Abstract
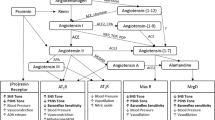
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is one of the best-studied enzyme-neuropeptide systems in the brain and can serve as a model for the action of peptides on neuronal function in general. It is now well established that the brain has its own intrinsic RAS with all its components present in the central nervous system. The RAS generates a family of bioactive angiotensin peptides with variable biological and neurobiological activities. These include angiotensin-(1–8) [Ang II], angiotensin-(3–8) [Ang IV], and angiotensin-(1–7) [Ang-(1–7)]. These neuroactive forms of angiotensin act through specific receptors. Only Ang II acts through two different high-specific receptors, termed AT1 and AT2. Neuronal AT1 receptors mediate the stimulatory actions of Ang II on blood pressure, water and salt intake, and the secretion of vasopressin. In contrast, neuronal AT2 receptors have been implicated in the stimulation of apoptosis and as being antagonistic to AT1 receptors. Among the many potential effects mediated by stimulation of AT2 are neuronal regeneration after injury and the inhibition of pathological growth. Ang-(1–7) mediates its antihypertensive effects by stimulating the synthesis and release of vasodilator prostaglandins and nitric oxide and by potentiating the hypotensive effects of bradykinin. New data concerning the roles of Ang IV and Ang-(1–7) in cognition also support the existence of complex site-specific interactions between multiple angiotensins and multiple receptors in the mediation of important central functions of the RAS. Thus, the RAS of the brain is involved not only in the regulation of blood pressure, but also in the modulation of multiple additional functions in the brain, including processes of sensory information, learning, and memory, and the regulation of emotional responses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albiston AL, McDowall SG, Matsacos D, Sim P, Clune E, Mustafa T, Lee J, Mendelsohn FAO, Simpson RJ, Connolly LM, Chai SY (2001) Evidence that the angiotensin IV (AT4) receptor is the enzyme insulin-regulated aminopeptidase. J Biol Chem 276:48623–48626
Albiston AL, Fernando R, Ye S, Peck GR, Chai SY (2004a) Alzheimer’s, angiotensin IV and an aminopeptidase. Biol Pharm Bull 27:765–767
Albiston AL, Pederson ES, Burns P, Purcell B, Wright JW, Harding JW, Mendelsohn FA, Weisinger RS, Chai SY (2004b) Attenuation of scopolamine-induced learning deficits by LVV-hemorphin-7 in rats in the passive avoidance and water maze paradigms. Behav Brain Res 154:239–243
Albrecht D, Nitschke T (1998) The responsivity to angiotensins of neurons in different subnuclei of the rat’s amygdala. Eur J Neurosci 10:35
Albrecht D, Broser M, Krüger H (1997a) Excitatory action of angiotensins II and IV on hippocampal neuronal activity in urethane anesthetized rats. Regul Pept 70:105–109
Albrecht D, Broser M, Krüger H, Bader M (1997b) Effects of angiotensin II and IV on geniculate activity in nontransgenic and transgenic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 332:53–63
Albrecht D, Henklein P, Ganten D (1997c) Actions of angiotensin and lisinopril on thalamic somatosensory neurons in normotensive, non-transgenic and hypertensive, transgenic rats. Hypertension 15:1151–1157
Albrecht D, Nitschke T, von Bohlen und Halbach O (2000) Various effects of angiotensin II on amygdaloid neuronal activity in normotensive control and hypertensive transgenic [TGR(mREN-2)27] rats. FASEB J 14:925–931
Albrecht D, Hellner K, Walther T, von Bohlen und Halbach O (2003) Angiotensin II and the amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:498–500
Allen AM, MacGregor DP, Chai SY, Donnan GA, Kaczmarczyk S, Richardson K, Kalnins R, Ireton J, Mendelsohn FA (1992) Angiotensin II receptor binding associated with nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in human basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 32:339–344
Almeida AP, Frabregas BC, Madureira MM, Santos RJ, Campagnole-Santos MJ, Santos RA (2000) Angiotensin-(1–7) potentiates the coronary vasodilatatory effect of bradykinin in the isolated rat heart. Braz J Med Biol Res 33:709–713
Alvarez R, Alvarez V, Lahoz CH, Martinez C, Pena J, Sanchez JM, Guisasola LM, Salas-Puig J, Moris G, Vidal JA, Ribacoba R, Menes BB, Uria D, Coto E (1999) Angiotensin converting enzyme and endothelial nitric oxide synthase DNA polymorphisms and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:733–736
Ambuhl P, Felix D, Imboden H, Khosla MC, Ferrario CM (1992) Effects of angiotensin II and its selective antagonists on inferior olivary neurones. Regul Pept 41:19–26
Ambuhl P, Felix D, Khosla MC (1994) [7-D-ALA]-angiotensin-(1–7): selective antagonism of angiotensin-(1–7) in the rat paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res Bull 35:289–291
Amouyel P, Richard F, Berr C, vid-Fromentin I, Helbecque N (2000) The renin angiotensin system and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 903:437–441
Ardaillou R, Chansel D (1997) Synthesis and effects of active fragments of angiotensin II. Kidney Int 52:1458–1468
Arinami T, Li L, Mitsushio H, Itokawa M, Hamaguchi H, Toru M (1996) An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin converting enzyme gene is associated with both brain substance P contents and affective disorders. Biol Psychiatry 40:1122–1127
Armando I, Seltzer A, Bregonzio C, Saavedra JM (2003) Stress and angiotensin II: novel therapeutic opportunities. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2:413–419
Armstrong DL, Garcia EA, Ma T, Quinones B, Wayner MJ (1996) Angiotensin II blockade of long-term potentiation at the perforant path-granule cell synapse in vitro. Peptides 17:689–693
Barnes NM, Costall B, Kelly ME, Murphy DA, Naylor RJ (1990) Anxiolytic-like action of DuP753, a non-peptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Neuroreport 1:20–21
Barnes JM, Barnes NM, Costall B, Coughlan J, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ, Tomkins DM, Williams TJ (1992) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition, angiotensin, and cognition. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 19 (Suppl 6):S63–S71
Barnes JM, Steward LJ, Barber PC, Barnes NM (1993) Identification and characterisation of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in human brain. Eur J Pharmacol 230:251–258
Barnes KL, DeWeese DM, Andresen MC (2003) Angiotensin potentiates excitatory sensory synaptic transmission to medial solitary tract nucleus neurons. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284:R1340–R1353
Bauer EP, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2002) NMDA receptors and L-type voltage-gated calcium channels contribute to long-term potentiation and different components of fear memory formation in the lateral amygdala. J Neurosci 22:5239–5249
Benarroch EE, Schmeichel AM (1998) Immunohistochemical localization of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in human hypothalamus and brainstem. Brain Res 812:292–296
Bickerton R, Buckley J (1961) Evidence for a central mechanism in angiotensin induced hypertension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 106:834–836
Block CH, Santos RA, Brosnihan KB, Ferrario CM (1988) Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensin-(1–7) in the rat forebrain. Peptides 9:1395–1401
Braszko JJ (1996) The contribution of AT1 and AT2 angiotensin receptors to its cognitive effects. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 56:49–54
Braszko JJ (2002) AT(2) but not AT(1) receptor antagonism abolishes angiotensin II increase of the acquisition of conditioned avoidance responses in rats. Behav Brain Res 131:79–86
Braszko JJ (2004) Involvement of D1 dopamine receptors in the cognitive effects of angiotensin IV and des-Phe6 angiotensin IV. Peptides 25:1195–1203
Braszko JJ, Wisniewski K (1988) Effect of angiotensin II and saralasin on motor activity and the passive avoidance behavior of rats. Peptides 9:475–479
Braszko JJ, Kupryszewski G, Witczuk B, Wisniewski K (1988) Angiotensin II(3–8) hexapeptide affects motor activity, performance of passive avoidance and a conditioned avoidance response in rats. Neuroscience 27:777–783
Braszko JJ, Karwowska-Polecka W, Halicka D, Gard PR (2003a) Captopril and enalapril improve cognition and depressed mood in hypertensive patients. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 14:323–343
Braszko JJ, Kulakowska A, Winnicka MM (2003b) Effects of angiotensin II and its receptor antagonists on motor activity and anxiety in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 54:271–281
Braun-Menendez E, Fasciolo J, Leloir L, Munoz J (1940) The substance causing renal hypertension. J Physiol (Lond) 98:283–298
Brede M, Hein L (2001) Transgenic mouse models of angiotensin receptor subtype function in the cardiovascular system. Regul Pept 96:125–132
Brown K (1989) Angiotensin receptors are implicated in the mechanism of mas action. Trends Pharmacol Sci 10:87–89
Buisson B, Laflamme L, Bottari SP, Gasparo M de, Gallo PN, Payet MD (1995) A G protein is involved in the angiotensin AT2 receptor inhibition of the T-type calcium current in non-differentiated NG108-15 cells. J Biol Chem 270:1670–1674
Bunnemann B, Fuxe K, Metzger R, Mullins J, Jackson TR, Hanley MR, Ganten D (1990) Autoradiographic localization of mas proto-oncogene mRNA in adult rat brain using in situ hybridization. Neurosci Lett 114:147–153
Campbell DJ (2003) The renin-angiotensin and the kallikrein-kinin systems. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:784–791
Capdeville C, Bouhtoury F el, Parache RM, Boulu RG, Guillou J, Atkinson J (1990) The angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors, captopril and Wy-44,655 attenuate the consequences of cerebral ischemia in renovascular hypertensive rats. Life Sci 47:539–546
Chai SY, Bastias MA, Clune EF, Matsacos DJ, Mustafa T, Lee JH, McDowall SG, Paxinos G, Mendelsohn FA, Albiston AL (2000) Distribution of angiotensin IV binding sites (AT4 receptor) in the human forebrain, midbrain and pons as visualised by in vitro receptor autoradiography. J Chem Neuroanat 20:339–348
Chappell MC, Brosnihan KB, Diz DI, Ferrario CM (1989) Identification of angiotensin-(1–7) in rat brain. Evidence for differential processing of angiotensin peptides. J Biol Chem 264:16518–16523
Chappell MC, Tallant EA, Brosnihan KB, Ferrario CM (1990) Processing of angiotensin peptides by NG108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cell line. Peptides 11:375–380
Chen JK, Zimpelmann J, Harris RC, Burns KD (2001) Angiotensin IV induces tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase and paxillin in proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F980–F988
Chiu AT, Ryan JW, Stewart JM, Dorer FE (1976) Formation of angiotensin III by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Biochem J 155:189–192
Clark MA, Diz DI, Tallant EA (2001) Angiotensin-(1–7) downregulates the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 37:1141–1146
Coffman TM (1997) A genetic approach for studying the physiology of the type 1A (AT1A) angiotensin receptor. Semin Nephrol 17:404–411
Costall B, Coughlan J, Horovitz ZP, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ, Tomkins DM (1989) The effects of ACE inhibitors captopril and SQ29,852 in rodent tests of cognition. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:573–579
Croog SH, Levine S, Testa MA, Brown B, Bulpitt CJ, Jenkins CD, Klerman GL, Williams GH (1986) The effects of antihypertensive therapy on the quality of life. N Engl J Med 314:1657–1664
Csikos T, Balmforth AJ, Grojec M, Gohlke P, Culman J, Unger T (1998) Angiotensin AT2 receptor degradation is prevented by ligand occupation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 243:142–147
Currie D, Lewis RV, McDevitt DG, Nicholson AN, Wright NA (1990) Central effects of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril. I. Performance and subjective assessments of mood. Br J Clin Pharmacol 30:527–536
Daniels D, Fluharty SJ (2004) Salt appetite: a neurohormonal viewpoint. Physiol Behav 81:319–337
Daniels D, Yee DK, Faulconbridge LF, Fluharty SJ (2005) Divergent behavioral roles of angiotensin receptor intracellular signaling cascades. Endocrinology 146:5552–5560
Davis CJ, Kramar EA, De A, Meighan PC, Simasko SM, Wright JW, Harding JW (2006) AT4 receptor activation increases intracellular calcium influx and induces a non-N-methyl-d-aspartate dependent form of long-term potentiation. Neurosci 137:1369–1379
Davisson RL (2003) Physiological genomic analysis of the brain renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:R498–R511
de Gasparo M, Siragy HM (1999) The AT2 receptor: fact, fancy and fantasy. Regul Pept 81:11–24
de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev 52:415–472
Deicken RF (1986) Captopril treatment of depression. Biol Psychiatry 21:1425–1428
Dendorfer A, Raasch W, Tempel K, Dominiak P (1998) Interactions between the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and the sympathetic system. Basic Res Cardiol 93 (Suppl 2):24–29
Denny JB, Polan Curtain J, Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL (1991) Angiotensin II blocks hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res 567:312–324
DeNoble VJ, DeNoble KF, Spencer KR, Chiu AT, Wong PC, Timmermans BM (1991) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist and angiotensin- converting enzyme inhibitor: effect on a renin-induced deficit of a passive avoidance response in rats. Brain Res 561:230–235
Domeney AM (1994) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors as potential cognitive enhancing agents. J Psychiatry Neurosci 19:46–50
Drephal C, Schubert M, Albrecht D (2006) Input-specific long-term potentiation in the rat lateral amygdala of horizontal slices. Neurobiol Learn Mem (in press)
Dudley DT, Hubbell SE, Summerfelt RM (1991) Characterization of angiotensin II (AT2) binding sites in R3T3 cells. Mol Pharmacol 40:360–367
Dulin N, Madhun ZT, Chang CH, Berti-Mattera L, Dickens D, Douglas JG (1995) Angiotensin IV receptors and signaling in opossum kidney cells. Am J Physiol 269:F644–F652
Epstein AN, Fitzsimons JT, Simons BJ (1969) Drinking caused by the intracranial injection of angiotensin into the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 200:98P–100P
Epstein AN, Fitzsimons JT, Rolls BJ (1970) Drinking induced by injection of angiotensin into the rain of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 210:457–474
Felix D, Khosla MC, Barnes KL, Imboden H, Montani B, Ferrario CM (1991) Neurophysiological responses to angiotensin-(1–7). Hypertension 17:1111–1114
Ferguson AV, Washburn DLS, Bains JS (1999) Regulation of autonomic pathways by angiotensin. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes 6:19–25
Ferguson AV, Washburn DL, Latchford KJ (2001) Hormonal and neurotransmitter roles for angiotensin in the regulation of central autonomic function. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226:85–96
Ferrario CM, Barnes KL, Block CH, Brosnihan KB, Diz DI, Khosla MC, Santos RA (1990) Pathways of angiotensin formation and function in the brain. Hypertension 15:I13–I19
Ferrario CM, Brosnihan KB, Diz DI, Jaiswal N, Khosla MC, Milsted A, Tallant EA (1991) Angiotensin-(1–7): a new hormone of the angiotensin system. Hypertension 18:III126–III133
Feterik K, Smith L, Katusic ZS (2000) Angiotensin-(1–7) causes endothelium-dependent relaxation in canine middle cerebral artery. Brain Res 873:75–82
Fitzsimons JT (1998) Angiotensin, thirst, and sodium appetite. Physiol Rev 78:583–686
Fogari R, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, Derosa G, Pasotti C, Fogari E, Preti P (2003) Influence of losartan and atenolol on memory function in very elderly hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 17:781–785
Fruitier-Arnaudin I, Cohen M, Bordenave S, Sannier F, Piot JM (2002) Comparative effects of angiotensin IV and two hemorphins on angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Peptides 23:1465–1470
Gallinat S, Busche S, Raizada MK, Sumners C (2000) The angiotensin II type 2 receptor: an enigma with multiple variations. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E357–E374
Gard PR (2002) The role of angiotensin II in cognition and behaviour. Eur J Pharmacol 438:1–14
Gard PR (2004) Angiotensin as a target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety and depression. Expert Opin Ther Targets 8:7–14
Gard PR, Rusted JM (2004) Angiotensin and Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic prospects. Expert Rev Neurother 4:87–96
Garreau I, Chansel D, Vandermeersch S, Fruitier I, Piot JM, Ardaillou R (1998) Hemorphins inhibit angiotensin IV binding and interact with aminopeptidase N. Peptides 19:1339–1348
Ge J, Barnes NM (1996) Alterations in angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes level in brain regions from patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 297:299–306
Gelband CH, Sumners C, Lu D, Raizada MK (1998) Angiotensin receptors and norepinephrine neuromodulation: implications of functional coupling. Regul Pept 73:141–147
Gendron L, Payet MD, Gallo-Payet N (2003) The angiotensin type 2 receptor of angiotensin II and neuronal differentiation: from observation to mechanisms. J Mol Endocrinol 31:359–372
Georgiev V (1990) Involvement of transmitter mechanisms in the behavioural effects of angiotensin II. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 42:553–562
Georgiev V, Getova D, Opitz M (1991) Mechanisms of the angiotensin II effects on exploratory behavior of rats in open field. III. Modulatory role of GABA. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 13:5–9
Gironacci MM, Yujnovsky I, Gorzalczany S, Taira C, Pena C (2004) Angiotensin-(1–7) inhibits the angiotensin II-enhanced norepinephrine release in coarcted hypertensive rats. Regul Pept 118:45–49
Gross V, Schunck WH, Honeck H, Milia AF, Kargel E, Walther T, Bader M, Inagami T, Schneider W, Luft FC (2000) Inhibition of pressure natriuresis in mice lacking the AT2 receptor. Kidney Int 57:191–202
Guo D-F, Sun Y, Hamet P, Inagami T (2001) The angiotensin II type 1 receptor and receptor-associated proteins. Cell Res 11:165–180
Haas HL, Felix D, Celio MR, Inagami T (1980) Angiotensin II in the hippocampus. A histochemical and electrophysiological study. Experientia 36:1394–1395
Hajjar I, Catoe H, Sixta S, Boland R, Johnson D, Hirth V, Wieland D, Eleazer P (2005) Cross-sectional and longitudinal association between antihypertensive medications and cognitive impairment in an elderly population. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 60:67–73
Hall KL, Hanesworth JM, Ball AE, Felgenhauer GP, Hosick HL, Harding JW (1993) Identification and characterization of a novel angiotensin binding site in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells that is specific for the hexapeptide (3–8) fragment of angiotensin II, angiotensin IV. Regul Pept 44:225–232
Hallberg M, Nyberg F (2003) Neuropeptide conversion to bioactive fragments-an important pathway in neuromodulation. Curr Protein Pept Sci 4:31–44
Handa RK (2001) Characterization and signaling of the AT4 receptor in human proximal tubule epithelial (HK-2) cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:440–449
Hanesworth JM, Sardinia MF, Krebs LT, Hall KL, Harding JW (1993) Elucidation of a specific binding site for angiotensin II(3–8), angiotensin IV, in mammalian heart membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1036–1042
Harding JW, Sullivan MJ, Hanesworth JM, Cushing LL, Wright JW (1988) Inability of [125I]Sar1, Ile8-angiotensin II to move between the blood and cerebrospinal fluid compartments. J Neurochem 50:554–557
Harding JW, Cook VI, Miller Wing AV, Hanesworth JM, Sardinia MF, Hall KL, Stobb JW, Swanson GN, Coleman JKM, Wright JW, Harding EC (1992) Identification of an AII (3–8) [AIV] binding site in guinea pig hippocampus. Brain Res 583:340–343
Hauser W, Johren O, Saavedra JM (1998) Characterization and distribution of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol 348:101–114
Heemskerk FM, Saavedra JM (1995) Quantitative autoradiography of angiotensin II AT2 receptors with [125I]CGP 42112. Brain Res 677:29–38
Heemskerk FM, Zorad S, Seltzer A, Saavedra JM (1993) Characterization of brain angiotensin II AT2 receptor subtype using [125I] CGP 42112A. NeuroReport 4:103–105
Hein L, Barsh GS, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ, Kobilka BK (1995) Behavioural and cardiovascular effects of disrupting the angiotensin II type-2 receptor in mice. Nature 377:744–747
Hellner K, Walther T, Schubert M, Albrecht D (2005) Angiotensin-(1–7) enhances LTP in the hippocampus through the G-protein-coupled receptor Mas. Mol Cell Neurosci 29:427–435
Hong CJ, Wang YC, Tsai SJ (2002) Association study of angiotensin I-converting enzyme polymorphism and symptomatology and antidepressant response in major depressive disorders. J Neural Transm 109:1209–1214
Hu J, Igarashi A, Kamata M, Nakagawa H (2001) Angiotensin-converting enzyme degrades Alzheimer amyloid ß-peptide (Aß) aggregation, deposition, fibril formation; and inhibits cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 276:47863–47868
Huang YY, Kandel ER (1998) Postsynaptic induction and PKA-dependent expression of LTP in the lateral amygdala. Neuron 21:169–178
Hunley TE, Tamura M, Stoneking BJ, Nishimura H, Ichiki T, Inagami T, Kon V (2000) The angiotensin type II receptor tonically inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme in AT2 null mutant mice. Kidney Int 57:570–577
Hunyady L, Bor M, Balla T, Catt KJ (1994) Identification of a cytoplasmic Ser-Thr-Leu motif that determines agonist-induced internalization of the AT1 angiotensin receptor. J Biol Chem 269:31378–31382
Ichiki T, Labosky PA, Shiota C, Okuyama S, Imagawa Y, Fogo A, Niimura F, Ichikawa I, Hogan BL, Inagami T (1995) Effects on blood pressure and exploratory behaviour of mice lacking angiotensin II type-2 receptor. Nature 377:748–750
Inagami T, Iwai N, Sasaki K, Yamano Y, Bardhan S, Chaki S, Guo DF, Furuta H, Ohyama K, Kambayashi Y (1994) Cloning, expression and regulation of angiotensin II receptors. Eur Heart J 15:104–107
Iwai N, Inagami T (1992) Identification of two subtypes in the rat type I angiotensin II receptor. FEBS Lett 298:257–260
Jarvis MF, Gessner GW, Ly CQ (1992) The angiotensin hexapeptide 3–8 fragment potently inhibits [125I]angiotensin II binding to non-AT1 or -AT2 recognition sites in bovine adrenal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 219:319–322
Johnston CI (1990) Biochemistry and pharmacology of the renin-angiotensin system. Drugs 39:21–31
Jöhren O, Imboden H, Hauser W, Maye I, Sanvitto GL, Saavedra JM (1997) Localization of angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin II, angiotensin II receptor subtypes, and vasopressin in the mouse hypothalamus. Brain Res 757:218–227
Jones DL (1986) Cardiovascular and drinking responses elicited by central administration of angiotensin II: differential effects of GABA injected into the ventral tegmental area and spiperone injected into the nucleus accumbens. Brain Res Bull 17:265–269
Jones DL, Mogenson GJ (1982) Central injections of spiperone and GABA: attenuation of angiotensin II stimulated thirst. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60:720–726
Kambayashi Y, Bardhan S, Takahashi K, Tsuzuki S, Inui H, Hamakubo T, Inagami T (1993) Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem 268:24543–24546
Kang J, Sumners C, Posner P (1993) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor-modulated changes in potassium currents in cultured neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 265:C607–C616
Kang J, Richards EM, Posner P, Sumners C (1995) Modulation of the delayed rectifier K+ current in neurons by an angiotensin II type 2 receptor fragment. Am J Physiol 268:C278–C282
Kerins DM, Hao Q, Vaughan DE (1995) Angiotensin induction of PAI-1 expression in endothelial cells is mediated by the hexapeptide angiotensin IV. J Clin Invest 96:2515–2520
Kerr DS, Bevilaqua LR, Bonini JS, Rossato JI, Kohler CA, Medina JH, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M (2005) Angiotensin II blocks memory consolidation through an AT2 receptor-dependent mechanism. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:529–535
Kohara K, Brosnihan KB, Chappell MC, Khosla MC, Ferrario CM (1991) Angiotensin-(1–7). A member of circulating angiotensin peptides. Hypertension 17:131–138
Kolsch H, Jessen F, Freymann N, Kreis M, Hentschel F, Maier W, Heun R (2005) ACE I/D polymorphism is a risk factor of Alzheimer’s disease but not of vascular dementia. Neurosci Lett 377:37–39
Kostenis E, Milligan G, Christopoulos A, Sanchez-Ferrer CF, Heringer-Walther S, Sexton PM, Gembardt F, Kellett E, Martini L, Vanderheyden P, Schultheiss HP, Walther T (2005) G-protein-coupled receptor Mas is a physiological antagonist of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circulation 111:1806–1813
Kramar EA, Krishnan R, Harding JW, Wright JW (1998) Role of nitric oxide in angiotensin IV-induced increases in cerebral blood flow. Regul Pept 74:185–192
Kramar EA, Armstrong DL, Ikeda S, Wayner MJ, Harding JW, Wright JW (2001) The effects of angiotensin IV analogs on long-term potentiation within the CA1 region of the hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res 897:114–121
Kumar M, Grammas P, Giacomelli F, Wiener J (1996) Selective expression of c-mas proto-oncogene in rat cerebral endothelial cells. NeuroReport 8:93–96
Landas S, Phillips MI, Stamler JF, Raizada MK (1980) Visualization of specific angiotensin II binding sites in the brain by fluorescent microscopy. Science 210:791–793
Lavoie JL, Sigmund CD (2003) Minireview: overview of the renin-angiotensin system—an endocrine and paracrine system. Endocrinology 144:2179–2183
Lee EHY, Ma YL, Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL (1995) Impaired retention by angiotensin-II mediated by the AT(1) receptor. Peptides 16:1069–1071
Lee J, Chai SY, Mendelsohn FAO, Morris MJ, Allen AM (2001) Potentiation of cholinergic transmission in the rat hippocampus by angiotensin IV and LVV-hemorphin-7. Neuropharmacology 40:618–623
Lee J, Mustafa T, McDowall SG, Mendelsohn FA, Brennan M, Lew RA, Albiston AL, Chai SY (2003) Structure-activity study of LVV-hemorphin-7: angiotensin AT4 receptor ligand and inhibitor of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:205–211
Lehmann DJ, Cortina-Borja M, Warden DR, Smith AD, Sleegers K, Prince JA, van Duijn CM, Kehoe PG (2005) Large meta-analysis establishes the ACE insertion-deletion polymorphism as a marker of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Epidemiol 162:305–317
Lemos VS, Silva DM, Walther T, Alenina N, Bader M, Santos RA (2005) The endothelium-dependent vasodilator effect of the nonpeptide Ang(1–7) mimic AVE 0991 is abolished in the aorta of mas-knockout mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 46:274–279
Lendon CL, Thaker U, Harris JM, McDonagh AM, Lambert JC, Chartier-Harlin MC, Iwatsubo T, Pickering-Brown SM, Mann DMA (2002) The angiotensin 1-converting enzyme insertion (I)/deletion (D) polymorphism does not influence the extent of amyloid or tau pathology in patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 328:314–318
Lew RA, Mustafa T, Ye S, McDowall SG, Chai SY, Albiston AL (2003) Angiotensin AT4 ligands are potent, competitive inhibitors of insulin regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP). J Neurochem 86:344–350
Li DP, Chen SR, Pan HL (2003) Angiotensin II stimulates spinally projecting paraventricular neurons through presynaptic disinhibition. J Neurosci 23:5041–5049
Lin JJ, Yueh KC, Chang DC, Lin SZ (2002) Association between genetic polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 199:25–29
Lippoldt A, Paul M, Fuxe K, Ganten D (1995) The brain renin-angiotensin system: molecular mechanisms of cell to cell interactions. Clin Exp Hypertens 17:251–266
Lucius R, Gallinat S, Rosenstiel P, Herdegen T, Sievers J, Unger T (1998) The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor promotes axonal regeneration in the optic nerve of adult rats. J Exp Med 188:661–670
Martin KA, Grant SG, Hockfield S (1992) The mas proto-oncogene is developmentally regulated in the rat central nervous system. Dev Brain Res 68:75–82
Maul B, Krause W, Pankow K, Becker M, Gembardt F, Alenina N, Walther T, Bader M, Siems WE (2005) Central angiotensin II controls alcohol consumption via its AT1 receptor. FASEB J 19:1474–1481
McKinley MJ, Albiston AL, Allen AM, Mathai ML, May CN, McAllen RM, Oldfield BJ, Mendelsohn FA, Chai SY (2003) The brain renin-angiotensin system: location and physiological roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:901–918
Mehta JL, Li DY, Yang H, Raizada MK (2002) Angiotensin II and IV stimulate expression and release of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured human coronary artery endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 39:789–794
Mellick GD, Buchanan DD, McCann SJ, Davis DR, Le Couteur DG, Chan D, Johnson AG (1999) The ACE deletion polymorphism is not associated with Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 41:103–106
Mentlein R, Roos T (1996) Proteases involved in the metabolism of angiotensin II, bradykinin, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), and neuropeptide Y by vascular smooth muscle cells. Peptides 17:709–720
Metzger R, Bader M, Ludwig G, Berberich C, Bunnemann B, Ganten D (1995) Expression of the mouse and rat mas proto-oncogene in the brain and peripheral tissue. FEBS Lett 357:27–32
Millan MA, Jacobowitz DM, Aguilera G, Catt KJ (1991) Differential distribution of AT1 and AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat brain during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:11440–11444
Miller Wing AV, Hanesworth JM, Sardinia MF, Hall KL, Wright JW, Speth RC, Grove KL, Harding JW (1993) Central angiotensin IV binding sites: distribution and specificity in guinea pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1718–1726
Moeller I, Chai SY, Oldfield BJ, McKinley MJ, Casley D, Mendelsohn FAO (1995) Localization of angiotensin IV binding sites to motor and sensory neurons in the sheep spinal cord and hindbrain. Brain Res 701:301–306
Moeller I, Lew RA, Mendelsohn FA, Smith AI, Brennan ME, Tetaz TJ, Chai SY (1997) The globin fragment LVV-hemorphin-7 is an endogenous ligand for the AT4 receptor in the brain. J Neurochem 68:2530–2537
Moeller I, Chai SY, Smith I, Lew R, Mendelsohn FA (1998) Haemorphin peptides may be endogenous ligands for brain angiotensin AT4 receptors. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl 25:S68–S71
Moeller I, Albiston AL, Lew RA, Mendelsohn FA, Chai SY (1999) A globin fragment, LVV-hemorphin-7, induces [3H]thymidine incorporation in a neuronal cell line via the AT4 receptor. J Neurochem 73:301–308
Monastero R, Caldarella R, Mannino M, Cefalu AB, Lopez G, Noto D, Camarda C, Camarda LK, Notarbartolo A, Averna MR, Camarda R (2002) Lack of association between angiotensin converting enzyme polymorphism and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 335:147–149
Mooney RD, Zhang Y, Rhoades RW (1994) Effects of angiotensin II on visual neurons in the superficial laminae of the hamster’s superior colliculus. Vis Neurosci 11:1163–1173
Morgan JM, Routtenberg A (1977) Angiotensin injected into the neostriatum after learning disrupts retention performance. Science 196:87–89
Morris M, Li P, Callahan MF, Oliverio MI, Coffman TM, Bosch SM, Diz DI (1999) Neuroendocrine effects of dehydration in mice lacking the angiotensin AT1a receptor. Hypertension 33:482–486
Mukoyama M, Nakajima M, Horiuchi M, Sasamura H, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ (1993) Expression cloning of type 2 angiotensin II receptor reveals a unique class of seven-transmembrane receptors. J Biol Chem 268:24539–24542
Murphy TJ, Alexander RW, Griendling KK, Runge MS, Bernstein KE (1991) Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature 351:233–236
Nahmod VE, Finkielman S, Benarroch EE, Pirola CJ (1978) Angiotensin regulates release and synthesis of serotonin in brain. Science 202:1091–1093
Nakajima M, Mukoyama M, Pratt RE, Horiuchi M, Dzau VJ (1993) Cloning of cDNA and analysis of the gene for mouse angiotensin II type 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197:393–399
Naveri L (1995) The role of angiotensin receptor subtypes in cerebrovascular regulation in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 630:1–48
Nguyen G, Delarue F, Burckle C, Bouzhir L, Giller T, Sraer JD (2002) Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest 109:1417–1427
Nguyen G, Burckle C, Sraer JD (2003) The renin receptor: the facts, the promise and the hope. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:51–55
Nikolova JG, Getova DP, Nikolov FP (2000) Effects of ACE-inhibitors on learning and memory processes in rats. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 42:47–51
Oba R, Igarashi A, Kamata M, Nagata K, Takano S, Nakagawa H (2005) The N-terminal active centre of human angiotensin-converting enzyme degrades Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide. Eur J Neurosci 21:733–740
Okuyama S, Sakagawa T, Chaki S, Imagawa Y, Ichiki T, Inagami T (1999) Anxiety-like behavior in mice lacking the angiotensin II type-2 receptor. Brain Res 821:150–159
Olson ML, Olson EA, Qualls JH, Stratton JJ, Harding JW, Wright JW (2004) Norleucine1-Angiotensin IV alleviates mecamylamine-induced spatial memory deficits. Peptides 25:233–241
Oz M, Yang KH, O’Donovan MJ, Renaud LP (2005) Presynaptic angiotensin II AT1 receptors enhance inhibitory and excitatory synaptic neurotransmission to motoneurons and other ventral horn neurons in neonatal rat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 94:1405–1412
Ozaki Y, Soya A, Nakamura J, Matsumoto T, Ueta Y (2004) Potentiation by angiotensin II of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in rat supraoptic magnocellular neurones. J Neuroendocrinol 16:871–879
Page I, Helmer O (1940) A crystalline pressor substance (angiotensin) resulting from the reaction between renin and renin activator. J Exp Med 71:29–42
Pan HL (2004) Brain angiotensin II and synaptic transmission. Neuroscientist 10:422–431
Patel JM, Martens JR, Li YD, Gelband CH, Raizada MK, Block ER (1998) Angiotensin IV receptor-mediated activation of lung endothelial NOS is associated with vasorelaxation. Am J Physiol 275:L1061–L1068
Pauls J, Bandelow B, Ruther E, Kornhuber J (2000) Polymorphism of the gene of angiotensin converting enzyme: lack of association with mood disorder. J Neural Transm 107:1361–1366
Pederson ES, Krishnan R, Harding JW, Wright JW (2001) A role for the angiotensin AT4 receptor subtype in overcoming scopolamine-induced spatial memory deficits. Regul Pept 102:147–156
Phillips MI (1987) Functions of angiotensin in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol 49:413–435
Phillips MI, Shen L, Richards EM, Raizada MK (1993) Immunohistochemical mapping of angiotensin AT1 receptors in the brain. Regul Pept 44:95–107
Printz MP (1988) Regulation of the brain angiotensin system: a thesis of multicellular involvement. Clin Exp Hypertens [A] 10:17–35
Raghavendra V, Chopra K, Kulkarni SK (2001) Comparative studies on the memory-enhancing actions of captopril and losartan in mice using inhibitory shock avoidance paradigm. Neuropeptides 35:65–69
Ramser J, Abidi FE, Burckle CA, Lenski C, Toriello H, Wen G, Lubs HA, Engert S, Stevenson RE, Meindl A, Schwartz CE, Nguyen G (2005) A unique exonic splice enhancer mutation in a family with X-linked mental retardation and epilepsy points to a novel role of the renin receptor. Hum Mol Genet 14:1019–1027
Reagan LP, Flanagan Cato LM, Yee DK, Ma LY, Sakai RR, Fluharty SJ (1994) Immunohistochemical mapping of angiotensin type 2 (AT2) receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 662:45–59
Richards EM, Raizada MK, Gelband CH, Sumners C (1999) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-modulated signaling pathways in neurons. Mol Neurobiol 19:25–41
Roberts KA, Krebs LT, Kramar EA, Shaffer MJ, Harding JW, Wright JW (1995) Autoradiographic identification of brain angiotensin IV binding sites and differential c-Fos expression following intracerebroventricular injection of angiotensin II and IV in rats. Brain Res 682:13–21
Rowe BP, Grove KL, Saylor DL, Speth RC (1990) Angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 186:339–342
Rowe BP, Saylor DL, Speth RC (1992) Analysis of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in individual rat brain nuclei. Neuroendocrinology 55:563–573
Rowe BP, Saylor DL, Speth RC, Absher DR (1995) Angiotensin-(1–7) binding at angiotensin II receptors in the rat brain. Regul Pept 56:139–146
Saavedra JM (1999) Emerging features of brain angiotensin receptors. Regul Pept 85:31–45
Saavedra JM (2005) Brain angiotensin II: new developments, unanswered questions and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25:485–512
Sadoshima S, Fujii K, Ooboshi H, Ibayashi S, Fujishima M (1993) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors attenuate ischemic brain metabolism in hypertensive rats. Stroke 24:1561–1566
Sakagawa T, Okuyama S, Kawashima N, Hozumi S, Nakagawasai O, Tadano T, Kisara K, Ichiki T, Inagami T (2000) Pain threshold, learning and formation of brain edema in mice lacking the angiotensin II type 2 receptor. Life Sci 67:2577–2585
Sampaio WO, Nascimento AA, Santos RA (2003) Systemic and regional hemodynamic effects of angiotensin-(1–7) in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H1985–H1994
Santos RA, Campagnole-Santos MJ (1994) Central and peripheral actions of angiotensin-(1–7). Braz J Med Biol Res 27:1033–1047
Santos RA, Simoes e Silva AC, Maric C, Silva DM, Machado RP, Buhr I de, Heringer-Walther S, Pinheiro SV, Lopes MT, Bader M, Mendes EP, Lemos VS, Campagnole-Santos MJ, Schultheiss HP, Speth R, Walther T (2003) Angiotensin-(1–7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8258–8263
Sardinia MF, Hanesworth JM, Krishnan F, Harding JW (1994) AT4 receptor structure-binding relationship: N-terminal-modified angiotensin IV analogues. Peptides 15:1399–1406
Sasaki K, Yamano Y, Bardhan S, Iwai N, Murray JJ, Hasagawa M, Matsuda Y, Inagami T (1991) Cloning and expression of a complimentary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature 351:230–232
Sasamura H, Hein L, Saruta T, Pratt RE (1997) Evidence for internalization of both type 1 angiotensin receptor subtypes (AT1a, AT1b) by a protein kinase C independent mechanism. Hypertens Res 20:295–300
Savaskan E (2005) The role of the brain renin-angiotensin system in neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Alzheimer Res 2:29–35
Schmitz U, Berk BC (1997) Angiotensin II signal transduction: stimulation of multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Trends Endocrinol Metab 8:261–266
Segman RH, Shapira Y, Modai I, Hamdan A, Zislin J, Heresco-Levy U, Kanyas K, Hirschmann S, Karni O, Finkel B, Schlafman M, Lerner A, Shapira B, Macciardi F, Lerer B (2002) Angiotensin converting enzyme gene insertion/deletion polymorphism: case-control association studies in schizophrenia, major affective disorder, and tardive dyskinesia and a family-based association study in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 114:310–314
Shepherd J, Bill DJ, Dourish CT, Grewal SS, Mclenachan A, Stanhope KJ (1996) Effects of the selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists losartan and PD123177 in animal models of anxiety and memory. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 126:206–218
Shibata K, Makino I, Shibaguchi H, Niwa M, Katsuragi T, Furukawa T (1997) Up-regulation of angiotensin type 2 receptor mRNA by angiotensin II in rat cortical cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 239:633–637
Sim MK, Qiu XS (1994) Formation of des-Asp-angiotensin I in the hypothalamic extract of normo- and hypertensive rats. Blood Press 3:260–264
Sim MK, Choo MH, Qiu XS (1994) Degradation of angiotensin I to [des-Asp1]angiotensin I by a novel aminopeptidase in the rat hypothalamus. Biochem Pharmacol 48:1043–1046
Song K, Allen AM, Paxinos G, Mendelsohn FAO (1992) Mapping of angiotensin II receptor subtype heterogeneity in rat brain. J Comp Neurol 316:467–484
Stoll M, Unger T (2001) Angiotensin and its AT2 receptor: new insights into an old system. Regul Pept 99:175–182
Sugaya T, Nishimatsu S, Tanimoto K, Takimoto E, Yamagishi T, Imamura K, Goto S, Imaizumi K, Hisada Y, Otsuka A, et al (1995) Angiotensin II type 1a receptor-deficient mice with hypotension and hyperreninemia. J Biol Chem 270:18719–18722
Sumitomo T, Suda T, Nakano Y, Tozawa F, Yamada M, Demura H (1991) Angiotensin II increases the corticotropin-releasing factor messenger ribonucleic acid level in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology 128:2248–2252
Sumners C, Woodruff GN, Poat JA (1981) Effects of specific dopamine lesions and dopamine receptor sensitivity on angiotensin II- and carbachol-induced thirst in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 73:180–183
Sumners C, Fleegal MA, Zhu M (2002) Angiotensin AT1 receptor signalling pathways in neurons. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29:483–490
Sun C, Sellers KW, Sumners C, Raizada MK (2005) NAD(P)H oxidase inhibition attenuates neuronal chronotropic actions of angiotensin II. Circ Res 96:659–666
Swanson GN, Hanesworth JM, Sardinia MF, Coleman JK, Wright JW, Hall KL, Miller Wing AV, Stobb JW, Cook VI, Harding EC, et al (1992) Discovery of a distinct binding site for angiotensin II (3–8), a putative angiotensin IV receptor. Regul Pept 40:409–419
Tallant EA, Higson JT (1997) Angiotensin II activates distinct signal transduction pathways in astrocytes isolated from neonatal rat brain. Glia 19:333–342
Tanaka M, Tsuchida S, Imai T, Fujii N, Miyazaki H, Ichiki T, Naruse M, Inagami T (1999) Vascular response to angiotensin II is exaggerated through an upregulation of AT1 receptor in AT2 knockout mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258:194–198
Tchekalarova J, Georgiev V (1998) Further evidence for interaction between angiotensin II and dopamine receptors (experiments on apomorphine stereotypy). Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 20:419–424
Thomas WG, Mendelsohn FA (2003) Angiotensin receptors: form and function and distribution. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:774–779
Thone-Reineke C, Zimmermann M, Neumann C, Krikov M, Li J, Gerova N, Unger T (2004) Are angiotensin receptor blockers neuroprotective? Curr Hypertens Rep 6:257–266
Tigerstedt R, Bergman P (1898) Niere und Kreislauf. Skand Arch Physiol 8:223–271
Tom B, Dendorfer A, Jan Danser AH (2003) Bradykinin, angiotensin-(1–7), and ACE inhibitors: how do they interact? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:792–801
Tsutsumi K, Saavedra JM (1991) Characterization and development of angiotensin II receptor subtypes (AT1 and AT2) in rat brain. Am J Physiol 261:R209–R216
van Houten M, Mangiapane ML, Reid IA, Ganong WF (1983) [Sar,Ala]angiotensin II in cerebrospinal fluid blocks the binding of blood-borne [125I]angiotensin II to the circumventricular organs. Neuroscience 10:1421–1426
Vervoort VS, Beachem MA, Edwards PS, Ladd S, Miller KE, de Mollerat X, Clarkson K, DuPont B, Schwartz CE, Stevenson RE, Boyd E, Srivastava AK (2002) AGTR2 mutations in X-linked mental retardation. Science 296:2401–2403
von Bohlen und Halbach O (2005) The renin-angiotensin system in the mammalian central nervous system. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:355–371
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Albrecht D (1998) Angiotensin II inhibits long-term potentiation within the lateral nucleus of the amygdala through AT1-receptors. Peptides 19:1031–1036
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Albrecht D (2000) Identification of angiotensin IV binding sites in the mouse brain by a fluorescent binding study. Neuroendocrinology 72:218–223
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Walther T, Bader M, Albrecht D (2000) Interaction between Mas and the angiotensin AT1 receptor in the amygdala. J Neurophysiol 83:2012–2021
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Walther T, Bader M, Albrecht D (2001) Genetic deletion of angiotensin AT2 receptor leads to increased cell numbers in different brain structures of mice. Regul Pept 99:209–216
Walther T, Balschun D, Voigt JP, Fink H, Zuschratter W, Birchmeier C, Ganten D, Bader M (1998) Sustained long term potentiation and anxiety in mice lacking the Mas protooncogene. J Biol Chem 273:11867–11873
Walther T, Voigt JP, Fink H, Bader M (2000) Sex specific behavioural alterations in Mas-deficient mice. Behav Brain Res 107:105–109
Watanabe T, Hashimoto M, Okuyama S, Inagami T, Nakamura S (1999) Effects of targeted disruption of the mouse angiotensin II type 2 receptor gene and stress-induced hyperthermia. J Physiol (Lond) 515:881–885
Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL, Polan Curtain JL, Denny JB (1993a) Ethanol and diazepam inhibition of hippocampal LTP is mediated by angiotensin II and AT-1 receptors. Peptides 14:441–444
Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL, Polan Curtain JL, Denny JB (1993b) Role of angiotensin II and AT-1 receptors in hippocampal LTP. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:455–464
Wayner MJ, Polan Curtain JL, Chiu SC, Armstrong DL (1994) Losartan reduces ethanol intoxication in the rat. Alcohol 11:343–346
Wayner MJ, Chitwood R, Armstrong DL, Phelix C (1997) Ethanol affects hypothalamic neurons projecting to the hippocampus and inhibits dentate granule cell LTP. Alcohol 14:1–7
Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL, Phelix CF, Wright JW, Harding JW (2001) Angiotensin IV enhances LTP in rat dentate gyrus in vivo. Peptides 22:1403–1414
Werner C, Hoffman WE, Kochs E, Rabito SF, Miletich DJ (1991) Captopril improves neurologic outcome from incomplete cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 22:910–914
Wright JW, Harding JW (1994) Brain angiotensin receptor subtypes in the control of physiological and behavioral responses. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 18:21–53
Wright JW, Harding JW (1995) Brain angiotensin receptor subtypes AT-1, AT-2, and AT-4 and their functions. Regul Pept 59:269–295
Wright JW, Harding JW (1997) Important roles for angiotensin III and IV in the brain renin-angiotensin system. Brain Res Rev 25:96–124
Wright JW, Harding JW (2004) The brain angiotensin system and extracellular matrix molecules in neural plasticity, learning, and memory. Prog Neurobiol 72:263–293
Wright JW, Miller Wing AV, Shaffer MJ, Higginson C, Wright DE, Hanesworth JM, Harding JW (1993) Angiotensin II(3–8) (ANG IV) hippocampal binding: potential role in the facilitation of memory. Brain Res Bull 32:497–502
Wright JW, Krebs LK, Stobb JW, Harding JW (1995) The angiotensin IV system: functional implications. Front Neuroendocrin 16:23–52
Wright JW, Stubley L, Pederson ES, Kramar EA, Hanesworth JM, Harding JW (1999) Contributions of the brain angiotensin IV-AT4 receptor subtype system to spatial learning. J Neurosci 19:3952–3961
Wright JW, Reichert JR, Davis CJ, Harding JW (2002) Neural plasticity and the brain renin-angiotensin system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:529–552
Wright JW, Kramar EA, Myers ED, Davis CJ, Harding JW (2003) Ethanol-induced suppression of LTP can be attenuated with an angiotensin IV analog. Regul Pept 113:49–56
Yonkov D, Georgiev V, Kambourova T, Opitz M (1987) Participation of angiotensin II in learning and memory. III. Interactions of angiotensin II with GABAergic drugs. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 9:205–208
Yonkov D, Georgiev V, Kambourova T (1989) Further evidence for the GABAergic influence on memory. Interaction of GABAergic transmission with angiotensin II on memory processes. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 11:603–606
Young D, Waitches G, Birchmeier C, Fasano O, Wigler M (1986) Isolation and characterization of a new cellular oncogene encoding a protein with multiple potential transmembrane domains. Cell 45:711–719
Zhu Z, Zhang SH, Wagner C, Kurtz A, Maeda N, Coffman T, Arendshorst WJ (1998) Angiotensin AT1B receptor mediates calcium signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells of AT1A receptor-deficient mice. Hypertension 31:1171–1177
Zhu M, Sumners C, Gelband CH, Posner P (2001) Chronotropic effect of angiotensin II via type 2 receptors in rat brain neurons. J Neurophysiol 85:2177–2183
Zhuo J, Moeller I, Jenkins T, Chai SY, Allen AM, Ohishi M, Mendelsohn FA (1998) Mapping tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin AT1, AT2 and AT4 receptors. J Hypertens 16:2027–2037
Zubenko GS, Nixon RA (1984) Mood-elevating effect of captopril in depressed patients. Am J Psychiatry 141:110–111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Bohlen und Halbach, O., Albrecht, D. The CNS renin-angiotensin system. Cell Tissue Res 326, 599–616 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0190-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0190-8