Abstract
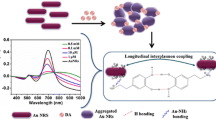
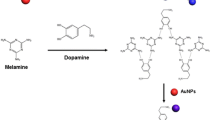
A highly sensitive and selective method is presented for colorimetric determination of dopamine using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Dopamine induces the aggregation of AuNPs, this resulting in a color change from red to blue or purple. Aggregation is accelerated by the presence of Cu(II), especially at low concentrations of dopamine. The concentration of dopamine can be quantified visually or using a UV-vis spectrometer. The detection limit is as low as 30 nM. The assay is simple, inexpensive, and highly sensitive. Ascorbic acid in even 100-fold molar excess does not interfere. The mechanism of the aggregation of the AuNPs is discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arreguin S, Nelson P, Padway S, Shirazi M, Pierpont C (2009) Dopamine complexes of iron in the etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Inorg Biochem 103:87–93
Clarke SJ, Hollmann CA, Aldaye FA, Nadeau JL (2008) Effect of ligand density on the spectral, physical, and biological characteristics of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Bioconjugate Chem 19:562–568
Wu HP, Cheng TL, Tseng WL (2007) Nanoparticles for selective detection of dopamine, levodopa, adrenaline, and catechol based on fluorescence quenching. Langmuir 23:7880–7885
Toma’s P-R, Carmen ML, Toma’s V, Encarna R (2007) Flow injection fluorimetric determination of L-dopa and dopamine based on a photochemical inhibition process. Microchim Acta 158:299–305
Hu YY, Wu X, Su YY, Hou XD, Zhang JY (2009) Capillary zone electrophoresis hyphenatedwith laser-induced fluorescence detection for sensitive determination of noradrenaline and dopamine with 5-(4, 6-dichloro-s-triazin-2-ylamino) fluorescein as fluorescent label. Microchim Acta 166:289–294
Voegel PD, Zhou WH, Baldwin RP (1997) Integrated capillary electrophoresis/electrochemical detection with metal film electrodes directly deposited onto the capillary tip. Anal Chem 69:951–957
Uutela P, Karhu L, Piepponen P, Kaenmaki M, Ketola RA, Kostiainen R (2009) Discovery of dopamine glucuronide in rat and mouse brain microdialysis samples using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:427–434
Hermans A, Keithley RB, Kita JM, Sombers LA, Wightman RM (2008) Dopamine detection with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry used with analog background subtraction. Anal Chem 80:4040–4048
Mullane APO, Zhang J, Toth AB, Bond AM (2008) Higher harmonic large-amplitude fourier transformed alternating current voltammetry: analytical attributes derived from studies of the oxidation of ferrocenemethanol and uric acid at a glassy carbon electrode. Anal Chem 80:4614–4626
Ali SR, Ma YF, Parajuli RR, Balogun Y, Lai WYC, He HX (2007) A nonoxidative sensor based on a self-doped polyaniline/carbon nanotube composite for sensitive and selective detection of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Anal Chem 79:2583–2587
Sun YX, Fei JJ, Hou J, Zhang Q, Liu YL, Hu BN (2009) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin using a carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 165:373–379
Wang GF, Sun JG, Zhang W, Jiao SF, Fang B (2009) Simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid with LaFeO3 nanoparticles modified electrode. Microchim Acta 164:357–362
Zhang L (2008) Covalent modification of glassy carbon electrode with cysteine for the determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 161:191–200
Baron R, Zayats M, Willner I (2005) Dopamine-, L-DOPA-, adrenaline-, and noradrenaline-induced growth of Au nanoparticles: assays for the detection of neurotransmitters and of tyrosinase activity. Anal Chem 77:1566–1571
Zhao W, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) Design of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensing assays. ChemBioChem 9:2363–2371
Zhao WA, Ali MM, Aguirre SD, Brook MA, Li YF (2008) Paper-based bioassays using gold nanoparticle colorimetric probes. Anal Chem 80:8431–8437
Ghosh SK, Pal T (2007) Coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: from theory to applications. Chem Rev 107:4797–4862
Stehr J, Hrelescu C, Sperling RA, Raschke G, Wunderlich M, Nichtl A, Heindl D, Kulrzinger K, Parak WJ, Klar TA, Feldmann J (2008) Gold nanostoves for microsecond DNA melting analysis. Nano Lett 8:619–623
Hurst SJ, Han MS, Jean ALKRL, Mirkin CA (2007) Screening the sequence selectivity of DNA-binding molecules using a gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric approach. Anal Chem 79:7201–7205
Li Y, Qi HL, Yang J, Zhang CX (2009) Detection of DNA immobilized on bare gold electrodes and gold nanoparticle-modified electrodes via electrogenerated chemiluminescence using a ruthenium complex as a tag. Microchim Acta 164:69–76
Takeda Y, Mafune F, Kondo T (2009) Selective degradation of proteins by laser irradiation onto gold nanoparticles in solution. J Phys Chem C 113:5027–5030
Zhang DM, Neumann O, Wang H, Yuwono VM, Barhoumi A, Perham M, Hartgerink JD, Stafshede PW, Halas NJ (2009) Gold nanoparticles can induce the formation of protein-based aggregates at physiological pH. Nano Lett 9:666–671
Laaksonen P, Kivioja J, Paananen A, Kainlauri M, Kontturi K, Ahopelto J, Linder MB (2009) Selective nanopatterning using citrate-stabilized Au nanoparticles and cystein-modified amphiphilic protein. Langmuir 25:5185–5192
Lim IS, Mott D, Ip W, Njoki PN, Pan Y, Zhou S, Zhong CJ (2008) Interparticle interactions in glutathione mediated assembly of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:8857–8863
Liu YX, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Hong CL, Liu KG, Guan S (2010) Ultrasensitive amperometric immunosensor for the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen based on a porous chitosan and gold nanoparticles functionalized interface. Microchim Acta in press (doi:10.1007/s00604–009–0243–2)
Li L, Li B, Qi Y, Jin Y (2009) Label-free aptamer-based colorimetric detection of mercury ions in aqueous media using unmodified gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Anal Bioanal Chem 93:2051–2057
Si S, Kotal A, Mandal TK (2007) One-dimensional assembly of peptide-functionalized gold nanoparticles: an approach toward mercury ion sensing. J Phys Chem C 111:1248–1255
Kelley AM (2007) A molecular spectroscopic description of optical spectra of J-aggregated dyes on gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 7:3235–3240
Liu SP, Chen YH, Liu ZF, Hu XL, Wang F (2006) A highly sensitive resonance rayleigh scattering method for the determination of vitamin B1 with gold nanoparticles probe. Microchim Acta 154:87–93
Zhong ZY, Patskovskyy S, Bouvrette P, Luong JHT, Gedanken A (2004) The surface chemistry of Au colloids and their interactions with functional amino acids. J Phys Chem B 108:4046–4052
Li L, Li B (2009) Sensitive and selective detection of cysteine using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Analyst 134:1361–1365
Wei H, Li B, Li J, Wang EK, Dong SJ (2007) Simple and sensitive aptamer-based colorimetric sensing of protein using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes. Chem Commun 3735–3737
Grabar KC, Freeman RG, Hommer MB, Natan M (1995) Preparation and characterization of Au colloid monolayers. Anal Chem 67:735–743
Daniel M-C, Astruc D (2004) Gold Nanoparticles: sssembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Kiss T, Gergely A (1979) Complexes of 3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl derivatives, III. Equilibrium study of parentand some mixed ligand complexes of dopamine, alanine and pyrocatechol with nickel (II), copper (II) and zinc (II) ions. Inorg Chim Acta 36:31–36
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277:1078–1081
Charkoudian LK, Franz KJ (2006) Fe (III)-coordination properties of neuromelanin components: 5, 6-dihydroxyindole and 5, 6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic Acid. Inorg Chem 45:3657–3664
Lamarque L, Navarro P, Miranda C, Aran VJ, Ochoa C, Escartı F, Latorre EGEJ, Luis SV, Miravet JF (2001) Dopamine interaction in the absence and in the presence of Cu2+ ions with macrocyclic and macrobicyclic polyamines containing pyrazole units. crystal structures of [Cu2(L1)(H2O)2](ClO4)4 and [Cu2(H-1L3)](ClO4)3·2H2O. J Am Chem Soc 123:10560–10570
Kuznar BG, Simeon V, Weber OA (1974) Complexes of adrenaline and related compounds with Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+. J Inorg Metal Chem 36:2151–2154
Burlamacchi L, Lai A, Monduzzi M, Saba G (1983) NMR, EPR, and INDO studies on the complexes of dopamine with Cu2+, Mn2+, and Fe3+ in aqueous solution. J Magn Reson 53:39–50
Luczak T (2009) Electroanalysis of norepinephrine at bare gold electrode pure and modified with gold nanoparticles and S-functionalized self-assembled layers in aqueous solution. Electroanalysis 21:1539–1549
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (No. 109150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supporting information
(DOC 1079 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, B. & Chen, X. Simple and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Microchim Acta 168, 107–113 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0269-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0269-5