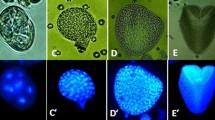
Abstract
Microspore embryogenesis involves reprogramming of the pollen immature cell towards embryogenesis. We have identified and characterized a collection of 14 genes induced along different morphological phases of microspore-derived embryo development in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) anther culture. SERKs and FLAs genes previously associated with somatic embryogenesis and reproductive tissues, respectively, were also included in this analysis. Genes involved in signalling mechanisms such as TaTPD1-like and TAA1b, and two glutathione S-transferase (GSTF2 and GSTA2) were induced when microspores had acquired a ‘star-like’ morphology or had undergone the first divisions. Genes associated with control of plant development and stress response (TaNF-YA, TaAGL14, TaFLA26, CHI3, XIP-R; Tad1 and WALI6) were activated before exine rupture. When the multicellular structures have been released from the exine, TaEXPB4, TaAGP31-like and an unknown embryo-specific gene TaME1 were induced. Comparison of gene expression, between two wheat cultivars with different response to anther culture, showed that the profile of genes activated before exine rupture was shifted to earlier stages in the low responding cultivar. This collection of genes constitutes a value resource for study mechanism of intra-embryo communication, early pattern formation, cell wall modification and embryo differentiation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baudino S, Hansen S, Brettschneider R, Hecht VFG, Dresselhaus T, Lörz H, Dumas C, Rogowsky PM (2001) Molecular characterization of two novel maize LRR receptor-like kinases, which belong to the SERK gene family. Planta 213:1–10
Borderies G, Le Bèchec M, Rossignol M, Lafitte C, Le Deunff E, Beckert M, Dumas C, Matthys-Rochon E (2004) Characterization of proteins secreted during maize microspore culture: arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) stimulate embryo development. Eur J Cell Biol 83:205–212
Boutilier KA, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L, Hattori J, Liu C-H, Van Lammeren AAM, Miki BLA, Clustres JBM, Van Lookeren Campagne MM (2002) Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryogenic growth. Plant Cell 14:1737–1749
Boutilier K, Fiers M, Liu C-M, van der Geest AHM (2005) Biochemical and molecular aspects of haploid embryogenesis. In: Palmer CE, Keller WA, Kasha KJ (eds) Haploids in Crop Improvement II. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 73–96
Broughton S (2008) Ovary co-culture improves embryo and green plant production in anther culture of Australian spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 95:185–195
Cao S, Kumimoto RW, Siriwardana CL, Risinger JR, Holt III BF (2011) Identification and characterization of NF-Y transcription factor families in the monocot model plant Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS ONE 6(6):e21805
Castillo AM, Vallés MP, Cistué L (2000) Comparison of anther and isolated microspore cultures in barley. Effects of culture density and regeneration medium. Euphytica 113:1–8
Cummins I, O’Hagan D, Jablonkai I, Cole DJ, Hehn A, Werck-Reichhart D, Edwards R (2003) Cloning, characterization and regulation of a family of phi class glutathione transferases from wheat. Plant Mol Biol 52:591–603
Dornez E, Croes E, Gebruers K, De Coninck B, Cammue BPA, Delcour JA, Courtin CM (2010) Accumulated evidence substantiates a role for three classes of wheat xylanase inhibitors in plant defense. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29:244–264
Faik A, Abouzouhair J, Sarhan F (2006) Putative fasciclin-like arabinogalactan-proteins (FLA) in wheat (Triticum aestivum) and rice (Oryza sativa): identification and bioinformatic analyses. Mol Gen Genomics 276:478–494
Forster BP, Heberle-Bors E, Kasha KJ, Touraev A (2007) The resurgence of haploids in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci 12:368–375
Grover A (2012) Plant chitinases: genetic diversity and physiological roles. Crit Rev Plant Sci 31:57–73
Hosp J, Tashpulatov A, Roessner U, Barsova E, Katholnigg H, Steinborn R, Melikant B, Lukyanov S, Heberle-Bors E, Touraev A (2007) Transcriptional and metabolic profiles of stress-induced, embryogenic tobacco microspores. Plant Mol Biol 63:137–149
Indrianto A, Barinova I, Touraev A (2001) Tracking individual wheat microspore in vitro: identification of embryogenic microspore and body axis formation in the embryo. Planta 212:163–174
Jauhar PP, Xu SS, Baenziger PS (2009) Haploidy in cultivated wheats: induction and utility in basic and applied research. Crop Sci 49:737–755
Joosen R, Cordewener J, Supena EDJ, Vorst O, Lammers M, Maliepaard C, Zeilmaker T, Miki B, America T, Custers J, Boutilier K (2007) Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis identifies pathways and markers associated with the establishment of rapeseed microspore-derived embryo development. Plant Physiol 144:155–172
Koike M, Okamoto T, Tsuda S, Imai R (2002) A novel plant defensin-like gene of winter wheat is specifically induced during cold acclimation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298:46–53
Lantos C, Weyen J, Orsini JM, Gnad H, Schlieter B, Lein V, Kontowski S, Jacobi A, MihÁly R, Broughton S, Pauk J (2013) Efficient application of in vitro anther culture for different European winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) breeding programmes. Plant Breeding 132:149–154
Leljak-Levanić D, Juranić M, Sprunck S (2013) Markers for early zygotic reprogramming in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) encode small putative secreted peptides and proteins involved in proteasomal degradation. Submitted to plant reproduction, this issue
Letarte J, Simion E, Miner M, Kasha KJ (2006) Arabinogalactans and arabinogalactan-proteins induce embryogenesis in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) microspore culture. Plant Cell Rep 24:691–698
Li J (2010) Multi-tasking of somatic embryogenesis receptor-like protein kinases. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:509–514
Lin Z, Ni Z, Zhang Y, Yao Y, Wu H, Sun Q (2005) Isolation and characterization of 18 genes encoding α- and β-expansins in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Gen Genomics 274:548–556
Liu C, Mehdy MC (2007) A nonclassical arabinogalactan protein gene highly expressed in vascular tissues, AGP31, is transcriptionally repressed by methyl jasmonic acid in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145:863–874
Malik MR, Wang F, Dirpaul JM, Zhou N, Polowick PL, Ferrie AMR, Krochko JE (2007) Transcript profiling and identification of molecular markers for early microspore embryogenesis in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 144:134–154
Maraschin SF, Vennik M, Lamers GEM, Spaink HP, Wang M (2005a) Time-lapse tracking of barley androgenesis reveals position-determined cell death within pro-embryos. Planta 220:531–540
Maraschin SF, De Priester W, Spaink HP, Wang M (2005b) Androgenic switch: an example of plant embryogenesis from the male gametophyte perspective. J Exp Bot 56:1711–1726
Maraschin SF, Caspers M, Potokina E, Wülfert F, Graner A, Spaink HP, Wang M (2006) cDNA array analysis of stress-induced gene expression in barley androgenesis. Physiol Plantarum 127:535–550
Mauch F, Dudler R (1993) Differential induction of distinct glutathione-S-transferases of wheat by xenobiotics and by pathogen attack. Plant Physiol 102:1193–1201
Mu J, Tan H, Hong S, Liang Y, Zuo J (2013) Arabidopsis transcription factor genes NF-YA1, 5, 6, and 9 play redundant roles in male gametogenesis, embryogenesis, and seed development. Molecular Plant 6(1):188–201
Muñoz-Amatriaín M, Svensson JT, Castillo AM, Cistué L, Close TJ, Vallés MP (2006) Transcriptome analysis of barley anthers: effect of mannitol treatment on microspore embryogenesis. Physiol Plantarum 127:551–560
Muñoz-Amatriaín M, Svensson JT, Castillo AM, Cistué L, Close TJ, Vallés MP (2009) Transcriptome comparison of three barley lines after mannitol stress treatment reveals genes involved in genotype-dependent response to microspore embryogenesis. Funct Integr Genomic 9:321–323
Nobusawa T, Okushima Y, Nagata N, Kojima M, Sakakibara H et al (2013) Synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids in the epidermis controls plant organ growth by restricting cell proliferation. PLoS Biol 11(4):e1001531. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001531
Paire A, Devaux P, Lafitte C, Dumas C, Matthys-Rochon E (2003) Proteins produced by barley microspores and their derived androgenic structures promote in vitro zygotic maize embryo formation. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 73:167–176
Pulido A, Bakos F, Devic M, Barnabás B, Olmedilla A (2009) HvPG1 and ECA1: two genes activated transcriptionally in the transition of barley microspores from the gametophytic to the embryogenic pathway. Plant Cell Rep 28:551–559
Redha A, Suleman P (2011) Effects of exogenous application of polyamines on wheat anther cultures. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 105:345–353
Reynolds TL, Crawford RL (1996) Changes in abundance of an abscisic acid-responsive, early cysteine-labeled metallothionein transcript during pollen embryogenesis in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). Plant Molecular Biol 32:823–829
Reynolds TL, Kitto SL (1992) Identification of embryoid-abundant genes that are temporally expressed during pollen embryogenesis in wheat anther cultures. Plant Physiol 100:1744–1750
Richards KD, Snowden KC, Cardner RC (1994) wali6 and wali7, Genes induced by aluminum in wheat (Trificum aestivum 1.) roots. Plant Physiol 105:1455–1456
Sang X, Li Y, Luo Z, Ren D, Fang L, Wang N, Zhao F, Ling Y, Yang Z, Liu Y, He G (2012) CHIMERIC FLORAL ORGANS1, encoding a monocot-specific MADS box protein, regulates floral organ identity in rice. Plant Physiol 160:788–807
Seguí-Simarro JM, Nuez F (2008) How microspores transform into haploid embryos: changes associated with embryogenesis induction and microspore-derived embryogenesis. Physiol Plantarum 134:1–12
Seifert GJ, Roberts K (2007) The biology of arabinogalactan proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:137–161
Soriano M, Cistué L, Vallés MP, Castillo AM (2007) Effects of colchicine on anther and microspore culture of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 91:225–234
Soriano M, Cistué L, Castillo AM (2008) Enhanced induction of microspore embryogenesis after n-butanol treatment in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) anther culture. Plant Cell Rep 27:805–811
Soriano M, Li H, Boutilier K (2013) Microspore embryogenesis: establishment of embryo identity and pattern in culture. Submitted to plant reproduction, this issue
Sprunck S, Baumann U, Edwards K, Langridge P, Dresselhaus T (2005) The transcript composition of egg cells changes significantly following fertilization in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant J 41:660–672
Stasolla C, Belmonte MF, Tahir M, Elhiti M, Khamiss K, Joosen R, Maliepaard C, Sharpe A, Gjetvaj B (2008) Boutilier KA (2008) Buthionine sulfoximine (BSO)-mediated improvement in cultured embryo quality in vitro entails changes in ascorbate metabolism, meristem development and embryo maturation. Planta 228:255–272
Stephenson TJ, McIntyre L, Collet C, Xue G-P (2007) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y family of transcription factors in Triticum aestivum. Plant Mol Biol 65:77–92
Tsuwamoto R, Fukuoka H, Takahata Y (2007) Identification and characterization of genes expressed in early embryogenesis from microspores of Brassica napus. Planta 225:641–652
Vrinten PL, Nakamura T, Kasha KJ (1999) Characterization of cDNAs expressed in the early stages of microspore embryogenesis in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Mol Biol 41:455–463
Wang A, Xia Q, Xie W, Dumonceaux T, Zou J, Datla R, Selvaraj G (2002) Male gametophyte development in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): molecular, cellular, and biochemical analyses of a sporophytic contribution to pollen wall ontogeny. Plant J 30:613–623
West M, Yee KM, Danao J, Zimmerman JL, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (1994) LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is an essential regulator of late embryogenesis and cotyledon identity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 6:1731–1745
Yang S-L, Xie L-F, Mao H-Z, Puah ChS, Yang W-C, Jiang L, Sundaresan V, Ye D (2003) TAPETUM DETERMINANT1 is required for cell specialization in the arabidopsis anther. Plant Cell 15:2792–2804
Zhao T, Ni Z, Dai Y, Yao Y, Nie X, Sun Q (2006) Characterization and expression of 42 MADS-box genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Gen Genomics 276:334–350
Zheng MY (2003) Microspore culture in wheat (Triticum aestivum)—doubled haploid production via induced embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 73:213–230
Żur I, Dubas E, Sánchez-Díaz RA, Castillo AM, Krzewska M, Vallés MP (2013) Changes in gene expression pattern associated with microspore embryogenesis in triticale (×Triticosecale Wittm). Submitted to plant reproduction, this issue
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. María Muñoz-Amatriaín at the Department of Agronomy and Plant Genetics, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, USA, for her contribution in the barley candidate gene selection analysis. We are also grateful to Dr. Adela Olmedilla at the Estación Experimental del Zaidín, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (EEZ-CSIC), Granada (Spain), for their help with semithins sections preparation. RA Sánchez-Díaz was recipient of a predoctoral fellowship, from Junta Ampliación de Estudios, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (JAE-CSIC) of Spain. This work was supported by Project AGL2010-17509, from ‘Plan Nacional de Recursos y Tecnologías Agroalimentarias’ of Spain and by COST Action FAO0903 ‘Harnessing of Reproduction for Plant Improvement’ (HAPRECI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Dresselhaus.
A contribution to the Special Issue “HAPRECI—Plant Reproduction Research in Europe”.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Díaz, R.A., Castillo, A.M. & Vallés, M.P. Microspore embryogenesis in wheat: new marker genes for early, middle and late stages of embryo development. Plant Reprod 26, 287–296 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-013-0225-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-013-0225-8