Abstract
Purpose
A systematic review was conducted to answer the following questions: (1) Does kinematically aligned (KA) total knee arthroplasty (TKA) achieve clinical outcomes comparable to those of mechanically aligned (MA) TKA? (2) How do the limb, knee, and component alignments differ between KA and MA TKA? (3) How is joint line orientation angle (JLOA) changed from the native knee in KA TKA compared to that in MA TKA?
Methods
Nine full-text articles in English that reported the clinical and radiological outcomes of KA TKA were included. Five studies had a control group of patients who underwent MA TKA. Data on patient demographics, clinical scores, and radiological results were extracted. There were two level I, one level II, three level III, and three level IV studies. Six of the nine studies used patient-specific instrumentation, one study used computer navigation, and two studies used manual instrumentation.
Results
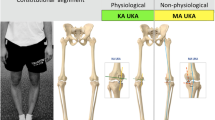
The clinical outcomes of KA TKA were comparable or superior to those of MA TKA with a minimum 2-year follow-up. Limb and knee alignment in KA TKA was similar to those in MA TKA, and component alignment showed slightly more varus in the tibial component and slightly more valgus in the femoral component. The JLOA in KA TKA was relatively parallel to the floor compared to that in the native knee and not oblique (medial side up and lateral side down) compared to that in MA TKA. The implant survivorship and complication rate of the KA TKA were similar to those of the MA TKA.
Conclusion
Similar or better clinical outcomes were produced by using a KA TKA at early-term follow-up and the component alignment differed from that of MA TKA. KA TKA seemed to restore function without catastrophic failure regardless of the alignment category up to midterm follow-up. The JLOA in KA TKA was relatively parallel to the floor similar to the native knee compared to that in MA TKA. The present review of nine published studies suggests that relatively new kinematic alignment is an acceptable and alternative alignment to mechanical alignment, which is better understood. Further validation of these findings requires more randomized clinical trials with longer follow-up.
Level of evidence
Level II.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Buzzi R (1988) Posteriorly stabilised total-condylar knee replacement. Three to eight years’ follow-up of 85 knees. J Bone Joint Surg Br 70:211–216
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O’Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schunemann HJ, Edejer T, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW Jr, Zaza S (2004) Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 328:1490
Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J (2012) The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:45–53
Benjamin J (2006) Component alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect 55:405–412
Bonner TJ, Eardley WG, Patterson P, Gregg PJ (2011) The effect of post-operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow-up of 15 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:1217–1222
Calliess T, Bauer K, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Windhagen H, Budde S, Ettinger M (2016) PSI kinematic versus non-PSI mechanical alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-016-4136-8
Dossett HG, Estrada NA, Swartz GJ, LeFevre GW, Kwasman BG (2014) A randomised controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee replacements: two-year clinical results. Bone Joint J 96-B:907–913
Eckhoff DG, Bach JM, Spitzer VM, Reinig KD, Bagur MM, Baldini TH, Flannery NM (2005) Three-dimensional mechanics, kinematics, and morphology of the knee viewed in virtual reality. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(Suppl 2):71–80
Freeman MA, Pinskerova V (2005) The movement of the normal tibio-femoral joint. J Biomech 38:197–208
Gu Y, Roth JD, Howell SM, Hull ML (2014) How frequently do four methods for mechanically aligning a total knee arthroplasty cause collateral ligament imbalance and change alignment from normal in white patients? AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96:e101
Hancock CW, Winston MJ, Bach JM, Davidson BS, Eckhoff DG (2013) Cylindrical axis, not epicondyles, approximates perpendicular to knee axes. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:2278–2283
Hollister AM, Jatana S, Singh AK, Sullivan WW, Lupichuk AG (1993) The axes of rotation of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290:259–268
Howell SM, Howell SJ, Kuznik KT, Cohen J, Hull ML (2013) Does a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty restore function without failure regardless of alignment category? Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:1000–1007
Howell SM, Papadopoulos S, Kuznik K, Ghaly LR, Hull ML (2015) Does varus alignment adversely affect implant survival and function six years after kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty? Int Orthop 39:2117–2124
Howell SM, Papadopoulos S, Kuznik KT, Hull ML (2013) Accurate alignment and high function after kinematically aligned TKA performed with generic instruments. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2271–2280
Hutt J, Massé V, Lavigne M, Vendittoli PA (2016) Functional joint line obliquity after kinematic total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 40:29–34
Jenny JY, Boeri C, Ballonzoli L (2005) Coronal alignment of the lower limb. Acta Orthop 76:403–407
Ji HM, Han J, Jin DS, Seo H, Won YY (2016) Kinematically aligned TKA can align knee joint line to horizontal. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:2436–2441
Li X, Yin L, Chen ZY, Zhu L, Wang HL, Chen W, Yang G, Zhang YZ (2014) The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: grading the evidence through an updated meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24:973–986
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S (2011) Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:3443–3450
Matziolis G, Adam J, Perka C (2010) Varus malalignment has no influence on clinical outcome in midterm follow-up after total knee replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:1487–1491
McGinn T, Wyer PC, Newman TB, Keitz S, Leipzig R, For GG (2004) Tips for learners of evidence-based medicine: 3. Measures of observer variability (kappa statistic). CMAJ 171:1369–1373
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62:1006–1012
Mugnai R, Digennaro V, Ensini A, Leardini A, Catani F (2014) Can TKA design affect the clinical outcome? Comparison between two guided-motion systems. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:581–589
Nunley RM, Ellison BS, Zhu J, Ruh EL, Howell SM, Barrack RL (2012) Do patient-specific guides improve coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:895–902
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA (2011) The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:1588–1596
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Roth JD, Howell SM, Hull ML (2015) Native Knee Laxities at 0 degrees, 45 degrees, and 90 degrees of Flexion and Their Relationship to the Goal of the Gap-Balancing Alignment Method of Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97:1678–1684
Thienpont E, Bellemans J, Victor J, Becker R (2013) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty, still more questions than answers. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2191–2193
Thienpont E, Cornu O, Bellemans J, Victor J (2015) Current opinions about coronal plane alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a survey article. Acta Orthop Belg 81:471–477
Thienpont E, Schwab PE, Fennema P (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis of patient-specific instrumentation for improving alignment of the components in total knee replacement. Bone Joint J 96-B:1052–1061
Vandekerckhove PJ, Lanting B, Bellemans J, Victor J, MacDonald S (2016) The current role of coronal plane alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty in a preoperative varus aligned population: an evidence based review. Acta Orthop Belg 82:129–142
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J (2013) Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2325–2330
Victor JM, Bassens D, Bellemans J, Gursu S, Dhollander AA, Verdonk PC (2014) Constitutional varus does not affect joint line orientation in the coronal plane. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:98–104
Young SW, Walker ML, Bayan A, Briant-Evans T, Pavlou P, Farrington B (2016) The Chitranjan S. Ranawat Award: no Difference in 2-year Functional Outcomes Using Kinematic versus Mechanical Alignment in TKA: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 475:9–20
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Funding
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
This is systematic review. Therefore, IRB was waived.
Informed consent
None.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.S., Howell, S.M., Won, YY. et al. Kinematic alignment is a possible alternative to mechanical alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25, 3467–3479 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4558-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4558-y