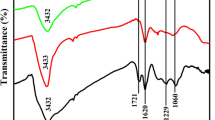
Abstract
We report on a colorimetric probe based on copper-gold alloy nanoparticles (NPs). The probe is capable of selectively detecting ascorbic acid (AA) as a result of the distance-dependent colour change of the nanoparticles immobilized in an electrospun nylon-6 nanofiber. The resulting white nanofibres undergo a colour change to blue as a result of the aggregation of the NPs induced by AA in the pH range 2–7. The probe is selective for AA even in the presence of dopamine, uric acid, saccharides, amino acids and certain organic acids. It covers the 1.76 x10−2 mg L−1 to 1.76 x105 mg L−1 concentration range, and exhibits a limit of detection of 1.76 x10−2 mg L−1 based on visual detection. Its application was demonstrated by the determination of ascorbic acid in fruit juices, urine, serum, and vitamin C tablets.

An electrospun colorimetric probe based on the growth of copper-gold alloy nanoparticles induced by ascorbic acid was developed. The white nanofiber turns blue in the pH range 2–7 and is selective for AA in the presence of possible interferences. Its limit of detection is 1.76 x10−2 mg L−1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Negulescu GP, Pisoschi A (2011) Determination of ascorbic acid content of some fruit juices and wine by voltammetry performed at Pt and carbon paste electrodes. Molecules 16:1349–1365
Okiei W, Ogunlesi M, Azeez L, Obakachi V, Osunsanmi M, Nkenchor G (2009) The voltammetric and titrimetric determination of ascorbic acid levels in tropical fruit samples. Int J Electrochem Sci 4:276–287
Ambrosi A, Morrin A, Smyth MR, Killard AJ (2008) The application of conducting polymer nanoparticle electrodes to the sensing of ascorbic acid. Anal Chim Acta 6:37–43
Liu Y, Huang J, Hou H, You T (2008) Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid with electrospun carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Electrochem Commun 10:1431–1434
Shi H, Xu Y, Wang Y, Song W (2010) Assembly of ferrocenylhexanethiol functionalized gold nanoparticles for ascorbic acid determination. Microchim Acta 171:81–89
Fujita Y, Mori I, Yamaguchi T, Hoshino M, Shigemura Y, Shimano M (2001) Spectrophotometric determination of ascorbic acid with iron(III) and p-carboxyphenylfluorone in a cationic surfactant micellar medium. Anal Sci 17:853–857
Zhu M, Huang X, Li J, Shen H (1997) Peroxidase-based spectrophotometric methods for the determination of ascorbic acid, norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and levodopa. Anal Chim Acta 357:261–267
Uchiyama S, Kobayashi Y, Suzuki S, Hamamoto O (1991) Selective biocoulometry of vitamin C using dithiothreithol, N-ethylmaleimide, and ascorbate oxidase. Anal Chem 63(20):2259–2262
Fatibello-Filho O, Vieira IDC (2000) L-Ascorbic Acid Determination in Pharmaceutical Formulations Using a Biosensor Based on Carbon Paste Modified with Crude Extract of Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo). J Braz Chem Soc 11:412–418
Iwase H (2000) Use of an amino acid in the mobile phase for the determination of ascorbic acid in food by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr A 881:317–326
Karlsen A, Blomhoff R, Gundersen TE (2005) High-throughput analysis of Vitamin C in human plasma with the use of HPLC with monolithic column and UV-detection. J Chromatogr B: Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 824:132–138
Wang X, Si Y, Wang J, Ding B, Yu J, Al-Deyab SS (2012) A facile and highly sensitive colorimetric sensor for the detection of formaldehyde based on electro-spinning/netting nano-fiber/nets. Sensor Actuat B: Chemical 163:186–193
Li Y, Si Y, Wang X, Ding B, Sun G, Zheng G, Luo W, Yu J (2013) Colorimetric sensor strips for lead (II) assay utilizing nanogold probes immobilized polyamide-6/nitrocellulose nano-fibers/nets. Biosens Bioelectron 48:244–250
Mit-uppatham C, Nithitanakul M, Supaphol P (2004) Effects of solution concentration, emitting electrode polarity, solvent type, and salt addition on electrospun polyamide-6 fibers: A preliminary report. Macromol Symp 216:293–299
Kalayci V, Ouyang M, Graham K (2006) Polymeric nanofibres in high efficiency filtration applications. Filtration 6:286–293
Han X-J, Huang Z-M, He C-L, Liu L, Wu Q-S (2008) Coaxial electrospinning of PC(shell)/PU(core) composite nanofibers for textile application. Polym Compos 29:579–584
Yand H, Li H, Shih WH, Ko F Electrospinning of quantum dot nanocomposite fibers. In, 2006. pp 561–571
Kumbar SG, James R, Nukavarapu SP, Laurencin CT (2008) Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds: Engineering soft tissues. Biomed Mater 3 (3)
Liz-Marzán LM (2006) Tailoring surface plasmons through the morphology and assembly of metal nanoparticles. Langmuir 22:32–41
Moores A, Goettmann F (2006) The plasmon band in noble metal nanoparticles: An introduction to theory and applications. New J Chem 30:1121–1132
Ma M, Wang J, Zheng X (2011) Enhancement of the colorimetric sensitivity of gold nanoparticles with triethanolamine to minimize interparticle repulsion. Microchim Acta 172:155–162
Zhang Y, Li B, Chen X (2010) Simple and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Microchim Acta 168:107–113
Zhao W, Ali MM, Aguirre SD, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) Paper-Based Bioassays Using Gold Nanoparticle Colorimetric Probes. Anal Chem 80:8431–8437
Jiang H, Chen Z, Cao H, Huang Y (2012) Peroxidase-like activity of chitosan stabilized silver nanoparticles for visual and colorimetric detection of glucose. Analyst 137:5560–5564
Xu Q, Du S, Jin G, Li H, Hu XY (2011) Determination of acetamiprid by a colorimetric method based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173:323–329
Shi Q, Vitchuli N, Nowak J, Noar J, Caldwell JM, Breidt F, Bourham M, McCord M, Zhang X (2011) One-step synthesis of silver nanoparticle-filled nylon 6 nanofibers and their antibacterial properties. J Mater Chem 21:10330–10335
Scampicchio M, Arecchi A, Mannino S (2009) Optical nanoprobes based on gold nanoparticles for sugar sensing. Nanotechnology 20 (13)
Link S, Wang ZL, El-Sayed MA (1999) Alloy formation of gold-silver nanoparticles and the dependence of the plasmon absorption on their composition. J Phys Chem B 103(18):3529–3533
Mallik K, Mandal M, Pradhan N, Pal T (2001) Seed Mediated Formation of Bimetallic Nanoparticles by UV Irradiation: A Photochemical Approach for the Preparation of “Core-Shell” Type Structures. Nano Letters 1:319–322
Darroudi M, Ahmad MB, Abdullah AH, Ibrahim NA, Shameli K (2010) Effect of accelerator in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 11:3898–3905
Pal U, Sanchez Ramirez JF, Liu HB, Medina A, Ascencio JA (2004) Synthesis and structure determination of bimetallic Au/Cu nanoparticles. Appl Phys A: Mater Sci Process 79:79–84
Zhao W, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) Design of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensing assays. ChemBioChem 9:2363–2371
Nadagouda MN, Varma RS (2007) A greener synthesis of core (Fe, Cu)-shell (Au, Pt, Pd, and Ag) nanocrystals using aqueous vitamin C. Cryst Growth Des 7(12):2582–2587
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the MINTEK, DST/NIC. The authors would like to thank the University of Free State (Physics Department) for the XPS analysis and Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University (Physics Department) for SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 289 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mudabuka, B., Ondigo, D., Degni, S. et al. A colorimetric probe for ascorbic acid based on copper-gold nanoparticles in electrospun nylon. Microchim Acta 181, 395–401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1114-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1114-4