Abstract
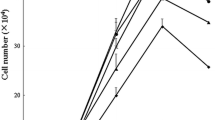
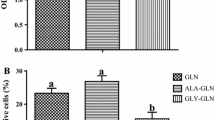
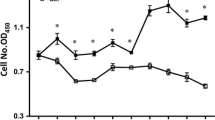
This study tested the hypothesis that L-glutamine (Gln) or L-alanyl-L-glutamine (Ala-Gln) prevents oxidant- or endotoxin-induced death of neonatal enterocytes. Enterocytes of neonatal pigs rapidly hydrolyzed Ala-Gln and utilized Gln. To determine whether Gln or Ala-Gln has a cytoprotective effect, IPEC-1 cells were cultured for 24 h in Gln-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s-F12 Ham medium containing 0, 0.5, 2.0 or 5.0 mM Gln or Ala-Gln, and 0, 0.5 mM H2O2 or 30 ng/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Without Gln or Ala-Gln, H2O2- or LPS-treated cells exhibited almost complete death. Gln or Ala-Gln at 0.5, 2 and 5 mM dose-dependently reduced H2O2- or LPS-induced cell death by 14, 54 and 95%, respectively, whereas d-glutamine, alanine, glutamate, ornithine, proline, glucosamine or nucleosides had no effect. To evaluate the effectiveness of Gln or Ala-Gln in vivo, 7-day-old piglets received one-week oral administration of Gln or Ala-Gln (3.42 mmol/kg body weight) twice daily and then a single intraperitoneal injection of LPS (0.1 mg/kg body weight); piglets were euthanized in 24 and 48 h to analyze intestinal apoptotic proteins and morphology. Administration of Gln or Ala-Gln to LPS-challenged piglets increased Gln concentrations in small-intestinal lumen and plasma, reduced intestinal expression of Toll-like receptor-4, active caspase-3 and NFkB, ameliorated intestinal injury, decreased rectal temperature, and enhanced growth performance. These results demonstrate a protective effect of Gln or Ala-Gln against H2O2- or LPS-induced enterocyte death. The findings support addition of Gln or Ala-Gln to current Gln-free pediatric amino acid solutions to prevent intestinal oxidative injury and inflammatory disease in neonates.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acid
- Ala:
-
l-Alanine
- Ala-Gln:
-
l-Alanyl-l-glutamine
- DMEM-F12:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s F12 Ham medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- Gln:
-
l-Glutamine
- IPEC-1:
-
Intestinal porcine epithelial cell line-1
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation factor 88
- NFkB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activator B cells
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
References
Agostoni C, Carratu B, Boniglia C et al (2000) Free glutamine and glutamic acid increase in human milk through a three-month lactation period. J Pediatr Gastroenter Nutr 31:508–512
Becker RM, Wu G, Galanko JA et al (2000) Reduced serum amino acid concentrations in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 137:785–793
Biener GP, Schjoerring JK, Jahn TP (2006) Membrane transport of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:994–1003
Blachier F, Mariotti F, Huneau JF, Tomé D (2007) Effects of amino acid-derived luminal metabolites on the colonic epithelium and physiopathological consequences. Amino Acids 33:547–562
Bröer S (2008) Amino acid transport across mammalian intestinal and renal epithelia. Physiol Rev 88:249–286
Chandra J, Samali A, Orrenius S (2000) Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radical Biol Med 29:323–333
Chang L, Geng B, Yu F et al (2008) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits myocardial injury induced by homocysteine in rats. Amino Acids 34:573–585
Coeffier M, Claeyssens S, Hecketsweiler B et al (2003) Enteral glutamine stimulates protein synthesis and decreases ubiquitin mRNA level in human gut mucosa. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G266–G273
Dekaney CM, Wu G, Yin YL, Jaeger LA (2008) Regulation of ornithine aminotransferase gene expression and activity by all-trans retinoic acid in Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. J Nutr Biochem 19:674–681
Deldicque L, Sanchez Canedo C, Horman S et al (2008) Antagonistic effects of leucine and glutamine on the mTOR pathway in myogenic C2C12 cells. Amino Acids 35:147–155
Deng D, Yin YL, Chu WY et al. (2008) Impaired translation initiation activation and reduced protein synthesis in weaned piglets fed a low-protein diet. J Nutr Biochem. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.05.014
Engel JM, Ruhs S, Mühling J et al. (2008) Perioperative application of l-alanyl-l-glutamine in cardiac surgery: effect on the polarized T cell cytokine expression. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0114-x
Evans ME, Jones DP, Ziegler TR (2003) Glutamine prevents cytokine-induced apoptosis in human colonic epithelial cells. J Nutr 133:3065–3071
Flynn NE, Bird JG, Guthrie AS (2008) Glucocorticoid regulation of amino acid and polyamine metabolism in the small intestine. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0206-7
Galli F (2007) Amino acid and protein modification by oxygen and nitrogen species. Amino Acids 32:497–499
Garcia RF, Gazola VA, Barrena HC et al (2007) Blood amino acids concentrations during insulin induced hypoglycemia in rats: the role of alanine and glutamine in glucose recovery. Amino Acids 33:151–155
Gribar SC, Richardson WM, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ (2008) No longer an innocent bystander: epithelial Toll-like receptor signaling in the development of mucosal inflammation. Mol Med 14:645–659
Han J, Liu YL, Fan W et al. (2008) Dietary l-arginine supplementation alleviates immunosuppression induced by cyclophosphamide in weaned pigs. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0184-9
Hu CA, Khalil S, Zhaorigetu S et al (2008) Human Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase: function and regulation. Amino Acids 35:665–672
Jones DP (2008) Radical-free biology of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295:C849–C868
Katayama M, Matsuda Y, Shimokawa K et al (2001) Simultaneous determination of six adenyl purines in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence derivatization. J Chromatogr B 760:159–163
Kessel A, Toubi E, Pavlotzky E et al (2008) Treatment with glutamine is associated with down-regulation of Toll-like receptor-4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 expression and decrease in intestinal mucosal injury caused by lipopolysaccharide endotoxaemia in a rat. Clin Exp Immunol 151:341–347
Kim SW, Wu G (2008) Regulatory role for amino acids in mammary gland growth and milk synthesis. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0151-5
Lagranha CJ, Doi SQ, Pithon-Curi SQ et al (2008a) Glutamine enhances glucose-induced mesangial cell proliferation. Amino Acids 34:683–685
Lagranha CJ, Levada-Pires AC, Sellitti DF et al (2008b) The effect of glutamine supplementation and physical exercise on neutrophil function. Amino Acids 34:337–346
Li P, Yin YL, Li D et al (2007) Amino acids and immune function. Br J Nutr 98:237–252
Li P, Kim SW, Li XL et al. (2008a) Dietary supplementation with cholesterol and docosahexaneoic acid affects concentrations of amino acids in tissues of young pigs. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0196-5
Li P, Kim SW, Li XL et al (2008b) Dietary supplementation with cholesterol and docosahexaenoic acid increases the activity of the arginine-nitric oxide pathway in tissues of young pigs. Nitric Oxide 19:259–265
Liao XH, Majithia A, Huang XL, Kimmel AR (2008) Growth control via TOR kinase signaling, an intracellular sensor of amino acids and energy availability, with crosstalk potential to proline metabolism. Amino Acids 35:761–770
Lin C, Mahan DC, Wu G, Kim SW (2008) Protein digestibility of porcine colostrum by neonatal pigs. Livest Sci. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2008.06.006
Lu S, Yao Y, Meng S, Cheng X, Black DD (2002) Overexpression of apolipoprotein A-IV enhances lipid transport in newborn swine intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:31929–31937
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS (2008) LPS/TLR4 signaling transduction pathway. Cytokine 42:145–151
Madden LA, Sandström ME, Lovell RJ, McNaughton L (2008) Inducible heat shock protein 70 and its role in preconditioning and exercise. Amino Acids 34:511–516
Mannick JB (2007) Regulation of apoptosis by protein S-nitrosylation. Amino Acids 32:523–526
Mühling J, Burchert D, Langefeld TW et al (2007) Pathways involved in alanyl-glutamine-induced changes in neutrophil amino- and α-keto acid homeostasis or immunocompetence. Amino Acids 33:511–524
Muz B, Kontny E, Marcinkiewicz J et al (2008) Heme oxygenase-1 participates in the anti-inflammatory activity of taurine chloramine. Amino Acids 35:397–402
Neville MC, Neifert MR (1983) Lactation: physiology, nutrition, and breast-feeding. Plenum Press, New York, pp 61–62
Olszanecki R, Kurnyta M, Biedron R et al (2008) The role of heme oxygenase-1 in down regulation of PGE2 production by taurine chloramines and taurine bromamine in J774.2 macrophages. Amino Acids 35:359–364
Orellana RA, Suryawan A, Kimball SR et al (2008) Insulin signaling in skeletal muscle and liver of neonatal pigs during endotoxemia. Pediatr Res 64:505–510
Ou DY, Li DF, Cao YH et al (2007) Dietary supplementation with zinc oxide decreases expression of the stem cell factor in the small intestine of weanling pigs. J Nutr Biochem 18:820–826
Reeds PJ, Burrin DG (2001) Glutamine and the bowel. J Nutr 131:2505S–2508S
Rhoads JM, Wu G (2008) Glutamine, arginine, and leucine signaling in the intestine. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0225-4
Rhoads JM, Argenzio RA, Chen W et al (1997) L-glutamine stimulates intestinal cell proliferation and activates mitogen-activated protein kinases. Am J Physiol 272:G943–G953
Rider JE, Hacker A, Mackintosh CA et al (2007) Spermine and spermidine mediate protection against oxidative damage caused by hydrogen peroxide. Amino Acids 33:231–240
Self JT, Spencer TE, Johnson GA et al (2004) Glutamine synthesis in the developing porcine placenta. Biol Reprod 70:1444–1451
Suryawan A, O’Connor PMJ, Bush JA et al. (2008) Differential regulation of protein synthesis by amino acids and insulin in peripheral and visceral tissues of neonatal pigs. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0149-z
Trottier NL, Shipley CF, Easter RA (1997) Plasma amino acid uptake by the mammary gland of the lactating sow. J Anim Sci 75:1266–1278
Tsao M, Otter DE (1999) Quantification of glutamine in proteins and peptides using enzymatic hydrolysis and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 269:143–148
Uehara K, Takahashi T, Fujii H et al (2005) The lower intestinal tract-specific induction of heme oxygenase-1 by glutamine protects against endotoximic intestinal injury. Crit Care Med 33:381–390
Umeda K, Takahashi T, Inoue K et al (2009) Prevention of hemorrhagic shock-induced intestinal tissue injury by glutamine via heme oxygenase-1 induction. Shock 31:40–49
Voss P, Grune T (2007) The nuclear proteasome and the degradation of oxidatively damaged proteins. Amino Acids 32:527–534
Wang JY (2007) Polyamines and mRNA stability in regulation of intestinal mucosal growth. Amino Acids 33:241–252
Wang W, Qiao S, Li D (2008a) Amino acids and gut function. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0152-4
Wang J, Chen L, Li P et al (2008b) Gene expression is altered in piglet small intestine by weaning and dietary glutamine supplementation. J Nutr 138:1025–1032
Wang XQ, Ou DY, Yin JD et al. (2009) Proteomic analysis reveals altered expression of proteins related to glutathione metabolism and apoptosis in the small intestine of zinc oxide-supplemented piglets. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0242-y
Wischmeyer P, Musch MW, Madonna MB et al (1997) Glutamine protects intestinal epithelial cells: role of inducible HSP70. Am J Physiol 272:G879–G884
Wu G (1998) Intestinal mucosal amino acid catabolism. J Nutr 128:1249–1252
Wu G, Knabe DA (1994) Free and protein-bound amino acids in sow’s colostrum and milk. J Nutr 124:415–424
Wu G, Meininger CJ (2002) Regulation of nitric oxide synthesis by dietary factors. Annu Rev Nutr 22:61–86
Wu G, Meininger CJ (2008) Analysis of citrulline, arginine, and methylarginines using high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol 440:177–189
Wu G, Morris SM Jr (1998) Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J 336:1–17
Wu G, Knabe DA, Flynn NE (1994) Synthesis of citrulline from glutamine in pig enterocytes. Biochem J 299:115–121
Wu G, Knabe DA, Yan W, Flynn NE (1995) Glutamine and glucose metabolism in enterocytes of the neonatal pig. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 268:R334–R342
Wu G, Meier SA, Knabe DA (1996) Dietary glutamine supplementation prevents jejunal atrophy in weaned pigs. J Nutr 126:2578–2584
Wu G, Flynn NE, Knabe DA (2000) Enhanced intestinal synthesis of polyamines from proline in cortisol-treated piglets. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E395–E402
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA et al (2007) Important roles for the arginine family of amino acids in swine nutrition and production. Livest Sci 112:8–22
Wu G, Bazer FW, Datta S et al (2008a) Proline metabolism in the conceptus: Implications for fetal growth and development. Amino Acids 35:691–702
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA et al. (2008b) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0210-y
Acknowledgments
We thank Scott Jobgen and Elaine Jobgen for technical support, as well as Frances Mutscher for assistance in manuscript preparation. This work was supported by the National Research Initiative Competitive Grant from the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (no. 2008-35206-18764), Texas AgriLife Research (H-8200), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30600434).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Unless indicated, amino acids used and analyzed in this study are l-isomers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haynes, T.E., Li, P., Li, X. et al. l-Glutamine or l-alanyl-l-glutamine prevents oxidant- or endotoxin-induced death of neonatal enterocytes. Amino Acids 37, 131–142 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0243-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0243-x