Abstract
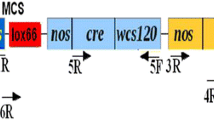
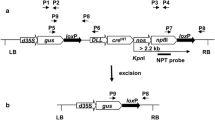
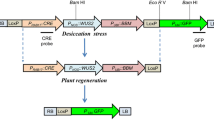
The Cre–loxP site-specific recombination system was deployed for removal of marker genes from Brassica juncea (Indian mustard). Excision frequencies, monitored by removal of nptII or gfp genes in F1 plants of crosses between LOX and CRE lines, were high in quiescent, differentiated somatic tissues but extremely poor in the meristematic regions (and consequently the germinal cells) thus preventing identification and selection of marker-free transgenic events which are devoid of both the marker gene as well as the cre gene, in F2 progeny. We show that a passage through in vitro culture of F1 leaf explants allows efficient development of marker-free transgenics in the F2 generation addressing current limitations associated with efficient use of the Cre/loxP technology for marker gene removal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen S, Li X, Liu X, Xu H, Meng K, Xiao G, Wei X, Wang F, Zhu Z (2005) Green fluorescent protein as a vital elimination marker to easily screen marker-free transgenic progeny derived from plants co-transformed with double T-DNA binary vector system. Plant Cell Rep 23:625–631
Cornielle S, Lutz K, Svab Z, Maliga P (2001) Efficient elimination of selectable marker genes from the plastid genome by CRE-lox site-specific recombination system. Plant J 27:171–178
Dale EC, Ow DW (1991) Gene transfer with subsequent removal of the selection gene from the host genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10558–10562
Dillon PJ, Rosen CA (1990) A rapid method for the construction of synthetic genes using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques 9:298–299
Gleave AP, Mitra DS, Mudge SR, Morris BAM (1999) Selectable marker-free transgenic plants without sexual crossing: transient expression of cre recombinase and use of a conditional lethal dominant gene. Plant Mol Biol 40:223–235
Goldsbrough AP, Lastrella CN, Yoder JI (1993) Transposition mediated re-positioning and subsequent elimination of marker genes from transgenic tomato. Bio/technology 11:1286–1292
Grover A, Pental D (2003) Breeding objectives and requirements for producing transgenics for major field crops of India. Curr Sci 84:310–320
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:939–994
Halpin C (2005) Gene stacking in transgenic plants – the challenge for 21st century plant biotechnology. Plant Biotech J 3:141–155
Hare PD, Chua N-H (2002) Excision of selectable marker genes from transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 20:575–580
Hoa TT, Bong BB, Huq E, Hodges TK (2002) Cre-lox site-specific recombination controls the excision of a transgene from the rice genome. Theor Appl Genet 104:518–525
Iamtham S, Day A (2000) Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from transgenic tobacco plastids. Nat Biotechnol 18:1172–1176
Klimyuk VI, Carroll BJ, Thomas CM, Jones JDG (1993) Alkali treatment for rapid preparation of plant tissue for reliable PCR analysis. Plant J 3:493–494
Konig A (2003) A framework for designing transgenic crops—science, safety and citizen’s concerns. Nat Biotechnol 21:1274–1279
Kumpatla SP, Chandrasekharan MB, Iyer LM, Li G, Hall TC (1998) Genome intruder scanning and modulation systems and transgene silencing. Trends Plant Sci 3:97–104
Lyznik LA, Gordon-Kamm WJ, Tao Y (2003) Site-specific recombination for genetic engineering in plants. Plant Cell Rep 21:925–932
Mattanovich D, Riiker F, Machado A, Laimer M, Regner F, Steinkellner H, Himmler G, Katinger H (1989) Efficient transformation of Agrobacterium spp by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6747
Matthews PR, Wang MB, Waterhouse PM, Thornton S, Fieg SJ, Gubler F, Jacobson JV (2001) Marker gene elimination from transgenic barley, using co-transformation with adjacent ‘twin T-DNA’ on a standard Agrobacterium transformation vector. Mol Breed 7:195–202
Mehra S, Pareek A, Bandyopadhyay P, Sharma P, Burma PK, Pental D (2000) Development of transgenics in Indian oilseed mustard (Brassica juncea) resistant to herbicide phosphinotricin. Curr Sci 78:1358–1364
Odell J, Caimi P, Sauer B, Russell S (1990) Site-directed recombination in the genome of transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 223:369–378
Ow DW (2002) Recombinase-directed plant transformation for the post-genomic era. Plant Mol Biol 48:183–200
Park J, Lee YK, Kang BK, Chung WH (2004) Co-transformation using a negative selectable marker gene for the production of selectable marker gene-free transgenic plants. Theor Appl Genet 109:1562–1567
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1994) Extraction of total cellular DNA from plants, algae and fungi. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RA (eds) Plant molecular biology manual, 2nd edn, vol D1. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1–8
Rommens CM, Humara JM, Ye J, Yan H, Richael C, Zhang L, Perry R, Swords K (2004) Crop improvement through modification of plant’s own genome. Plant Physiol 135:421–431
Russel SH, Hoopes JL, Odell JT (1992) Directed excision of a transgene from the plant genome. Mol Gen Genet 243:49–59
Salinas J, Matassi G, Montero LM, Bernardi G (1988) Compositional compartmentalization and compositional patterns in nuclear genomes of plant. Nucleic Acids Res 16:4269–4285
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sreekala C, Wu L, Gu K, Wang D, Tian D, Yin Z (2005) Excision of selectable marker in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chemically regulated Cre/loxP system. Plant Cell Rep 24:86–94
Vaucheret H (1993) Identification of a general silencer for 19S and 35S promoters in a transgenic tobacco plants: 90 bp of homology in the promoter sequence are sufficient for trans-inactivation. CR Acad Sci 316:1471–1483
Vergunst AC, Jansen LET, Hooykaas PJJ (1998) Site-specific integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA in Arabidopsis thaliana mediated by Cre recombinase. Nucleic Acids Res 26:2729–2734
Wang Y, Chen B, Hu Y, Li J, Lin Z (2005) Inducible excision of selectable marker gene from transgenic plants by Cre/lox site-specific recombination system. Transgenic Res 14:605–614
Yuan Y, Yun-Jun L, Tao W (2004) A new Cre/lox system for deletion of selectable marker gene. Acta Bot Sin 46:862–866
Zhang W, Subbarao S, Addae P, Shen A, Armstrong C, Peschke V, Gilbertson L (2003) Cre/lox-mediated marker gene excision in transgenic maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Theor Appl Genet 107:1157–1168
Zuo J, Niu Q-W, Moller SG, Chua N-H (2001) Chemical-regulated, site specific DNA excision in transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 19:157–161
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this research was provided by DOFCO, a subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB). B. S. Yadav provided technical support. The gfp gene was a kind gift from Prof Jen Sheen. We are grateful to the Department of Botany, University of Delhi for extending use of the confocal microscope facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
N. Arumugam and Vibha Gupta have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, N., Gupta, V., Jagannath, A. et al. A passage through in vitro culture leads to efficient production of marker-free transgenic plants in Brassica juncea using the Cre–loxP system. Transgenic Res 16, 703–712 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-006-9058-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-006-9058-7