Abstract
Arabidopsis hexokinase1 (HXK1) is a moonlighting protein that has separable functions in glucose signaling and in glucose metabolism. In this study, we have characterized expression features and glucose phosphorylation activities of the six HXK gene family members in Arabidopsis thaliana. Three of the genes encode catalytically active proteins, including a stromal-localized HXK3 protein that is expressed mostly in sink organs. We also show that three of the genes encode hexokinase-like (HKL) proteins, which are about 50% identical to AtHXK1, but do not phosphorylate glucose or fructose. Expression studies indicate that both HKL1 and HKL2 transcripts occur in most, if not all, plant tissues and that both proteins are targeted within cells to mitochondria. The HKL1 and HKL2 proteins have 6–10 amino acid insertions/deletions (indels) at the adenosine binding domain. In contrast, HKL3 transcript was detected only in flowers, the protein lacks the noted indels, and the protein has many other amino acid changes that might compromise its ability even to bind glucose or ATP. Activity measurements of HXKs modified by site-directed mutagenesis suggest that the lack of catalytic activities in the HKL proteins might be attributed to any of numerous existing changes. Sliding windows analyses of coding sequences in A. thaliana and A. lyrata ssp. lyrata revealed a differential accumulation of nonsynonymous changes within exon 8 of both HKL1 and HXK3 orthologs. We further discuss the possibility that the non-catalytic HKL proteins have regulatory functions instead of catalytic functions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- HA:
-
Hemagglutinin
- HKL:
-
Hexokinase-like
- HXK:
-
Hexokinase
- Indels:
-
Insertions/deletions
- K A :
-
Number of nonsynonymous substitutions per nonsynonymous site
- K S :
-
Number of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site
References
Balasubramanian R, Karve A, Kandasamy M, Meagher RB, Moore Bd (2007) A role for F-actin in hexokinase-mediated glucose signaling. Plant Physiol 145:1423–1434
Baena-González E, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Sheen J (2007) A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signaling. Nature 448:938–943
Bernardo SMH, Gray K-A, Todd RB, Cheetham BF, Katz ME (2007) Characterization of regulatory non-catalytic hexokinases in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Genet Genomics 277:519–532
Bork P, Sander C, Valencia A (1992) An ATPase domain common to prokaryotic cell cycle proteins, sugar kinases, actin, and hsp70 heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7290–7294
Cárdenas ML, Cornish-Bowden A, Ureta T (1998) Evolution and regulatory role of the hexokinases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1401:242–264
Cho J-I, Ryoo N, Ko S, Lee S-K, Lee J, Jung K-H, Lee Y-H, Bhoo SH, Winderickx J, An G, Hahn T-R, Jeon J-S (2006a) Structure, expression, and functional analysis of the hexokinase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 224:598–611
Cho Y-H, Yoo S-D, Sheen J (2006b) Regulatory functions of nuclear hexokinase1 complex in glucose signaling. Cell 127:579–589
Claeyssen E, Rivoal J (2007) Isozymes of plant hexokinase: occurrence, properties and functions. Phytochem 68:709–731
Damari-Weissler H, Kandel-Kfir M, Gidoni D, Mett A, Belausov E, Granot D (2006) Evidence for intracellular spatial separation of hexokinases and fructokinases in tomato plants. Planta 224:1495–1502
Damari-Weissler H, Ginzburg A, Gidoni D, Mett A, Krassovskaya I, Weber APM, Belausov E, Granot D (2007) Spinach SoHXK1 is a mitochondria-associated hexokinase. Planta 226:1053–1058
Daniel J (2005) Sir-dependent downregulation of various aging processes. Mol Genet Genomics 274:539–547
da-Silva WS, Rezende GL, Galina A (2001) Subcellular distribution and kinetic properties of cytosolic and non-cytosolic kexokinases in maize seedling roots: implications for hexose phosphorylation. J Exp Bot 52:1191–1201
Doehlert DC (1989) Separation and characterization of four hexose kinases from developing maize kernels. Plant Physiol 89:1042–1048
Francis D, Halford NG (2006) Nutrient sensing in plant meristems. Plant Mol Biol 60:981–993
Giese J-O, Herbers K, Hoffmann M, Klösgen RB, Sonnewald U (2005) Isolation and functional characterization of a novel plastidic hexokinase from Nicotiana tabacum. FEBS Lett 579:827–831
Graham JWA, Williams TCR, Morgan M, Fernie AR, Ratcliffe RG, Sweetlove LJ (2007) Glycolytic enzymes associate dynamically with mitochondria in response to respiratory demand and support substrate channeling. Plant Cell 19:3723–3738
Hall T (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Han S, Kim D (2006) AtRTPrimer: database for Arabidopsis genome-wide homogeneous and specific RT-PCR primer-pairs. BMC Bioinfor 7:179
Heazlewood JL, Tonti-Fillippini JS, Gout AM, Day DA, Whelan J, Millar AH (2004) Experimental analysis of the Arabidopsis mitochondrial proteome highlights signaling and regulatory components, provides assessment of targeting prediction programs, and indicates plant-specific mitochondrial proteins. Plant Cell 16:241–256
Heyer AG, Raap M, Schroeer B, Marty B, Willmitzer L (2004) Cell wall invertase expression at the apical meristem alters floral, architectural, and reproductive traits in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 39:161–169
Hwang I, Sheen J (2001) Two-component circuitry in Arabidopsis cytokinin signal transduction. Nature 413:383–389
Jang J-C, León P, Zhou L, Sheen J (1997) Hexokinase as a sugar sensor in higher plants. Plant Cell 9:5–19
Jang J-C, Sheen J (1994) Sugar sensing in higher plants. Plant Cell 6:1665–1679
Jeffery CJ (2004) Molecular mechanisms for multitasking: recent crystal structures of moonlighting proteins. Curr Opin Struc Biol 14:663–668
Kandel-Kfir M, Damari-Weissler H, German MA, Gidoni D, Mett A, Belausov E, Petreikov M, Adir N, Granot D (2006) Two newly identified membrane-associated and plastidic tomato HXKs: characteristics, predicted structure and intracellular localization. Planta 224:1341–1352
Katz ME, Masoumi A, Burrows SR, Shirtliff CG, Cheetham BF (2000) The Aspergillus nidulans xprF gene encodes a hexokinase-like protein involved in the regulation of extracellular proteases. Genetics 156:1559–1571
Koch MA, Matschinger M (2007) Evolution and genetic differentiation among relatives of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 104:6272–6277
Kojima H, Suzuki T, Kato T, Enomoto K-I, Sato S, Kato T, Tabata S, Sáez-Vasquez J, Echeverría M, Nakagawa T, Ishiguro S, Nakamura K (2007) Sugar-inducible expression of the nucleolin-1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana and its role in ribosome synthesis, growth and development. Plant J 49:1053–1063
Kovtun Y, Chiu W-L, Zeng W, Sheen J (1998) Suppression of auxin signal transduction by a MAPK cascade in higher plants. Nature 395:716–720
Kulkarni GV, Deobagkar DN, Deobagkar DD (2002) Hexokinase like protein fromDrosophila melanogaster. Dros Inf Serv 85:65–68
Kuser PR, Krauchenco S, Antunes OAC, Polikarpov I (2000) The high resolution crystal structure of yeast hexokinase PII with the correct primary sequence provides new insights into its mechanism of action. J Biol Chem 275:20814–20821
Moore B, Zhou L, Rolland F, Hall Q, Cheng W-H, Liu Y-X, Hwang I, Jones T, Sheen J (2003) Role of the Arabidopsis glucose sensor HXK1 in nutrient, light, and hormonal signaling. Science 300:332–336
Moore Bd (2004) Bifunctional and moonlighting enzymes: lighting the way to regulatory control. Trends Plant Sci 9:221–228
Moreno F, Herrero P (2002) The hexokinase 2-dependent glucose signal transduction pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:83–90
Morton BR (1993) Chloroplast DNA codon use: evidence for selection at the psbA locus based on tRNA availability. J Mol Evol 37:273–280
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Olsson T, Thelander M, Ronne H (2003) A novel type of chloroplast stromal hexokinase is the major glucose-phosphorylating enzyme in the moss Physcomitrella patens. J Biol Chem 278:44439–44447
Osuna D, Usadel B, Morcuende R, Gibon Y, Bläsing OE, Höhne M, Günter M, Kamlage B, Trethewey R, Scheible W-R, Stitt M (2007) Temporal responses of transcripts, enzyme activities and metabolites after adding sucrose to carbon-deprived Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 49:463–491
Parmley JL, Hurst LD (2007) How common are intragene windows with KA > KS owing to purifying selection on synonymous mutations? J Mol Evol 64:646–655
Price J, Laxmi A, St Martin SK, Jang J-C (2004) Global transcription profiling reveals multiple sugar signal transduction mechanisms in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2128–2150
Rolland F, Baena-Gonzalez E, Sheen J (2006) Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:675–709
Rolland F, Moore B, Sheen J (2002) Sugar sensing and signaling in plants. Plant Cell 14(Suppl):S185–S205
Rontein D, Dieuaide-Noubhani M, Dufourc EJ, Raymond P, Rolin D (2002) The metabolic architecture of plant cells. J Biol Chem 277:43948–43960
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497
Santangelo GM (2006) Glucose signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:253–282
Sheen J, Zhou L, Jang J-C (1999) Sugars as signaling molecules. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:410–418
Smeekens S (2000) Sugar-induced signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:49–81
Tamura K, Dudley J, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 10:1093
Tocquin P, Corbesier L, Havelange A, Pieltain A, Kurtem E, Bernier G, Périlleux C (2003) A novel high efficiency, low maintenance, hydroponic system for synchronous growth and flowering of Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 3:2
Wright F (1990) The “effective number of codons” used in a gene. Gene 87:23–29
Xiao W, Sheen J, Jang J-C (2000) The role of hexokinase in plant sugar signal transduction and growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 44:451–461
Yoo S-D, Cho Y-H, Sheen J (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Prot 2:1565–1572
Acknowledgments
We appreciate technical assistance from Ms. Betsy Metters. We thank also Dr. Amy Lawton-Rauh for consultation on nucleotide sequence analyses and for supplying A. lyrata tissue and DNA. This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture-National Research Initiative Plant Biochemistry Program (grant no. 2001-035318) and the South Carolina Agricultural Experiment Station (technical contribution No. 5389 of the Clemson University Experiment Station). This material is based upon work supported by CSREES/USDA, under project number SC-170090.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
425_2008_746_MOESM1_ESM.tif
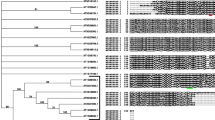
Supplemental Fig. 1 Sequence analyses of HXK family genes from A. lyrata. a Illustrations of gene structures were determined from genomic sequence data. Exons are indicated by rectangles, introns by lines. The lengths of both are proportional to the number of nucleotides that are present. b Phylogenetic relationships of predicted HXK family proteins from A. thaliana and A. lyrata. Phylogenetic reconstruction was done using MEGA4 (Tamura et al. 2007). The scale bar = the frequency of amino acid substitutions per unit length (TIFF 3321 kb)
425_2008_746_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 2 Amino acid sequence alignment for predicted HXK family proteins from A. thaliana and A. lyrata. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW in BioEdit (Hall 1999). (TIFF 5546 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karve, A., Rauh, B.L., Xia, X. et al. Expression and evolutionary features of the hexokinase gene family in Arabidopsis . Planta 228, 411–425 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0746-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0746-9