Abstract
Rationale and objectives
Several studies suggest that the brain renin–angiotensin system is involved in memory consolidation. However, the participation of angiotensin II (AII) in this process is controversial. This is probably due to the fact that many of the studies carried out to elucidate this matter employed multitrial learning paradigms together with pretraining intracerebroventricular infusions, and therefore were unable to distinguish between consolidation and retrieval related events and lacked anatomical specificity. To circumvent this problem, we analyzed the role played in memory consolidation by AII using the hippocampal-dependent, one-trial, step-down inhibitory avoidance task (IA) in combination with stereotaxically localized intrahippocampal infusion of drugs.
Methods and results
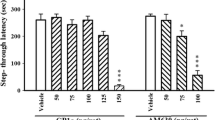
Rats bilaterally implanted with infusion cannulae into the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus (CA1) were trained in IA and tested for memory retention 24 h later. We found that when infused into CA1 immediately or 30 min after training but not later, AII produced a dose-dependent amnesic effect without altering locomotor activity, exploratory behavior or anxiety state. The amnesic effect of AII was not mimicked by angiotensin IV (AIV) and was totally blocked by the AII-type 2 receptor (AT2) antagonist, PD123319, but not by the AII-type 1 receptor (AT1) antagonist, losartan. Importantly, when infused alone, neither PD123319 nor losartan produced any effect on memory retention.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that, when given into CA1, AII blocks memory formation through a mechanism involving activation of AT2 receptors; however, endogenous AII does not seem to participate in the consolidation of IA long-term memory.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong DL, Garcia EA, Ma T, Quinones B, Wayner MJ (1996) Angiotensin II blockade of long-term potentiation at the perforant path-granule cell synapse in vitro. Peptides 17:689–693
Barnes JM, Barnes NM, Costall B, Coughlan J, Horovitz ZP, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ, Tomkins DM (1989) ACE inhibition and cognition. In: MacGregor GA, Sever PS (eds) Current advances in ACE inhibition. Proceedings of an International Symposium. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 159–171
Belcheva I, Ternianov A, Georgiev V (2000) Lateralized learning and memory effects of angiotensin II microinjected into the rat CA1 hippocampal area. Peptides 21:407–411
Bernabeu R, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M, Jerusalinsky D, Medina JH (1995) Learning-specific, time-dependent increase in [3H]phorbol dibutyrate binding to protein kinase C in selected regions of the rat brain. Brain Res 685:163–168
Bernabeu R, Bevilaqua LR, Ardenghi P, Bromberg E, Schmitz P, Bianchin M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) Involvement of hippocampal cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathways in a late memory consolidation phase of aversively motivated learning in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7041–7046
Bevilaqua LR, Ardenghi P, Schroder N, Bromberg E, Schmitz PK, Schaeffer E, Quevedo J, Bianchin M, Walz R, Medina JH, Izquierdo I (1997) Drugs acting upon the cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A signalling pathway modulate memory consolidation when given late after training into rat hippocampus but not amygdala. Behav Pharmacol 8:331–338
Bevilaqua LR, Cammarota M, Paratcha G, de Stein ML, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1999) Experience-dependent increase in cAMP-responsive element binding protein in synaptic and nonsynaptic mitochondria of the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 11:3753–3756
Bevilaqua LR, Rossato JI, Medina JH, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M (2003a) Src kinase activity is required for avoidance memory formation and recall. Behav Pharmacol 14:649–652
Bevilaqua LR, Kerr DS, Medina JH, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M (2003b) Inhibition of hippocampal Jun N-terminal kinase enhances short-term memory but blocks long-term memory formation and retrieval of an inhibitory avoidance task. Eur J Neurosci 17:897–902
Bonini JS, Rodrigues L, Kerr DS, Bevilaqua LR, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I (2003) AMPA/kainate and group-I metabotropic receptor antagonists infused into different brain areas impair memory formation of inhibitory avoidance in rats. Behav Pharmacol 14:161–166
Braszko JJ (2002) AT(2) but not AT(1) receptor antagonism abolishes angiotensin II increase of the acquisition of conditioned avoidance responses in rats. Behav Brain Res 131:79–86
Braszko JJ, Wisniewski K (1988) Effect of angiotensin II and saralasin on motor activity and the passive avoidance behavior of rats. Peptides 9:475–479
Braszko JJ, Kulakowska A, Wisniewski K (1995) Angiotensin II and its 3–7 fragment improve recognition but not spatial memory in rats. Brain Res Bull 37:627–633
Braszko JJ, Kulakowska A, Karwowska-Polecka W (1998) CGP 42112A antagonism of the angiotensin II and angiotensin II(3–7) facilitation of recall in rats. Pharmacol Res 38:461–468
Braszko JJ, Kulakowska A, Winnicka MM (2003) Effects of angiotensin II and its receptor antagonists on motor activity and anxiety in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 54:271–281
Brun VH, Ytterbo K, Morris RG, Moser MB, Moser EI (2001) Retrograde amnesia for spatial memory induced by NMDA receptor-mediated long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 21:356–362
Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Wolfman C, Levi de Stein M, Bernabeu R, Jerusalinsky D, Medina JH (1995) Inhibitory avoidance training induces rapid and selective changes in 3[H]AMPA receptor binding in the rat hippocampal formation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 64:257–264
Cammarota M, Paratcha G, Levi de Stein M, Bernabeu R, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) B-50/GAP-43 phosphorylation and PKC activity are increased in rat hippocampal synaptosomal membranes after inhibitory avoidance training. Neurochem Res 22:499–505
Cammarota M, Bernabeu R, Levi De Stein M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1998) Learning-specific, time-dependent increases in hippocampal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity and AMPA GluR1 subunit immunoreactivity. Eur J Neurosci 10:2669–2676
Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LR, Ardenghi P, Paratcha G, Levi de Stein M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2000) Learning-associated activation of nuclear MAPK, CREB and Elk-1, along with Fos production, in the rat hippocampus after a one-trial avoidance learning: abolition by NMDA receptor blockade. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 76:36–46
Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LR, Dunkley PR, Rostas JA (2001) Angiotensin II promotes the phosphorylation of cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) at Ser133 through an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Neurochem 79:1122–1128
Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LR, Kerr D, Medina JH, Izquierdo I (2003) Inhibition of mRNA and protein synthesis in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus blocks reinstallment of an extinguished conditioned fear response. J Neurosci 23:737–741
Chalas A, Conway EL (1996) No evidence for involvement of angiotensin II in spatial learning in water maze in rats. Behav Brain Res 81:199–205
Croog SH, Levine S, Testa MA, Brown B, Bulpitt CJ, Jenkins CD, Klerman GL, Williams GH (1986) The effects of antihypertensive therapy on the quality of life. N Engl J Med 314:1657–1664
Denny JB, Polan-Curtain J, Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL (1991) Angiotensin II blocks hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res 567:321–324
DeNoble VJ, DeNoble KF, Spencer KR, Chiu AT, Wong PC, Timmermans BM (1991) Non-peptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor: effect on a renin-induced deficit of a passive avoidance response in rats. Brain Res 561:230–235
Fischer TA, Singh K, O’Hara DS, Kaye DM, Kelly RA (1998) Role of AT1 and AT2 receptors in regulation of MAPKs and MKP-1 by ANG II in adult cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol 275:906–916
Fitzsimons JT, Kucharczyk J (1978) Drinking and haemodynamic changes induced in the dog by intracranial injection of components of the renin–angiotensin system. J Physiol 276:419–434
Fleegal MA, Sumners C (2003) Drinking behavior elicited by central injection of angiotensin II: roles for protein kinase C and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Am J Physiol, Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:632–640
Georgiev VP, Yonkov DI, Kambourova TS (1988) Interactions between angiotensin II and baclofen in shuttle-box and passive avoidance performance. Neuropeptides 12:155–158
Haas HL, Felix D, Celio MR, Inagami T (1980) Angiotensin II in the hippocampus. A histochemical and electrophysiological study. Experientia 36:1394–1395
Holscher C (2003) Time, space and hippocampal functions. Rev Neurosci 14:253–284
Horiuchi M, Hayashida W, Akishita M, Tamura K, Daviet L, Lehtonen JY, Dzau VJ (1999) Stimulation of different subtypes of angiotensin II receptors, AT1 and AT2 receptors, regulates STAT activation by negative crosstalk. Circ Res 84:876–882
Huang XC, Richards EM, Sumners C (1995) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor-mediated stimulation of protein phosphatase 2A in rat hypothalamic/brainstem neuronal cocultures. J Neurochem 65:2131–2137
Huang XC, Richards EM, Sumners C (1996) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in rat brain neuronal cultures are activated by angiotensin II type 1 receptors and inhibited by angiotensin II type 2 receptors. J Biol Chem 271:15635–15641
Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) Memory formation: the sequence of biochemical events in the hippocampus and its connection to activity in other brain structures. Neurobiol Learn Mem 68:285–316
Köller M, Krause HP, Hoffmeister F, Ganten D (1979) Endogenous brain angiotensin II disrupts passive avoidance behavior in rats. Neurosci Lett 14:71–75
Kramar EA, Armstrong DL, Ikeda S, Wayner MJ, Harding JW, Wright JW (2001) The effects of angiotensin IV analogs on long-term potentiation within the CA1 region of the hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res 897:114–121
Lee EH, Ma YL, Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL (1995) Impaired retention by angiotensin II mediated by the AT1 receptor. Peptides 16:1069–1971
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136
Martin SJ, Grimwood PD, Morris RG (2000) Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:649–711
McCloskey CA, Zuckerbraun BS, Gallo DJ, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR (2003) A role for angiotensin II in the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases in the liver during hemorrhagic shock. Shock 20:316–319
Moita MA, Rosis S, Zhou Y, LeDoux JE, Blair HT (2003) Hippocampal place cells acquire location-specific responses to the conditioned stimulus during auditory fear conditioning. Neuron 37:485–497
Morgan JM, Routtenberg A (1977) Angiotensin injected into the neostriatum after learning disrupts retention performance. Science 196:87–89
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–167
Picard P, Chretien L, Couture R (1995) Functional interaction between losartan and central tachykinin NK3 receptors in the conscious rat. Br J Pharmacol 114:1563–1570
Raghavendra V, Chopra K, Kulkarni SK (1998) Involvement of cholinergic system in losartan-induced facilitation of spatial and short-term working memory. Neuropeptides 32:417–421
Reagan LP, Flanagan-Cato LM, Yee DK, Ma LY, Sakai RR, Fluharty SJ (1994) Immunohistochemical mapping of angiotensin type 2 (AT2) receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 662:45–59
Richter-Levin G (2004) The amygdala, the hippocampus, and emotional modulation of memory. Neuroscientist 10:31–39
Servant MJ, Giasson E, Meloche S (1996) Inhibition of growth factor-induced protein synthesis by a selective MEK inhibitor in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 271:16047–16052
Sirett NE, Bray JJ, Hubbard JI (1981) Localization of immunoreactive angiotensin II in the hippocampus and striatum of rat brain. Brain Res 217:405–411
Sudilovsky A, Croog S, Crook T, Turnbull B, Testa M, Levine S, Klerman GL (1989) Differential effects of antihypertensive medications on cognitive functioning. Psychopharmacol Bull 25:133–138
Sumners C, Gelband CH (1998) Neuronal ion channel signalling pathways: modulation by angiotensin II. Cell Signal 10:303–311
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Albrecht D (1998) Angiotensin II inhibits long-term potentiation within the lateral nucleus of the amygdala through AT1 receptors. Peptides 19:1031–1036
Walther T, Voigt JP, Fukamizu A, Fink H, Bader M (1999) Learning and anxiety in angiotensin-deficient mice. Behav Brain Res 100:1–4
Wayner MJ, Polan-Curtain J, Armstrong DL (1995) Dose and time dependency of angiotensin II inhibition of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Peptides 16:1079–1082
Wayner MJ, Phelix CF, Armstrong DL (1997) Lateral hypothalamic stimulation inhibits dentate granule cell LTP: direct connections. Brain Res Bull 43:5–15
Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL, Phelix CF, Wright JW, Harding JW (2001) Angiotensin IV enhances LTP in rat dentate gyrus in vivo. Peptides 22:1403–1414
Winnicka MM, Braszko JJ, Wisniewski K (1998) 6-OHDA lesions to amygdala and hippocampus attenuate memory-enhancing effect of the 3–7 fragment of angiotensin II. Gen Pharmacol 30:801–805
Wright JW, Miller-Wing AV, Shaffer MJ, Higginson C, Wright DE, Hanesworth JM, Harding JW (1993) Angiotensin II(3–8) (ANG IV) hippocampal binding: potential role in the facilitation of memory. Brain Res Bull 32:497–502
Wright JW, Stubley L, Pederson ES, Kramar EA, Hanesworth JM, Harding JW (1999) Contributions of the brain angiotensin IV-AT4 receptor subtype system to spatial learning. J Neurosci 19:3952–3961
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from ANPCyT (to M. Cammarota) and CONICET (to M. Cammarota and J.H. Medina), Argentine and CNPq, FAPERGS and CAPES (to L.R.M. Bevilaqua and I. Izquierdo), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kerr, D.S., Bevilaqua, L.R.M., Bonini, J.S. et al. Angiotensin II blocks memory consolidation through an AT2 receptor-dependent mechanism. Psychopharmacology 179, 529–535 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2074-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2074-5