Abstract
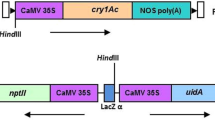
A binary expression vector was constructed containing the insecticidal gene Allium sativum leaf agglutinin (ASAL), and a selectable nptII marker gene cassette, flanked by lox sites. Similarly, another binary vector was developed with the chimeric cre gene construct. Transformed tobacco plants were generated with these two independent vectors. Each of the T0 lox plants was crossed with T0 Cre plants. PCR analyses followed by the sequencing of the target T-DNA part of the hybrid T1 plants demonstrated the excision of the nptII gene in highly precised manner in certain percentage of the T1 hybrid lines. The frequency of such marker gene excision was calculated to be 19.2% in the hybrids. Marker free plants were able to express ASAL efficiently and reduce the survivability of Myzus persiceae, the deadly pest of tobacco significantly, compared to the control tobacco plants. Results of PCR and Southern blot analyses of some of the T2 plants detected the absence of cre as well as nptII genes. Thus, the crossing strategy involving Cre/lox system for the excision of marker genes appears to be very effective and easy to execute. Documentation of such marker excision phenomenon in the transgenic plants expressing the important insecticidal protein for the first time has a great significance from agricultural and biotechnological points of view.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumugam N, Gupta V, Jagannath A, Mukhopadhyay A, Pradhan AK, Burma PK, Pental D (2007) A passage through in vitro culture leads to efficient production of marker-free transgenic plants in Brassica juncea using the Cre-lox system. Transgenic Res 16:703–712
Bai X, Wang Q, Chu C (2008) Excision of a selective marker in transgenic rice using a novel Cre/loxP system controlled by a floral specific promoter. Transgenic Res doi: 10.1007/s11248-008-9182-7
Baisakh N, Rehana S, Rai M, Oliva N, Tan J, Mackill D, Khush GS, Datta K, Datta S (2006) Marker free transgenic (MFT) near isogenic introgression lines (NILs) of ‘golden’ indica rice (cv. IR64) with accumulation of provitamine A in the endosperm tissue. Plant Biotechnol J 4:467–475
Bandyopadhyay S, Roy A, Das S (2001) Binding of garlic (Allium sativum) leaf lectin to the gut receptors of homopteran pests is correlated to its insecticidal activity. Plant Sci 161:1025–1033
Banerjee S, Hess D, Majumder P, Roy D, Das S (2004) The interactions of Allium sativum leaf agglutinin with a chaperonin group of unique receptor protein isolated from a bacterial endosymbiont of the mustard aphid. J Biol Chem 279:23782–23789
Bar M, Lesham B, Gilboa N, Gidoni D (1996) Visual characterization of recombination at FRT-gusA loci in transgenic tobacco mediated by constitutive expression of the native FLP recombinase. Theor Appl Genet 43:407–413
Bayley CC, Morgan M, Dale EC, Ow DW (1992) Exchange of gene activity in transgenic plants catalyzed by the Cre- lox site-specific recombination system. Plant Mol Biol 18:353–362
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of proteins using the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chakraborti D, Sarkar A, Gupta S, Das S (2006) Small and large scale genomic DNA isolation protocol for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.), suitable for molecular marker and transgenic analyses. Afr J Biotechnol 5:585–589
Cotsaftis O, Sallaud C, Breitler JC, Meynard D, Greco R, Pereira A, Guiderdoni E (2002) Transposon-mediated generation of T-DNA-and marker-free rice plants expressing a Bt endotoxin gene. Mol Breed 10:165–180
Cuellar W, Gaudin A, Solorzano D, Casas A, Nopo L, Chudalayandi P, Medrano G, Kreuze J, Ghislain M (2006) Self-excision of the antibiotic resistance gene nptII using a heat inducible Cre-loxP system from transgenic potato. Plant Mol Biol 62:71–82
Dale EC, Ow DW (1990) Intra-and intermolecular site-specific recombination in plant cells mediated by bacteriophage P1 recombinase. Gene 91:79–85
Dale EC, Ow DW (1991) Gene transfer with subsequent removal of the selection gene from the host genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10558–10562
Daley M, Knauf V, Summerfelt KR, Turner JC (1998) Co-transformation with one Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain containing two binary plasmids as a method for producing marker-free transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 17:489–496
Dutta I, Saha P, Majumder P, Sarkar A, Chakraborti D, Banerjee S, Das S (2005a) The efficacy of a novel insecticidal protein, Allium sativum leaf lectin (ASAL) against homopteran insect monitored in transgenic tobacco. Plant Biotechnol J 3:601–611
Dutta I, Majumder P, Saha P, Ray K, Das S (2005b) Constitutive and phloem specific expression of Allium sativum leaf agglutinin (ASAL) to engineer aphid (Lipaphis erysimi) resistance in transgenic Indian mustard (Brassica juncea). Plant Sci 169:996–1007
Endo S, Sujita K, Sakai M, Tanaka H, Ebinuma H (2002) Single step transformation for generating marker-free transgenic rice using the ipt -type MAT vector system. Plant J 30:115–122
Foissac X, Loc NT, Christou P, Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA (2000) Resistance to green leafhopper (Nephotettix virescens) and brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) in transgenic rice expressing snowdrop lectin (Galanthus nivalis agglutinin; GNA). J Insect Physiol 46:573–583
Hoa TTC, Bong BB, Huq E, Hodge TK (2002) Cre/lox site-specific recombination controls the excision of a transgene from the rice genome. Theor Appl Genet 104:518–525
Hoff T, Schnorr KM, Mundy J (2001) A recombinase-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 45:41–49
Hohn B, Levy AA, Puchta H (2001) Elimination of selection markers from transgenic plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:139–143
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffman NL, Wallroth M, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Kerbach S, Lörz H, Becker D (2005) Site-specific recombination in Zea mays. Theor Appl Genet 111:1608–1616
Kopertekh L, Jüttner G, Schiemann J (2004) PVX-Cre-mediated marker gene elimination from transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 55:491–500
Lu H-J, Zhou X-R, Gong Z-X, Upadhyaya NM (2001) Generation of selectable marker-free transgenic rice using double right-border (DRB) binary vectors. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:241–248
Luo H, Lyznik LA, Gidoni D, Hodges TK (2000) FLP-mediated recombination for use in hybrid plant production. Plant J 23:423–430
Maeser S, Kahmann R (1991) The Gin recombinase of phage Mu can catalyse site-specific recombination in plant protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet 230:170–176
Majumder P, Banerjee S, Das S (2004) Identification of receptors responsible for binding of the mannose specific lectin to the gut epithelial membrane of the target insects. Glycoconj J 20:525–530
Mlynarova L, Nap J-P (2003) A self-excising Cre recombinase allows efficient recombination of multiple ectopic heterospecific lox sites in transgenic tobacco. Trans Res 12:45–57
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised method for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Onouchi H, Nishimana R, Kudo M, Machida Y, Machida C (1995) Visualization of site-specific recombination catalyzed by a recombinase from Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 247:653–660
Parkhi V, Rai M, Tan J, Oliva N, Rehana S, Bandyopadhyay A, Torrizo L, Ghole V, Datta K, Datta SK (2005) Molecular characterization of marker-free transgenic lines of indica rice that accumulate carotenoids in seed endosperm. Mol Gen Genomics 274:325–336
Radhakrishnan P, Srivastava V (2005) Utility of the FLP-FRT recombination system for genetic manipulation of rice. Plant Cell Rep 23:721–726
Rao KV, Rathore KS, Hodges TK, Fu X, Stoger E, Sudhakar S, Williams P, Christou P, Bharathi M, Bown DP, Powell KS, Spence J, Gatehouse A, Gatehouse JA (1998) Expression of snowdrop lectin (GNA) in transgenic plants confers resistance to rice brown plant hopper. Plant J 15:469–477
Russell SH, Hoopes JL, Odell JT (1992) Directed excision of a transgene from the plant genome. Mol Gen Genet 234:49–59
Saha P, Chakraborti D, Sarkar A, Dutta I, Basu D, Das S (2007) Characterization of vascular-specific RSs1 and rolC promoters for their utilization in engineering plants to develop resistance against hemipteran insect pests. Planta 226:429–442
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Scholz S, Lörz H, Lutticke S (2001) Transposition of the maize transposable element Ac in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Mol Gen Genet 264:653–661
Sreekala C, Wu L, Gu K, Wang D, Tian D, Yin Z (2005) Excision of a selectable marker in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chemically regulated Cre/loxP system. Plant Cell Rep 24:86–94
Srivastava V, Ow DW (2003) Rare instances of Cre-mediated deletion product maintained in transgenic wheat. Plant Mol Biol 52:661–668
Stuurman J, de Vroomen MJ, Nijkamp HJJ, Haaren MJJ (1996) Single-site manipulation of tomato chromosomes in vitro and in vivo using Cre-lox site-specific recombination. Plant Mol Biol 32:901–913
Sugita K, Kasahara T, Matsunaga E, Ebinuma H (2000) A transformation vector for the production of marker-free transgenic plants containing a single copy transgene at high frequency. Plant J 22:461–469
Tu J, Datta K, Oliva N, Zhang G, Xu C, Khush GS, Zhang Q, Datta SK (2003) Site-independent integrated transgenes in the elite restorer rice line Minghui 63 allow removal of a selectable marker from the gene of interest by self-segregation. Plant Biotechnol J 1:155–165
Vergunst AC, Jansen LET, Fransz PF, Hans de Jong J, Hooykaas PJJ (2000) Cre/lox-mediated recombination in Arabidopsis: evidence for transmission of a translocation and a deletion event. Chromosoma 109:287–297
Xiang C, Han P, Lutziger I, Wang K, Oliver DJ (1999) A mini binary vector series for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 40:711–717
Zhang W, Subbarao S, Addae P, Shen A, Armstrong C, Peschke V, Gilbertson L (2003) Cre/lox-mediated marker gene excision in transgenic maize (Zea mays L) plants. Theor Appl Genet 107:1157–1168
Zubko E, Scutt C, Meyer P (2000) Intrachromosomal recombination between attP regions as a tool to remove selectable marker genes from tobacco transgenes. Nat Biotechnol 18:442–445
Zuo J, Niu QW, Moller SG, Chua NH (2001) Chemical-regulated, site-specific DNA excision in transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 19:157–161
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation, Government of Switzerland and the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India under the Indo-Swiss Collaboration in Biotechnology for financial contributions and Bose Institute, Kolkata, India for providing infrastructure for carrying out the work described here. B. Hohn and D. Schuermann acknowledge the financial help of the Novartis Research Foundation. The authors are thankful to Dr. J. Mundy for providing the pCrox18 plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Jouanin.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2008_585_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. 9 (Supplementary) PCR analyses of 7 T1 hybrid progenies [1433(7), 1433(12), 1735(3), 1938(2), 1938(6), 1938(7) and 1938(14)] for the (a) absence of nptII and (b) presence of ASAL coding sequence. Lane ‘+’, plasmid pBK12.1 as positive control; lane M, DNA ladder mix (Generuler™, MBI Fermentas). (PDF 146 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborti, D., Sarkar, A., Mondal, H.A. et al. Cre/lox system to develop selectable marker free transgenic tobacco plants conferring resistance against sap sucking homopteran insect. Plant Cell Rep 27, 1623–1633 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0585-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0585-y