Abstract
Background
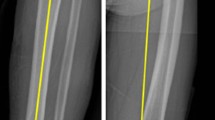
Postoperative varus alignment has been associated with lower IKS scores and increased failure rates. Appropriate positioning of TKA components therefore is a key concern of surgeons. However, obtaining neutral alignment can be challenging in patients with substantial preoperative varus deformity and it is unclear whether residual deformity influences revision rates.
Questions/purposes
We asked: (1) in patients with preoperative varus deformities, does residual postoperative varus limb alignment lead to increased revision rates or lower IKS scores compared with correction to neutral alignment, (2) does placing the tibial component in varus alignment lead to increased revision rates and lower IKS scores, (3) does femoral component alignment affect revision rates and IKS scores, and (4) do these findings change in patients with at least 10° varus alignment preoperatively?
Patients and Methods
From a prospective database, we identified 553 patients undergoing TKAs for varus osteoarthritis. Patients were divided into those with residual postoperative varus and those with neutral postoperative alignment. Revision rates and International Knee Society (IKS) scores were compared between the two groups and assessed based on postoperative component alignment. Survival analysis was conducted with revision as the endpoint. The analysis was repeated in a subgroup of patients with at least 10° preoperative varus. Minimum followup was 2 years (median, 4.7 years; range, 2–19.8 years).
Results
The two groups had similar survival rates to 10 years and similar IKS scores. Varus tibial component alignment and valgus femoral component alignment were associated with lower mean scores. Revision rates and scores were similar in a subgroup of patients with substantial preoperative varus.
Conclusions
Our data suggest residual postoperative varus deformity after TKA does not increase survival rates at medium-term in patients with preoperative varus deformities, providing tibial component varus is avoided. Tibial component varus negatively influences IKS score.
Level of Evidence
Level III, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty: correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;173:178–183.
Bellemans J, Vandenneucker H, Vanlauwe J, Victor J. The influence of coronal plane deformity on mediolateral ligament status: an observational study in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:152–156.
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, Faris PM, Keating EM, Redelman R, Faris GW, Davis KE. Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;428:26–34.
Bonutti PM, Dethmers D, Ulrich SD, Seyler TM, Mont MA. Computer navigation-assisted versus minimally invasive TKA: benefits and drawbacks. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:2756–2762.
Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Brouwer KH, Verhaar JA. Pitfalls in determining knee alignment: a radiographic cadaver study. J Knee Surg. 2007;20:210–215.
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD. Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:560–569.
Cooke TD, Sled EA, Scudamore RA. Frontal plane knee alignment: a call for standardized measurement. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:1796–1801.
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:39–43.
Heyse TJ, Decking R, Davis J, Boettner F, Laskin RS. Varus gonarthrosis predisposes to varus malalignment in TKA. HSS J. 2009;5:143–148.
Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, Mestriner LA. Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;192:13–22.
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;248:13–14.
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:709–714.
Kamat YD, Aurakzai KM, Adhikari AR, Matthews D, Kalairajah Y, Field RE. Does computer navigation in total knee arthroplasty improve patient outcome at midterm follow-up? Int Orthop. 2009;33:1567–1570.
Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53:457–481.
Lewallen DG, Bryan RS, Peterson LF. Polycentric total knee arthroplasty: a ten-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66:1211–1218.
Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp N, Scaddan M, Beaver R. Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:570–578.
Lonner JH, Laird MT, Stuchin SA. Effect of rotation and knee flexion on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;331:102–106.
Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:77–79.
Marx RG, Grimm P, Lillemoe KA, Robertson CM, Ayeni OR, Lyman S, Bogner EA, Pavlov H. Reliability of lower extremity alignment measurement using radiographs and PACS. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011 March 23. [Epub ahead of print]
Moreland JR. Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;226:49–64.
Morgan SS, Bonshahi A, Pradhan N, Gregory A, Gambhir A, Porter ML. The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008;32:639–642.
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:2143–2149.
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB. Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement: its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;299:153–156.
Sampath SA, Voon SH, Sangster M, Davies H. The statistical relationship between varus deformity, surgeon’s experience, BMI and tourniquet time for computer assisted total knee replacements. Knee. 2009;16:121–124.
Schroer WC, Calvert GT, Diesfeld PJ, Reedy ME, LeMarr AR. Effects of increased surgical volume on total knee arthroplasty complications. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:61–67.
Siu D, Cooke TD, Broekhoven LD, Lam M, Fisher B, Saunders G, Challis TW. A standardized technique for lower limb radiography: practice, applications, and error analysis. Invest Radiol. 1991;26:71–77.
Tew M, Waugh W. Tibiofemoral alignment and the results of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985;67:551–556.
Verdonk PC, Pernin J, Pinaroli A, Ait Si Selmi T, Neyret P. Soft tissue balancing in varus total knee arthroplasty: an algorithmic approach. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17:660–666.
Yaffe MA, Koo SS, Stulberg SD. Radiographic and navigation measurements of TKA limb alignment do not correlate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:2736–2744.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Philippe Neyret of the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hôpital de la Croix-Rousse, Centre Albert Trillat, Lyon, France, for guidance and assistance with this project. We also thank Frédéric Marcelli and William H. Beasley for assistance with statistics and data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more authors (RAM, SL, ES) have received funding from Tornier, Inc. GD has received funding from Tornier, Inc. and DePuy, Inc. Each remaining author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
This study was performed at Hôpital de la Croix-Rousse, Centre Albert Trillat, Lyon, France.
About this article
Cite this article
Magnussen, R.A., Weppe, F., Demey, G. et al. Residual Varus Alignment does not Compromise Results of TKAs in Patients with Preoperative Varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469, 3443–3450 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1988-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1988-6