Dorut A, Coudore MA, Vein J, Cardot JM, et al. Use of domperidone as a galactagogue drug: a systematic review of the benefit-risk ratio. J Hum Lact. 2015;31(1):57–63.
Manisty C, Hughes-Roberts Y, Kaddoura S. Cardiac manifestations and sequelae of gastrointestinal disorders. Br J Cardiol. 2009;16(4):6.
Scott JW. Gastrointestinal symptoms in cardiovascular disease. Can Med Assoc J. 1945;52(2):128–30.
Chugh SS, Reinier K, Singh T, Uy-Evanado A, Socoteanu C, Peters D, et al. Determinants of prolonged QT interval and their contribution to sudden death risk in coronary artery disease: the Oregon Sudden Unexpected Death Study. Circulation. 2009;119(5):663–70.
Pun PH, Horton JR, Middleton JP. Dialysate calcium concentration and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest in hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8(5):797–803.
Asztalos EV, Campbell-Yeo M, daSilva OP, Kiss A, Knoppert DC, Ito S. Enhancing breast milk production with domperidone in mothers of preterm neonates (EMPOWER trial). BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2012;12:87.
Acknowledgments
Nattawut Leelakanok would like to acknowledge the support from The Royal Thai Government Scholarship. We thank Saket Girotra for his assistance. We also thank Xiaomei Gu for her help in developing search terms; Daniel Fife from Johnson & Johnson for his references list; Elizabeth Asztalos, Mathieu Pasquier, and Patrick Pun for providing useful information from their publications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
There was no external source of funding. MLS receives salary support from a VA Health Services and Research Career Development Award (CDA 11-215).
Conflict of interest
NL, AH and MLS have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leelakanok, N., Holcombe, A. & Schweizer, M.L. Domperidone and Risk of Ventricular Arrhythmia and Cardiac Death: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Drug Investig 36, 97–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0360-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0360-0