Abstract
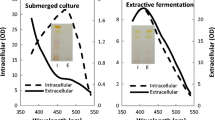
Growing cell submerged culture is usually applied for fermentative production of intracellular orange Monascus pigments, in which accumulation of Monascus pigments is at least partially associated to cell growth. In the present work, extractive fermentation in a nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution was utilized as a strategy for releasing of intracellular Monascus pigments. Those mycelia with low content of intracellular Monascus pigments were utilized as biocatalyst in resting cell submerged culture. By this means, resting cell submerged culture for production of orange Monascus pigments was carried out successfully in the nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution, which exhibited some advantages comparing with the corresponding conventional growing cell submerged culture, such as non-sterilization operation, high cell density (24 g/l DCW) leading to high productivity (14 AU of orange Monascus pigments at 470 nm per day), and recycling of cells as biocatalyst leading to high product yield (approximately 1 AU of orange Monascus pigments at 470 nm per gram of glucose) based on energy metabolism.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method for total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Chen W, He Y, Zhou Y, Shao Y, Feng Y, Li M, Chen F (2015) Edible filamentous fungi from the species Monascus: early traditional fermentations, modern molecular biology, and future genomics. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 14(5):555–567
Economou CN, Aggelis G, Pavlou S, Vayenas DV (2011) Modeling of single-cell oil production under nitrogen-limited and substrate inhibition conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(5):1049–1055
Evanst PJ, Wang HY (1984) Pigment production from immobilized Monascus sp. utilizing polymeric resin adsorption. Appl Environ Microbiol 47(6):1323–1326
Feng Y, Shao Y, Chen F (2012) Monascus pigments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(6):1421–1440
Fenice M, Federici F, Selbmann L, Petruccioli M (2000) Repeated-batch production of pigments by immobilized Monascus purpureus. J Biotechnol 80:271–276
Hirooka S, Higuchi S, Uzuka A, Nozaki H, Miyagishima S-Y (2014) Acidophilic green alga Pseudochlorella sp. YKT1 accumulates high amount of lipid droplets under a nitrogen-depleted condition at a low-pH. PLoS ONE 9(9):e107702. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107702
Hu Z, Zhang X, Wu Z, Qi H, Wang Z (2012a) Export of intracellular Monascus pigments by two-stage microbial fermentation in nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution. J Biotechnol 162:202–209
Hu Z, Zhang X, Wu Z, Qi H, Wang Z (2012b) Perstraction of intracellular pigments by submerged cultivation of Monascus in nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:81–89
Julsing MK, Kuhn D, Schmid D, Buhler B (2012) Resting cells of recombinant E. coli show high epoxidation yields on energy source and high sensitivity to product inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(5):1109–1119
Juzlova P, Martinkova L, Kren V (1996) Secondary metabolites of the fungus Monascus: review. J Ind Microbiol 16:163–170
Kang B, Zhang X, Wu Z, Qi H, Wang Z (2013a) Effect of pH and nonionic surfactant on profile of intracellular and extracellular Monascus pigments. Process Biochem 48:759–767
Kang B, Zhang X, Wu Z, Qi H, Wang Z (2013b) Solubilization capacity of nonionic surfactant micelles strong influence on export of intracellular pigments in Monascus fermentation. Microb Biotechnol 6(5):540–550
Kang B, Zhang X, Wu Z, Qi H, Wang Z, Park S (2014) Production of citrinin-free Monascus pigments by submerged culture at low pH. Enzym Microb Technol 55:50–57
Kitamoto D, Fuzishiro T, Yanagishita H, Nakanc T, Nakahara T (1992) Production of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants by resting cells of Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 14(4):305–310
Lin TF, Demain AL (1993) Resting cell studies on formation of water-soluble red pigments by Monascus sp. J Ind Microbiol 12:361–367
Lin J, Shen H, Tan H, Zhao X, Wu S, Hu C, Zhao ZK (2011) Lipid production by Lipomyces starkeyi cells in glucose solution without auxiliary nutrients. J Biotechnol 152:184–188
Liu JZ, Yang HY, Weng LP, Ji LN (1999) Synthesis of glucose oxidase and catalase by Aspergillus niger in resting cell culture system. Lett Appl Microbiol 29(5):337–341
Liu J, Ren Y, Yao S (2010) Repeated-batch cultivation of encapsulated Monascus purpureus by polyelectrolyte complex for natural pigment production. Chin J Chem Eng 18(6):1013–1017
Rasheva T, Kujumdzieva A, Hallet J-N (1997) Lipid production by Monascus purpureus albino strain. J Biotechnol 56:217–224
Sun W, Xiao F, Wei Z, Cui F, Yu L, Yu S, Zhou Q (2015) Non-sterile and buffer-free bioconversion of glucose to 2-keto-gluconic acid by using Pseudomonas fluorescens AR4 free resting cells. Process Biochem 50:493–499
Tsuge Y, Kawaguchi H, Sasaki K, Tanaka T, Kondo A (2014) Two-step production of D-lactate from mixed sugars by growing and resting cells of metabolically engineered Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4911–4918
Wang Z, Dai Z (2010) Extractive microbial fermentation in cloud point system. Enzym Microb Technol 46:407–418
Wang Z, Zhao F, Hao X, Chen D, Li D (2004) Microbial transformation of hydrophobic compound in cloud point system. J Mol Catal B 27:147–153
Wang Z, Zhao F, Chen D, Li D (2005) Cloud point system as a tool to improve the efficiency of biotransformation. Enzym Microb Technol 36:589–594
Wang Y, Zhang B, Lu L, Huang Y, Xu G (2013) Enhanced production of pigments by addition of surfactants in submerged fermentation of Monascus purpureus H1102. J Sci Food Agric 93:3339–3344
Wang B, Zhang X, Wu Z, Wang Z (2015) Investigation of relationship between lipid and Monascus pigment accumulation by extractive fermentation. J Biotechnol 212:167–173
Willrodt C, Hoschek A, Buhler B, Schmid A, Julsing MK (2015) Decoupling production from growth by magnesium sulfate limitation boosts De Novo limonene production. Biotechnol Bioeng. doi:10.1002/bit.25883
Wu S, Hu C, Jin G, Zhao X, Zhao ZK (2010) Phosphate-limitation mediated lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Bioresour Technol 101:6124–6129
Xiong X, Zhang X, Wu Z, Wang Z (2015) Accumulation of yellow Monascus pigments by extractive fermentation in nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1173–1180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 21276155)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhang, X., Wu, Z. et al. Biosynthesis of Monascus pigments by resting cell submerged culture in nonionic surfactant micelle aqueous solution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 7083–7089 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7434-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7434-7