Abstract
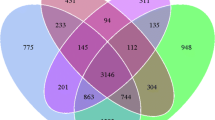
Microbial communities in oil-polluted desert soils have been rarely studied compared to their counterparts from freshwater and marine environments. We investigated bacterial diversity and changes therein in five desert soils exposed to different levels of oil pollution. Automated rRNA intergenic spacer (ARISA) analysis profiles showed that the bacterial communities of the five soils were profoundly different (analysis of similarities (ANOSIM), R = 0.45, P < 0.0001) and shared less than 20 % of their operational taxonomic units (OTUs). OTU richness was relatively higher in the soils with the higher oil pollution levels. Multivariate analyses of ARISA profiles revealed that the microbial communities in the S soil, which contains the highest level of contamination, were different from the other soils and formed a completely separate cluster. A total of 16,657 ribosomal sequences were obtained, with 42–89 % of these sequences belonging to the phylum Proteobacteria. While sequences belonging to Betaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, Bacilli, and Actinobacteria were encountered in all soils, sequences belonging to anaerobic bacteria from the classes Deltaproteobacteria, Clostridia, and Anaerolineae were only detected in the S soil. Sequences belonging to the genus Terriglobus of the class Acidobacteria were only detected in the B3 soil with the lowest level of contamination. Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that oil contamination level was the most determinant factor that explained variations in the microbial communities. We conclude that the exposure to different levels of oil contamination exerts a strong selective pressure on bacterial communities and that desert soils are rich in aerobic and anaerobic bacteria that could potentially contribute to the degradation of hydrocarbons.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RMM, Polerecky L, Al Najjar M, de Beer D (2006) Effect of temperature on photosynthesis, oxygen consumption and sulfide production in an extremely hypersaline cyanobacterial mat. Aquat Microb Ecol 44:21–30
Acosta-Gonzalez A, Rossello-Mora R, Marques S (2013) Characterization of the anaerobic microbial community in oil-polluted subtidal sediments: aromatic biodegradation potential after the prestige oil spill. Environ Microbiol 15:77–92
Aeckersberg F, Bak F, Widdel F (1991) Anaerobic oxidation of saturated-hydrocarbons to CO2 by a new type of sulfate-reducing bacterium. Arch Microbiol 156:5–14
Aeckersberg F, Rainey FA, Widdel F (1998) Growth, natural relationships, cellular fatty acids and metabolic adaptation of sulfate-reducing bacteria that utilize long-chain alkanes under anoxic conditions. Arch Microbiol 170:361–369
Ahn JH, Kim MS, Kim MC, Lim JS, Lee GT, Yun JK, Kim T, Kim T, Ka JO (2006) Analysis of bacterial diversity and community structure in forest soils contaminated with fuel hydrocarbon. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:704–715
Alonso-Gutierrez J, Costa MM, Figueras A, Albaiges J, Vinas M, Solanas AM, Novoa B (2008) Alcanivorax strain detected among the cultured bacterial community from sediments affected by the ‘Prestige’ oil spill. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 362:25–36
Al-Saleh E, Drobiova H, Obuekwe C (2009) Predominant culturable crude oil-degrading bacteria in the coast of Kuwait. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 63:400–406
Andrade LL, Leite DCA, Ferreira EM, Ferreira LQ, Paula GR, Maguire MJ, Hubert CRJ, Peixoto RS, Domingues RMCP, Rosado AS (2012) Microbial diversity and anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation potential in an oil-contaminated mangrove sediment. BMC Microbiol 12:186
Arulazhagan P, Vasudevan N (2011) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a halotolerant bacterial strain Ochrobactrum sp. VA1. Mar Pollut Bull 62:388–394
Arulazhagan P, Vasudevan N, Yeom IT (2010) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon by a halotolerant bacterial consortium isolated from marine environment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7:639–652
Baek KH, Yoon BD, Kim BH, Cho DH, Lee IS, Oh HM, Kim HS (2007) Monitoring of microbial diversity and activity during bioremediation of crude oil-contaminated soil with different treatments. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:67–73
Belyakova EV, Rozanova EP, Borzenkov IA, Tourova TP, Pusheva MA, Lysenko AM, Kolganova TV (2006) The new facultatively chemolithoautotrophic, moderately halophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovermiculus halophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from an oil field. Microbiology 75:161–171
Bhupathiraju VK, McInerney MJ, Woese CR, Tanner RS (1999) Haloanaerobium kushneri sp. nov., an obligately halophilic, anaerobic bacterium from an oil brine. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:953–960
Bhupathiraju VK, Oren A, Sharma PK, Tanner RS, Woese CR, McInerney MJ (1994) Haloanaerobium salsugo sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, anaerobic bacterium from a subterranean brine. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:565–572
Brady NC (1984) The nature and properties of soil. Macmillan Book Co, New York
Cappello S, Caruso G, Zampino D, Monticelli LS, Maimone G, Denaro R, Tripodo B, Troussellier M, Yakimov M, Giuliano L (2007) Microbial community dynamics during assays of harbour oil spill bioremediation: a microscale simulation study. J Appl Microbiol 102:184–194
Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia AM, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6147–6156
Chandankere R, Yao J, Choi MMF, Masakorala K, Chan Y (2013) An efficient biosurfactant-producing and crude-oil emulsifying bacterium Bacillus methylotrophicus USTBA isolated from petroleum reservoir. Biochem Eng J 74:46–53
Clarke KR (1993) Nonparametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145
Cubitto MA, Moran AC, Commendatore M, Chiarello MN, Baldini MD, Sineriz F (2004) Effects of Bacillus subtilis O9 biosurfactant on the bioremediation of crude oil-polluted soils. Biodegradation 15:281–287
Daane LL, Harjono I, Barns SM, Launen LA, Palleroni NJ, Haggblom MM (2002) PAH-degradation by Paenibacillus spp. and description of Paenibacillus naphthalenovorans sp. nov., a naphthalene-degrading bacterium from the rhizosphere of salt marsh plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:131–139
Das R, Tiwary BN (2013) Isolation of a novel strain of Planomicrobium chinense from diesel contaminated soil of tropical environment. J Basic Microbiol 53:723–732
dos Santos HF, Cury JC, do Carmo FL, dos Santos AL, Tiedje J, van Elsas JD, Rosado AS, Peixoto RS (2011) Mangrove bacterial diversity and the impact of oil contamination revealed by pyrosequencing: bacterial proxies for oil pollution. PloS ONE 6
Dowd SE, Callaway TR, Wolcott RD, Sun Y, McKeehan T, Hagevoort RG, Edrington TS (2008) Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle using 16s rDNA bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). BMC Microbiol 8:125
Dowd SF, Sun Y, Wolcott RD, Domingo A, Carroll JA (2008) Bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP) for microbiome studies: bacterial diversity in the ileum of newly weaned Salmonella-infected pigs. Foodborne Pathog Dis 5:459–472
Dowd SE, Zaragoza J, Rodriguez JR, Oliver MJ, Payton PR (2005) Windows.net network distributed basic local alignment search toolkit (W.ND-BLAST). BMC Bioinform 6:93
Eichorst SA, Breznak JA, Schmidt TM (2007) Isolation and characterization of soil bacteria that define Terriglobus gen. nov., in the phylum Acidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2708–2717
Gauthier E, Deziel E, Villemur R, Juteau P, Lepine F, Beaudet R (2003) Initial characterization of new bacteria degrading high-molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons isolated from a 2-year enrichment in a two-liquid-phase culture system. J Appl Microbiol 94:301–311
Ghosal D, Chakraborty J, Khara P, Dutta TK (2010) Degradation of phenanthrene via meta-cleavage of 2-hydroxy-1-naphthoic acid by Ochrobactrum sp. strain PWTJD. FEMS Microbiol Lett 313:103–110
Golby S, Ceri H, Gieg LM, Chatterjee I, Marques LLR, Turner RJ (2012) Evaluation of microbial biofilm communities from an Alberta oil sands tailings pond. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 79:240–250
Hamamura N, Olson SH, Ward DM, Inskeep WP (2006) Microbial population dynamics associated with crude-oil biodegradation in diverse soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6316–6324
Hanson KG, Nigam A, Kapadia M, Desai AJ (1997) Bioremediation of crude oil contamination with Acinetobacter sp. A3. Curr Microbiol 35:191–193
Hassanshahian M, Emtiazi G, Cappello S (2012) Isolation and characterization of crude-oil-degrading bacteria from the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 64:7–12
Hernandez-Raquet G, Budzinski H, Caumette P, Dabert P, Le Menach K (2006) Molecular diversity studies of bacterial communities of oil polluted microbial mats from the Etang de Berre (France). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:550–562
Ijah UJJ, Ukpe LI (1992) Biodegradation of crude oil by Bacillus strains 28a and 61b isolated from oil spilled soil. Waste Manag 12:55–60
Ilori MO, Amund D, Robinson CK (2000) Ultrastructure of two oil-degrading bacteria isolated from the tropical soil environment. Folia Microbiol 45:259–262
Jaekel U, Musat N, Adam B, Kuypers M, Grundmann O, Musat F (2013) Anaerobic degradation of propane and butane by sulfate-reducing bacteria enriched from marine hydrocarbon cold seeps. ISME J 7:885–895
Jin S, Fallgren PH, Bilgin AA, Morris JM, Barnes PW (2007) Bioremediation of benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes in groundwater under iron-amended, sulfate-reducing conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:249–253
Juck D, Charles T, Whyte LG, Greer CW (2000) Polyphasic microbial community analysis of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils from two northern Canadian communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 33:241–249
Jung SW, Park JS, Kown OY, Kang JN, Shim WJ, Kim YO (2010) Effects of crude oil on marine microbial communities in short term outdoor microcosms. J Microbiol 48:594–600
Kertesz M, Kawasaki A (2010) Hydrocarbon-degrading Sphingomonads: Sphingomonas, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis. In: Timmis K (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 1693–1705
Kleikemper J, Schroth MH, Sigler WV, Schmucki M, Bernasconi SM, Zeyer J (2002) Activity and diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1516–1523
Klute A (1986) Methods of soil analysis. Amer Soc Agron, Medison
Kostka JE, Prakash O, Overholt WA, Green SJ, Freyer G, Canion A, Delgardio J, Norton N, Hazen TC, Huettel M (2011) Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria and the bacterial community response in Gulf of Mexico beach sands impacted by the deepwater horizon oil spill. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:7962–7974
L’Haridon S, Miroshnichenko ML, Hippe H, Fardeau ML, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Stackebrandt E, Jeanthon C (2002) Petrotoga olearia sp. nov. and Petrotoga sibirica sp. nov., two thermophilic bacteria isolated from a continental petroleum reservoir in Western Siberia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1715–1722
La Montagne MG, Leifer I, Bergmann S, Van De Werfhorst LC, Holden PA (2004) Bacterial diversity in marine hydrocarbon seep sediments. Environ Microbiol 6:799–808
Lafortune I, Juteau P, Deziel E, Lepine F, Beaudet R, Villemur R (2009) Bacterial diversity of a consortium degrading high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a two-liquid phase biosystem. Microb Ecol 57:455–468
LaRoe SL, Wang B, Han JI (2010) Isolation and characterization of a novel polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium, Sphingopyxis sp strain M2R2, capable of passive spreading motility through soil. Environ Eng Sci 27:505–512
Lee E-H, Lee SH, Cho K-S (2011) Bacterial diversity dynamics in a long-term petroleum-contaminated soil. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 46:281–290
Liang Y, Li G, Van Nostrand JD, He Z, Wu L, Den Y, Zhang X, Zhou J (2009) Microarray-based analysis of microbial functional diversity along an oil contamination gradient in oil field. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:324–333
Lien T, Madsen M, Rainey FA, Birkeland NK (1998) Petrotoga mobilis sp. nov., from a north sea oil-production well. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:1007–1013
Liu R, Zhang Y, Ding R, Li D, Gao Y, Yang M (2009) Comparison of archaeal and bacterial community structures in heavily oil-contaminated and pristine soils. J Biosci Bioeng 108:400–407
Lovley DR (1997) Potential for anaerobic bioremediation of BTEX in petroleum-contaminated aquifers. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 18:75–81
Maila MP, Randima P, Dronen K, Cloete TE (2006) Soil microbial communities: influence of geographic location and hydrocarbon pollutants. Soil Biol Biochem 38:303–310
Mannisto MK, Rawat S, Starovoytov V, Haeggblom MM (2011) Terriglobus saanensis sp. nov., an acidobacterium isolated from tundra soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1823–1828
Mara K, Decorosi F, Viti C, Giovannetti L, Papaleo MC, Maida I, Perrin E, Fondi M, Vaneechoutte M, Nemec A, van den Barselaar M, Dijkshoom L, Fani R (2012) Molecular and phenotypic characterization of Acinetobacter strains able to degrade diesel fuel. Res Microbiol 163:161–172
Militon C, Boucher D, Vachelard C, Perchet G, Barra V, Troquet J, Peyretaillade E, Peyret P (2010) Bacterial community changes during bioremediation of aliphatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:669–681
Miralles G, Grossi V, Acquaviva M, Duran R, Bertrand JC, Cuny P (2007) Alkane biodegradation and dynamics of phylogenetic subgroups of sulfate-reducing bacteria in an anoxic coastal marine sediment artificially contaminated with oil. Chemosphere 68:1327–1334
Miralles G, Nerini D, Mante C, Acquaviva M, Doumenq P, Michotey V, Nazaret S, Bertrand JC, Cuny P (2007) Effects of spilled oil on bacterial communities of mediterranean coastal anoxic sediments chronically subjected to oil hydrocarbon contamination. Microb Ecol 54:646–661
Miranda-Tello E, Fardeau ML, Thomas P, Ramirez F, Casalot L, Cayol JL, Garcia JL, Ollivier B (2004) Petrotoga mexicana sp. nov., a novel thermophilic, anaerobic and xylanolytic bacterium isolated from an oil-producing well in the Gulf of Mexico. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:169–174
Muckian L, Grant R, Doyle E, Clipson N (2007) Bacterial community structure in soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 68:1535–1541
Najafi AR, Rahimpour MR, Jahanmiri AH, Roostaazad R, Arabian D, Soleimani M, Jamshidnejad Z (2011) Interactive optimization of biosurfactant production by Paenibacillus alvei ARN63 isolated from an Iranian oil well. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 82:33–39
Noble IR, Gitay H (1996) Desert in changing climate: impact. In: Watson RT, Zinyowera MC, Moss RH, Dokken DJ (eds) Climate change 1995: impact, adaptation and migration of climate change: scientific-technical analysis. Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, pp 159–165
Noy-Meir I (1973) Desert ecosystems: environment and producers. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 4:25–51
Orcutt BN, Joye SB, Kleindienst S, Knittel K, Ramette A, Reitz A, Samarkin V, Treude T, Boetius A (2010) Impact of natural oil and higher hydrocarbons on microbial diversity, distribution, and activity in Gulf of Mexico cold-seep sediments. Deep Sea Res Part 2 Top Stud Oceanogr 57:2008–2021
Paisse S, Coulon F, Goni-Urriza M, Peperzak L, McGenity TJ, Duran R (2008) Structure of bacterial communities along a hydrocarbon contamination gradient in a coastal sediment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:295–305
Paisse S, Goni-Urriza M, Coulon F, Duran R (2010) How a bacterial community originating from a contaminated coastal sediment responds to an oil input. Microb Ecol 60:394–405
Parales RE (2010) Hydrocarbon degradation by Betaproteobacteria. In: Timmis K (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 1716–1721
Perez-de-Mora A, Engel M, Schloter M (2011) Abundance and diversity of n-alkane-degrading bacteria in a forest soil co-contaminated with hydrocarbons and metals: a molecular study on alkB homologous genes. Microb Ecol 62:959–972
Perfumo A, Smyth T, Marchant R, Banat I (2010) Production and roles of biosurfactants and bioemulsifiers in accessing hydrophobic substrates. In: Timmis K (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 1501–1512
Peters F, Rother M, Boll M (2004) Selenocysteine-containing proteins in anaerobic benzoate metabolism of Desulfococcus multivorans. J Bacteriol 186:2156–2163
Prince R, Gramain A, McGenity T (2010) Prokaryotic hydrocarbon degraders. In: Timmis K (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 1672–1692
Qin X, Tang JC, Li DS, Zhang QM (2012) Effect of salinity on the bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in a saline-alkaline soil. Lett Appl Microbiol 55:210–217
Radwan S (2008) Microbiology of oil-polluted contaminated desert soils and coastal areas in the Arabian Gulf Region. In: Dion P, Nautiyal CS (eds) Microbiology of extreme soils. Soil biology 13. Springer, Berlin, pp 275–298
Radwan S (2009) Phytoremediation for oily desert soils. In: Singh A, Kuhad RC, Ward OP (eds) Advances in applied bioremediation. Springer, Berlin, pp 279–298
Radwan SS, Al-Hasan RH (2000) Oil pollution and cyanobacteria. In: Whitton BA, Potts M (eds) The ecology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 307–319
Ramette A (2007) Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:142–160
Ramette A (2009) Quantitative community fingerprinting methods for estimating the abundance of operational taxonomic units in natural microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2495–2505
Ravot G, Magot M, Ollivier B, Patel BKC, Ageron E, Grimont PAD, Thomas P, Garcica JL (1997) Haloanaerobium congolense sp. nov., an anaerobic, moderately halophilic, thiosulfate- and sulfur-reducing bacterium from an African oil field. FEMS Microbiol Lett 147:81–88
Rawat SR, Mannisto MK, Starovoytov V, Goodwin L, Nolan M, Hauser L, Land M, Davenport KW, Woyke T, Haggblom MM (2012) Complete genome sequence of Terriglobus saanensis type strain SP1PR4(T), an Acidobacteria from tundra soil. Stand. Genom Sci 7:59–69
Ribeiro H, Mucha AP, Almeida CMR, Bordalo AA (2013) Bacterial community response to petroleum contamination and nutrient addition in sediments from a temperate salt marsh. Sci Total Environ 458:568–576
Roling WFM, Milner MG, Jones DM, Lee K, Daniel F, Swannell RJP, Head IM (2002) Robust hydrocarbon degradation and dynamics of bacterial communities during nutrient-enhanced oil spill bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5537–5548
Saadoun I, Mohammad MJ, Hameed KM, Shawaqfah MA (2008) Microbial populations of crude oil spill polluted soils at the Jordan-Iraq desert (the Badia region). Braz J Microbiol 39:453–456
Saul DJ, Aislabie JM, Brown CE, Harris L, Foght JM (2005) Hydrocarbon contamination changes the bacterial diversity of soil from around Scott base, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:141–155
Sherry A, Gray ND, Ditchfield AK, Aitken CM, Jones DM, Roeling WFM, Hallmann C, Larter SR, Bowler BFJ, Head IM (2013) Anaerobic biodegradation of crude oil under sulphate-reducing conditions leads to only modest enrichment of recognized sulphate-reducing taxa. Int Biodeterior Biodegradradation 81:105–113
Singleton DR, Ramirez LG, Aitken MD (2009) Characterization of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation gene cluster in a phenanthrene-degrading Acidovorax strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2613–2620
So CM, Young LY (1999) Isolation and characterization of a sulfate-reducing bacterium that anaerobically degrades alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2969–2976
Stieb M, Schink B (1989) Anaerobic degradation of isobutyrate by methanogenic enrichment cultures and by a Desulfococcus multivorans strain. Arch Microbiol 151:126–132
Sun Y, Cai Y, Liu L, Yu F, Farrell ML, McKendree W, Farmerie W (2009) ESPRIT: estimating species richness using large collections of 16S rRNA pyrosequences. Nucleic Acids Res 37
Sutton NB, Maphosa F, Morillo JA, Abu Al-Soud W, Langenhoff AAM, Grotenhuis T, Rijnaarts HHM, Smidt H (2013) Impact of long-term diesel contamination on soil microbial community structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:619–630
Vazquez Nunez E, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Alcantara-Hernandez RJ, Navarro-Noya YE, Luna-Guido M, Marsch R, Dendooven L (2012) Modifications of bacterial populations in anthracene contaminated soil. Appl Soil Ecol 61:113–126
Vila J, Maria Nieto J, Mertens J, Springael D, Grifoll M (2010) Microbial community structure of a heavy fuel oil-degrading marine consortium: linking microbial dynamics with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon utilization. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:349–362
Vinas M, Sabate J, Espuny MJ, Solanas AM (2005) Bacterial community dynamics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation during bioremediation of heavily creosote-contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7008–7018
Volossiouk T, Robb EJ, Nazar RN (1995) Direct DNA extraction for PCR-mediated assays of soil organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3972–3976
Wang YF, Tam NFY (2011) Microbial community dynamics and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in polluted marine sediments in Hong Kong. Mar Pollut Bull 63:424–430
Weisman WH (1998) Total petroleum hydrocarbon criteria working group: a risk-based approach for the management of total petroleum hydrocarbons in soil. J Soil Contamination 7:1–15
Winderl C, Anneser B, Griebler C, Meckenstock RU, Lueders T (2008) Depth-resolved quantification of anaerobic toluene degraders and aquifer microbial community patterns in distinct redox zones of a tar oil contaminant plume. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:792–801
Yamane K, Maki H, Nakayama T, Nakajima T, Nomura N, Uchiyama H, Kitaoka M (2008) Diversity and similarity of microbial communities in petroleum crude oils produced in Asia. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:2831–2839
Yang S, Wen X, Jin H, Wu Q (2012) Pyrosequencing investigation into the bacterial community in permafrost soils along the China-Russia crude oil pipeline (CRCOP). PLoS ONE 7
Yoshida N, Yagi K, Sato D, Watanabe N, Kuroishi T, Nishimoto K, Yanagida A, Katsuragi T, Kanagawa T, Kurane R, Tani Y (2005) Bacterial communities in petroleum oil in stockpiles. J Biosci Bioeng 99:143–149
Zhang DC, Liu HC, Xin YH, Zhou YG, Schinner F, Margesin R (2010) Sphingopyxis bauzanensis sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2618–2622
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their great thanks to Mr. Abdulla Al-Harthy from Petroleum Development of Oman (PDO) for the organization of field trips to the sampling site and for his cooperation throughout the project. Mr. Jamal Al-Sabahi is also thanked for his assistance in the chemical analysis. This research was financially supported by The Research Council (TRC) of Oman (grant RC/SCI/BIOL/11/01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
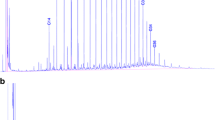
Figure 1S
GC/MS chromatograms showing the concentrations of crude oil fractions in the five studied oil-polluted desert soils performed directly after sampling (A) and concentrations (in ppm) of individual alkanes (C10-C30) in each sample as detected by GC analysis (B). (DOC 347 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abed, R.M.M., Al-Kindi, S. & Al-Kharusi, S. Diversity of Bacterial Communities Along a Petroleum Contamination Gradient in Desert Soils. Microb Ecol 69, 95–105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0475-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0475-5