Abstract
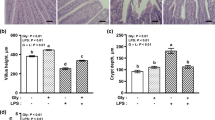
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of oral supplementation with a combination of arginine and glutamine on the intestinal mucosa and inflammatory cytokines of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced adult rats. Fifty Sprague–Dawley rats (average weight of 185 ± 15 g) were randomly divided into five groups: control group A (CA) and control group B (CB), both orally supplemented with 0.9% saline; group Arg, supplemented with 300 mg/kg day−1 arginine; group Gln, supplemented with 300 mg/kg day−1 glutamine; group AG, supplemented with 150 mg/kg day−1 arginine and 150 mg/kg day−1 glutamine. The experiment lasted for 2 weeks. Food intake and body weight were measured during the experiment. At 10.00 h of day 15, animals were injected with 4 mg/kg LPS (group CB, Arg, Gln, and AG) or sterile saline (group CA) after supplementation. Then at 14.00 h, all animals were killed and blood and tissue collected. The results showed that compared with group CB, arginine concentration tended to be increased (P > 0.05) in group Arg and AG, while there was no significant difference in glutamine concentration among the groups challenged with LPS. Oral supplementation with arginine or/and glutamine mitigated morphology impairment (lower villus height, P < 0.05) in the jejunum and ileum induced by LPS challenge. LPS administration resulted in a significant increase in TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 mRNA abundance. Arginine only significantly decreased TNF-α mRNA abundance in the ileum, while glutamine significantly decreased both TNF-α and IL-10 mRNA in the ileum. A combination of arginine and glutamine significantly decreased TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA abundance in both the jejunum and ileum, while they also significantly decreased anti-inflammatory IL-10 in the ileum. These results revealed that an oral supply of combined arginine and glutamine had more favorable effects on the intestinal mucosa and inflammatory cytokines than a supply of arginine or glutamine alone.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- DAO:
-
Diamine oxidase
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- RT-PCR:
-
Real-time polymerase chain reaction
- ADG:
-
Average daily weight gain
- ADFI:
-
Average daily food intake
- CD:
-
Crohn’s disease
- NT:
-
Nucleotide
References
Alverdy AM (1990) Effects of glutamine-supplementation diets on immunology of the gut. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 14:109S–113S
Ardawi MS, Newsholme EA (1994) Glutamine metabolism in lymphocytes of the rat. Biochem J 212:835–842
Baker DH (2009) Advances in protein-amino acid nutrition of poultry. Amino Acid 37:29–41
Blachier F, Darcy-Vrillon B, Sener A et al (1991) Arginine metabolism in rat enterocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1092(3):304–310
Blachier F, M’Robet-touil H, Posho L et al (1993) Intestinal arginine metabolism during development. Eur J Biochem 216(1):109–117
Blachier F, Selamnia M, Robert V et al (1995) Metabolism of l-arginine through polyamine and nitric oxide synthase pathways in proliferative or differentiated human colon carcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1268(3):255–262
Blachier F, Mariotti F, Huneau JF et al (2007) Effects of amino acid-derived luminal metabolites on the colonic epithelium and physiopathological consequences. Amino Acids 33:547–562
Blachier F, Bountry C, Bos C et al (2009) Metabolism and functions of l-glutamate in the epithelial cells of the small and large intestines. Am J Clin Nutr 90(suppl):814S–821S
Buffoni F (1966) Histaminase and related amine oxidases. Pharmacol Rev 18:1163–1199
Chamorro S, de Blas C, Grant G et al (2010) Effect of dietary supplementation with glutamine and a combination of glutamine–arginine on intestinal health in twenty-five-day-old weaned rabbits. J Anim Sci 88:170–180
Coeffier M, Marion R, Ducrotte P et al (2003) Modulating effect of glutamine on IL-1beta-induced cytokine production by human gut. Clin Nutr 22:407–413
Coeffier M, Dechelotte P (2010) Combined infusion of glutamine and arginine: does it make sense? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:70–74
Deng D, Yao K, Chu WY et al (2009) Impaired translation initiation activation and reduced protein synthesis in weaned piglets fed a low-protein diet. J Nutr Biochem 20:544–552
Deng J, Wu X, Bin S et al (2010) Dietary amylose and amylopectin ratio and resistant starch content affects plasma glucose, lactic acid, hormone levels and protein synthesis in splanchnic tissues. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 94:220–226
Dugan ME, Knabe DA, Wu G (1994) Glutamine and glucose metabolism in intraepithelial lymphocytes from pre- and post-weaning pigs. Comp Biochem Physiol 109B:675–681
Eklou-Lawson M, Bernard F, Neveux N et al (2009) Colonic luminal ammonia and portal blood l-glutamine and l-arginine concentrations: a possible link between colon mucosa and liver ureagenesis. Amino Acids 37(4):751–760
Flynn NE, Bird JG, Guthrie AS (2009) Glucocorticoid regulation of amino acid and polyamine metabolism in the small intestine. Amino Acids 37(1):123–129
Forget P, Saye Z, Van Cutsem JL et al (1985) Serum diamine oxidase activity in acute gastroenteritis in children. Pediatr Res 19:26–28
Fu WJ, Hu J, Spencer T et al (2006) Statistical models in assessing fold changes of gene expression in real-time RT-PCR experiments. Comput Biol Chem 30:21–26
Garrett-Cox RG, Stefanutti G et al (2009) Glutamine decreases inflammation in infant rat endotoxemia. J Pediatr Surg 44:523–529
Gennari R, Alexander JW, Eaves-Pyles T (1995) Effect of different combinations of dietary additives on bacterial translocation and survival in gut-derived sepsis. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 19:319–325
Han J, Liu YL, Fan W et al (2008) Dietary l-arginine supplementation alleviates immunosuppression induced by cyclophosphamide in weaned pigs. Amino Acids 37:643–651
Haynes TE, Li P, Li XL et al (2009) l-Glutamine or l-alanyl-l-glutamine prevents oxidant- or endotoxin-induced death of neonatal enterocytes. Amino Acids 37:131–142
He QH, Kong XF, Wu GY et al (2009) Metabolomic analysis of the response of growing pigs to dietary l-arginine supplementation. Amino Acids 37:199–208
Hou YQ, Wang L, Ding BY et al (2010) Dietary a-ketoglutarate supplementation ameliorates intestinal injury in lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. Amino Acids 39:555–564
Hou YQ, Kang Y, Lei W et al (2011) Effects of a-ketoglutarate on energy status in the intestinal mucosa of weaned piglets chronically challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Br J Nutr 106:357–363
Kong XF, Wu GY, Yin YL et al (2007) Dietary supplementation with Chinese herbal ultra-fine powder enhances cellular and humoral immunity in early weaned piglets. Livest Sci 108:94–98
Kong XF, Zhang YZ, Yin YL et al (2009) Chinese yam polysaccharide enhances growth performance and cellular immune response in weanling rats. J Sci Food Agric 89:2039–2044
Krebs H (1980) Glutamine metabolism in the animal body. In: Mora J, Palacios E (eds) Glutamine: metabolism, enzymology, and regulation. Academic Press, New York, pp 319–329
Kul M, Vurucu S, Demirkaya E et al (2009) Enteral glutamine and/or arginine supplementation have favorable effects on oxidative stress parameters in neonatal rat intestine. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 49:85–89
Lecleire S, Hassan A, Marion-Letellier R et al (2008) Combined glutamine and arginine decrease proinflammatory cytokine production by biopsies from Crohn’s patients in association with changes in nuclear factor-kappaB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Nutr 138:2481–2486
Li N, Lewis P, Samuelson D et al (2004) Glutamine regulates Caco-2 cell tight junction proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G726–G733
Liu XD, Wu X, Yin YL et al (2011) Effects of dietary l-arginine or N-carbamylglutamate supplementation during late gestation of sows on the miR-15b/16, miR-221/222, VEGFA and eNOS expression in umbilical vein. Amino Acid. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-0948-5
Li XL, Bazer FW, Gao HJ et al (2009) Amino acids and gaseous signaling. Amino Acids 37:65–78
Liu YL, Huang JJ, Hou YQ et al (2008) Dietary arginine supplementation alleviates intestinal mucosal disruption induced by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide in weaned pigs. Br J Nutr 100:552–560
Lortie MJ, Satriano J, Gabbai FB et al (2004) Production of arginine by the kidney is impaired in a model of sepsis: early events following LPS. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R1434–R1440
Luiking YC, Steens L, Poeze M et al (2003) Low plasma arginine concentration in septic patients is related to diminished de novo arginine production from citrulline. Clin Nutr 22(Suppl 1):S26
Luiking YC, Poeze M, Dejong CH et al (2004) Sepsis: an arginine deficiency state? Crit Care Med 32:2135–2145
Luiking YC, Deutz EP (2007) Exogenous arginine in sepsis. Crit Care Med 35(9):S557–S563
Luk CD, Bayless TM, Baylin SB (1980) Diamine oxidase(histaminase). A circulating marker for rat intestinal mucosal maturation and integrity. J Clin Invest 66:66–70
Mckay DM, Baird AW (1999) Cytokine regulation of epithelial permeability and ion transport. Gut 44:283–289
Mercer DW, Smith GS, Cross JM et al (1996) Effects of lipopolysaccharide on intestinal injury: potential role of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation. J Surg Res 63:185–192
Moinard C, Cynober L, de Bandt JP (2005) Polyamines: metabolism and implications in human diseases. Clin Nutr 24:184–197
Newsholme P (2001) Why is l-glutamine metabolism important to cells of the immune system in health, postinjury, surgery or infection? J Nutr 131:2515S–2522S
Panigrahi PI, Banford GP, Horvath K (1997) Role of glutamine in bacterial transcytosis and epithelial cell injury. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 21:75–80
Ren W, Yin YL, Liu G et al (2011) Effect of dietary arginine supplementation on reproductive performance of mice with porcine circovirus type 2 infection. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-0942-y
Rhoads JM, Wu G (2009) Glutamine, arginine, and leucine signaling in the intestine. Amino Acids 37:111–122
Souba WW, Austgen TR (2001) Interorgan glutamine flow following surgery and infection. J Parenteral Enteral Nutr 14:90S–93S
Stoll B, Burrin DG (2006) Measuring splanchnic amino acid metabolism in vivo using stable isotopic tracers. J Anim Sci 84(Suppl):E60–E72
Sukhotnik I, Mogilner J, Krausz MM et al (2004) Oral arginine reduces gut mucosal injury caused by lipopolysaccharide endotoxemia in rat. J Surg Res 122(2):256–262
Tan BE, Li XG, Kong XF et al (2009) Dietary l-arginine supplementation enhances the immune status in early-weaned piglets. Amino Acids 37:323–331
Tan BE, Yin YL, Kong XF et al (2010) l-Arginine stimulates proliferation and prevents endotoxin-induced death of intestinal cells. Amino Acids 38:1227–1235
Windmueller HG, Spaeth AE (1975) Intestinal metabolism of glutamine and glutamate from the lumen as compared to glutamine from blood. Arch Biochem Biophys 171:662–672
Windmueller HG, Spaeth AE (1980) Respiratory fuels and nitrogen metabolism in vivo in small intestine of fed rats. J Biol Chem 255:107–112
Wischmeyer PE, Kahana M, Wolfson R et al (2001) Glutamine induces heat shock protein and protects against endotoxin shock in the rat. J Appl Physiol 90:2403–2410
Wu G, Knabe DA, Yan W et al (1995) Glutamine and glucose metabolism in enterocytes of the neonatal pig. Am J Physiol 268:R334–R342
Wu G (1996) Effects of concanavalin A and phorbol myristate acetate on glutamine metabolism and proliferation of porcine intraepithelial lymphocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol 114A:363–368
Wu G, Meier SA, Knabe DA (1996) Dietary glutamine supplementation prevents jejunal atrophy in weaned pigs. J Nutr 126:2578–2584
Wu G, Flynn NE, Knabe DA (2000a) Enhanced intestinal synthesis of polyamines from proline in cortisol-treated piglets. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E395–E402
Wu G, Flynn NE, Knabe DA et al (2000b) A cortisol surge mediates the enhanced polyamine synthesis in porcine enterocytes during weaning. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R554–R559
Wu G, Meininger CJ (2008) Analysis of citrulline, arginine, and methylarginines using high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol 440:177–189
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA et al (2009) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 37:153–168
Wu X, Ruan Z, Gao YL et al (2010) Dietary supplementation with l-arginine or N-carbamylglutamate enhances intestinal growth and heat shock protein-70 expression in weanling pigs fed a corn-and soybean meal-based diet. Amino Acids 39:831–839
Yamauchi K, Komatsu T, Kulkarni AD et al (2002) Glutamine and arginine affect Caco-2 cell proliferation by promotion of nucleotide synthesis. Nutrition 18:329–333
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S (1988) A novel potent vasoconstrictive peptide produced by vascular endothelin cells. Nature 332:411–415
Yang CB, Albin DM, Wang ZR et al (2011) Apical Na+-d-glucose co-transporter 1(SGLT1) activity and protein abundance are expressed along the jejunal crypt–villus axis in the neonatal pig. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:G60–G70
Yi GF, Carroll JA, Allee GL et al (2005) Effect of glutamine and spray-dried plasma on growth performance, small intestinal morphology, and immune responses of Escherichia coli K88+-challenged weaned pigs. J Anim Sci 83:634–643
Yin YL, Zhong HY, Huang RL et al (1993) Nutritive value of feedstuffs and diets for pigs: I. Chemical composition, apparent ileal and faecal digestibility. Anim Feed Sci Technol 44:1–27
Yin YL, Huang RL, Jeaurond E et al (2004) Effect of including purified Jack Bean lectin in a casein based diet on apparent and true ileal amino acid digestibility in growing pigs. Anim Sci 79:283–291
Yin YL, Tang ZR, Sun ZH et al (2008) Effect of galacto-mannan-oligosaccharides or chitosan supplementation on cytoimmunity and humoral immunity response in early-weaned piglets. Asian Aust J Anim Sci 21:723–731
Yin FG, Zhang ZZ, Huang J et al (2010a) Digestion rate of dietary starch affects systemic circulation of amino acids in weaned pigs. Br J Nutr 103:1404–1412
Yin YL, Huang RL, Li TJ et al (2010b) Amino acid metabolism in the portal-drained viscera of young pigs: effects of dietary supplementation with chitosan and pea hull. Amino Acids 39:1581–1587
Yin FG, Yin YL, Li TJ et al (2011) Developmental changes of serum amino acids in suckling piglets. J Food Agric Environ 9:322–327
Yu J, Yin P, Yin J et al (2010) Involvement of ERK1/2 signalling and growth related molecules’ expression in response to heat stress induced damage in rat jejunum and IEC cells. Int J Hyperther 26:538–555
Acknowledgments
This research was jointly supported by grants from the NSFC (31101730, 31110103909, 30901040, 30901041, 30928018), Chinese Academy of Sciences and Knowledge Innovation Project (KZCX2-EW-412), National Basic Research Program of China (2009CB118806), National Fund of Agricultural Science and Technology outcome application (2006GB24910468), Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University (No. SKLF-KF-201005) and Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (11JJ4018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Wu, X., Yin, Y. et al. Preventive oral supplementation with glutamine and arginine has beneficial effects on the intestinal mucosa and inflammatory cytokines in endotoxemic rats. Amino Acids 43, 813–821 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1137-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1137-2