Abstract
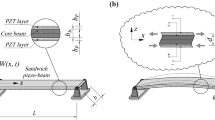
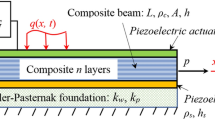
Passive vibration control of flexible structures can be achieved by bonding piezoelectric layers with attached electric circuits onto an elastic substrate. In this work, a new concept, denoted as single point control (SPC), is presented in order to cancel harmonic vibrations of slender beams. It is shown by an extended version of the Bernoulli–Euler theory for passive smart beams that the deflection or the slope at a specified location along the beam axis is nullified if the electric circuit is tuned and the shape of the piezoelastic layers are properly shaped. The proposed method holds for harmonic loads only, but the spatial part of the distributed external load may be unknown. A three-dimensional electromechanically coupled FE-analysis with ANSYS confirms these results obtained by the one-dimensional theory. The practical relevance of the derived theory becomes evident if optimal resistive-inductive shunts are used. The robustness of passively controlled systems is strongly increased if the piezoelectric layers are shaped according to the presented SPC-theory instead of using spatially uniformly distributed layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tauchert T.R.: Thermal stresses in plates-statical problems. In: Hetnarski, R.B. (eds) Thermal Stresses I, pp. 23–141. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1986)
Miu D.K.: Mechatronics: Electromechanics and Contromechanics. Springer, New York (1993)
Tzou H.S.: Piezoelectric Shells—Distributed Sensing and Control of Continua. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1993)
Reddy J.N.: A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates. J. Appl. Mech. 51, 745–752 (1984)
Reddy J.N.: On laminated composite plates with integrated sensors and actuators. Eng. Struct. 21, 568–593 (1997)
Zhou Y.G., Chen Y.M., Ding H.J.: Analytical solutions to piezoelectric bimorphs based on improved FSDT beam model. Smart Struct. Syst. 1, 309–324 (2005)
Krommer M., Irschik H.: An electromechanically coupled theory for piezoelastic beams taking into account the charge equation of electrostatics. Acta Mech. 154, 141–158 (2002)
Krommer M.: On the correction of the Bernoulli–Euler beam theory for smart piezoelectric beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 668–680 (2001)
Krommer M., Irschik H.: A Reissner-Mindlin-type plate theory including the direct piezoelectric and the pyroelectric effect. Acta Mech. 141, 51–69 (2000)
Krommer M.: On the influence of pyroelectricity upon thermally induced vibrations of piezothermoelastic plates. Acta Mech. 171, 59–73 (2004)
Benjeddou A., Deü J.F.: A two-dimensional closed-form solution for the free-vibration analysis of piezoelectric sandwich plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 1463–1486 (2002)
Heyliger P., Brooks S.: Exact solutions for laminated piezoelectric plates in cylindrical bending. J. Appl. Mech. 63, 903–910 (1996)
Jin C., Wang X.D., Zuo M.J.: The dynamic behaviour of surface-bonded piezoelectric actuators with debonded adhesive layers. Acta Mech. 211, 215–235 (2010)
Han L., Wang X.D., Zuo M.: The dynamic behavior of a surface-bonded piezoelectric actuator with a bonding layer. Acta Mech. 206, 193–205 (2009)
Heuer R., Adam C.: Piezoelectric vibrations of composite beams with interlayer slip. Acta Mech. 140, 247–263 (2000)
dell’Isola F., Maurini C., Porfiri M.: Passive damping of beam vibrations through distributed electric networks and piezoelectric transducers: prototype design and experimental validation. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 299–308 (2004)
Trindade, M.A., Maio, C.E.B.: Multimodal passive vibration control of sandwich beams with shunted shear piezoelectric materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 055015 (10pp) (2008)
Caruso G.: A critical analysis of electric shunt circuits employed in piezoelectric passive vibration damping. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 1059–1068 (2001)
Moheimani S.O.R., Fleming A.J.: Piezoelectric Transducers for Vibration Control and Damping. Springer, New York (2006)
Wang K.W., Tang J.: Adaptive Structural Systems with Piezoelectric Transducer Circuitry. Springer, New York (2008)
Irschik H., Nader M.: Actuator placement in static bending of smart beams utilizing Mohr’s analogy. Eng. Struct. 31, 1698–1706 (2009)
Irschik H.: A review on static and dynamic shape control of structures by piezoelectric actuation. Eng. Struct. 24, 5–11 (2002)
Irschik H., Krommer M., Pichler U.: Dynamic shape control of beam-type structures by piezoelectric actuation and sensing. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 17, 251–258 (2003)
Irschik H., Krommer M., Belayaev A.K., Schlacher K.: Shaping of piezoelectric sensors/actuators for vibrations of slender beams: coupled theory and inappropriate shape functions. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 9, 546–554 (1998)
Nader M., Gattringer H., Krommer M., Irschik H.: Shape control of flexural vibrations of circular plates by shaped piezoelectric actuation. J. Vib. Acoust. 125(1), 88–94 (2003)
Yu Y., Zhang X.N., Lie S.L.: Optimal shape control of a beam using piezoelectric actuators with low control voltage. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 095006 (2009)
Krommer M.: Dynamic shape control of sub-sections of moderately thick beams. Comput. Struct. 83, 1330–1339 (2005)
Ziegler F.: Computational aspects of structural shape control. J. Sound Vib. 83, 1191–1204 (2005)
Schoeftner, J., Irschik, H.: Passive damping and exact annihilation of vibrations of beams using shaped piezoelectric layers and tuned inductive networks. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 125008 (9pp) (2009)
Schoeftner, J., Irschik, H.: Piezoelastic structures interacting with electric networks: vibration canceling and shape control, Proceedings of Fifth World Conference on Structural Control and Monitoring (5WCSCM) (published on http://wcscm5.com), Tokyo, Japan (2010)
Schoeftner J., Irschik H.: Passive shape control of force-induced harmonic lateral vibrations for laminated piezoelastic Bernoulli–Euler beams- theory and practical relevance. Smart Struct. Syst. 7, 417–432 (2011)
Huber D., Krommer M.: Accurate modeling of moderately wide beams with attached piezoelectric actuator patches. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 18, 498–510 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoeftner, J., Krommer, M. Single point vibration control for a passive piezoelectric Bernoulli–Euler beam subjected to spatially varying harmonic loads. Acta Mech 223, 1983–1998 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-012-0686-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-012-0686-0