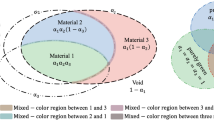
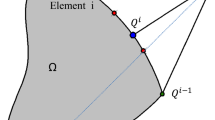
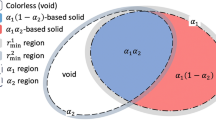
Abstract
This paper presents an immersed boundary approach for level set topology optimization considering stress constraints. A constraint agglomeration technique is used to combine the local stress constraints into one global constraint. The structural response is predicted by the eXtended Finite Element Method. A Heaviside enrichment strategy is used to model strong and weak discontinuities with great ease of implementation. This work focuses on low-order finite elements, which given their simplicity are the most popular choice of interpolation for topology optimization problems. The predicted stresses strongly depend on the intersection configuration of the elements and are prone to significant errors. Robust computation of stresses, regardless of the interface position, is essential for reliable stress constraint prediction and sensitivities. This study adopts a recently proposed fictitious domain approach for penalization of displacement gradients across element faces surrounding the material interface. In addition, a novel XFEM informed stabilization scheme is proposed for robust computation of stresses. Through numerical studies the penalized spatial gradients combined with the stabilization scheme is shown to improve prediction of stresses along the material interface. The proposed approach is applied to the benchmark topology optimization problem of an L-shaped beam in two and three dimensions using material-void and material-material problem setups. Linear and hyperelastic materials are considered. The stress constraints are shown to be efficient in eliminating regions with high stress concentration in all scenarios considered.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Amir O (2017) Stress-constrained continuum topology optimization: a new approach based on elasto-plasticity. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(5):1797–1818
Annavarapu C, Hautefeuille M, Dolbow JE (2012) A robust nitsche’s formulation for interface problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 225–228:44–54
Babuška I, Melenk JM (1997) The partition of unity method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 40(4):727–758
Bendsøe M, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bruggi M, Duysinx P (2012) Topology optimization for minimum weight with compliance and stress constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(3):369–384
Burger M, Hackl B, Ring W (2004) Incorporating topological derivatives into level set methods. J Comput Phys 194(1):344– 362
Burman E, Hansbo P (2014) Fictitious domain methods using cut elements: III. a stabilized nitsche method for stokes’ problem. ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis 48(3):859–874
Cai S, Zhang W, Zhu J, Gao T (2014) Stress constrained shape and topology optimization with fixed mesh: A B-spline finite cell method combined with level set function. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 278:361–387
Cheng G, Guo X (1997) ε-relaxed approach in structural topology optimization. Structural Optimization 13(4):258–266
Cheng G, Jiang Z (1992) Study on topology optimization with stress constraints. Eng Optim 20(2):129–148
Coffin P, Maute K (2016) A level-set method for steady-state and transient natural convection problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(5):1047–1067
Dijk N, Maute K, Langelaar M, Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):437–472
Duysinx P, Bendsøe MP (1998) Topology optimization of continuum structures with local stress constraints. Int J Numer Methods Eng 43(8):1453–1478
Duysinx P, Sigmund O (1998) New developments in handling stress constraints in optimal material distributions. In: Proceedings of 7th AIAA/USAF/NASA/ISSMO symposium on Multidisciplinary Design Optimization, AIAA
Duysinx P, Van Miegroet L, Jacobs T, Fleury C (2006) Generalized shape optimization using x-FEM and level set methods. In: IUTAM symposium on topological design optimization of structures, machines and materials. Springer, Netherlands, pp 23–32
Fries T, Belytschko T (2010) The extended/generalized finite element method: an overview of the method and its applications. Int J Numer Methods Eng 84(3):253–304
Guo X, Zhang W, Wang MY, Wei P (2011) Stress-related topology optimization via level set approach. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(47–48):3439–3452
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhong W (2014) Stress-related topology optimization of continuum structures involving multi-phase materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 268:632–655
Haber R, Jog C, Bendsøe M (1996) A new approach to variable-topology shape design using a constraint on perimeter. Structural Optimization 11(1):1–12
Hansbo A, Hansbo P (2004) A finite element method for the simulation of strong and weak discontinuities in solid mechanics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(33–35):3523–3540
Holmberg E, Torstenfelt B, Klarbring A (2014) Fatigue constrained topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50(2):207–219
Holzapfel GA (2000) Nonlinear solid mechanics. Wiley, West Sussex
James KA, Waisman H (2014) Failure mitigation in optimal topology design using a coupled nonlinear continuum damage model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 268:614–631
Jenkins N, Maute K (2015) Level set topology optimization of stationary fluid-structure interaction problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52(1):179–195
Kreissl S, Maute K (2012) Levelset based fluid topology optimization using the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(3):311–326
Lang C, Sharma A, Doostan A, Maute K (2015) Heaviside enriched extended stochastic fem for problems with uncertain material interfaces. Comput Mech 56(5):753–767
Le C, Norato J, Bruns T, Ha C, Tortorelli D (2010) Stress-based topology optimization for continua. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(4):605–620
Makhija D, Maute K (2014) Numerical instabilities in level set topology optimization with the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(2):185–197
Moës N, Dolbow J, Belytschko T (1999) A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing. Int J Numer Methods Eng 46(1):131–150
Noël L, Duysinx P (2017) Shape optimization of microstructural designs subject to local stress constraints within an xfem-level set framework. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(6):2323–2338
Osher S, Santosa F (2001) Level set methods for optimization problems involving geometry and constraints: i. frequencies of a two-density inhomogeneous drum. J Comput Phys 171(1):272–288
Osher SJ, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79(1):12–49
París J, Navarrina F, Colominas I, Casteleiro M (2008) Topology optimization of continuum structures with local and global stress constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 39(4):419–437
París J, Navarrina F, Colominas I, Casteleiro M (2010) Block aggregation of stress constraints in topology optimization of structures. Adv Eng Softw 41(3):433–441
Polajnar M, Kosel F, Drazumeric R (2017) Structural optimization using global stress-deviation objective function via the level-set method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(1):91–104
Sethian J, Wiegmann A (2000) Structural boundary design via level set and immersed interface methods. J Comput Phys 163(2):489–528
Sharma A, Villanueva H, Maute K (2017) On shape sensitivities with heaviside-enriched xfem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(2):385–408
Stenberg R (1995) On some techniques for approximating boundary conditions in the finite element method. J Comput Appl Math 63(1-3):139–148
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J Optim 12(2):555–573
Terada K, Asai M, Yamagishi M (2003) Finite cover method for linear and non-linear analyses of heterogeneous solids. Int J Numer Methods Eng 58(9):1321–1346
Van Miegroet L, Duysinx P (2007) Stress concentration minimization of 2D filets using x-FEM and level set description. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4-5):425–438
Verbart A, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2016) Damage approach: a new method for topology optimization with local stress constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(5):1081–1098
Villanueva CH, Maute K (2014) Density and level set-XFEM schemes for topology optimization of 3-D structures. Comput Mech 54(1):133–150
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(1-2):227–246
Yang RJ, Chen CJ (1996) Stress-based topology optimization. Structural Optimization 12(2-3):98–105
Zhang WS, Guo X, Wang MY, Wei P (2013) Optimal topology design of continuum structures with stress concentration alleviation via level set method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 93(9):942– 959
Zienkiewicz OC, Zhu JZ (1992) The superconvergent patch recovery and a posteriori error estimates. part 1: The recovery technique. Int J Numer Methods Eng 33(7):1331–1364
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Science Foundation under Grant EFRI-ODISSEI 1240374 and of the US Air Force of Scientific Research under Grant FA9550-16-1-0169. The second author also acknowledges the support of the National Science Foundation under Grant CMMI 1463287. The opinions and conclusions presented in this paper are those the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsoring organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Maute, K. Stress-based topology optimization using spatial gradient stabilized XFEM. Struct Multidisc Optim 57, 17–38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1833-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1833-y