Abstract
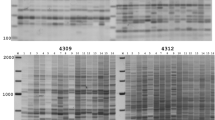
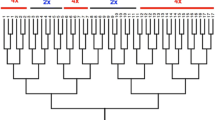
Fast and efficient DNA fingerprinting of crop cultivars and individuals is frequently used in both theoretical population genetics and in practical breeding. Numerous DNA marker technologies exist and the ratio of speed, cost and accuracy are of importance. Therefore even in species where highly accurate and polymorphic marker systems are available, such as microsatellite SSR (simple sequence repeats), also alternative methods may be of interest. Thanks to their high abundance and ubiquity, temporary mobile retrotransposable elements come into recent focus. Their properties, such as genome wide distribution and well-defined origin of individual insertions by descent, predetermine them for use as molecular markers. In this study, severalTy3-gypsy type retrotransposons have been developed and adopted for the inter-retrotransposon amplified polymorphism (IRAP) method, which is suitable for fast and efficient pea cultivar fingerprinting. The method can easily distinguish even between genetically closely related pea cultivars and provide high polymorphic information content (PIC) in a single PCR analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baranger A, Aubert G, Arnau G, Lainé AL, Deniot G, Potier J, et al. 2004. Genetic diversity withinPisum sativum using protein- and PCR-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 108: 1309–1321.
Batzer MA, Deininger PL, 2002.Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nature Rev Genet 3: 370–379.
Baumel A, Ainouche M, Kalendar R, Schulman AH, 2002. Inter-retrotransposon amplified polymorphism (IRAP), and retrotransposon-microsatellite amplified polymorphism (REMAP) in populations of the young allopolyploid speciesSpartina angelica Hubbard (Poaceae). Mol Biol Evol 19: 1218–1227.
Becher SA, Steinmetz K, Weising K, Boury S, Peltier D, 2000. Microsatellites for cultivar identification inPelargonium. Theor Appl Genet 101: 643–651.
Boyko E, Kalendar R, Korzun V, Gill B, Schulman AH, 2002. Combined mapping ofAegilops tauschii by retrotransposon, microsatellite, and gene markers. Plant Mol Biol 48: 767–790.
Burstin J, Deniot G, Potier J, Weinachter C, Aubert G, Baranger A, 2001. Microsatellite polymorphism inPisum sativum. Plant Breeding 120: 311–317.
Cooke RJ, 1999. Modern methods for cultivar verification and the transgenic plant challenge. Seed Sci and Technol 27: 669–680.
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL, 1987. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19: 11–15.
Ellis THN, Poyser SJ, Knox MR, Vershinin AV, Ambrose MJ, 1998. Polymorphism of insertion sites ofTy1-copia class retrotransposons and its use for linkage and diversity analysis in pea. Mol Gen Genet 260: 9–19.
Flavell AJ, Bolshakov VN, Booth A, Jing R, Russell J, Ellis THN, Isaac P, 2003. A microarray-based high throughput molecular marker genotyping method: the tagged microarray marker (TAM) approach. Nucleic Acids Res 31: e115.
Flavell AJ, Knox MR, Pearce SR, Ellis THN, 1998. Retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphisms (RBIP) for high throughput marker analysis. The Plant J 16: 643–650.
Ford R, Le Roux K, Itman C, Brouwer JB, Taylor PWJ, 2002. Diversity analysis and genotyping inPisum with sequence tagged microsatellite site (STMS) primers. Euphytica 124: 397–405.
Guillemaut P, Marechal-Drouard L, 1992. Isolation of plant DNA: A fast, inexpensive and reliable method. Plant Mol Biol Rep 10: 60–65.
Chang RY, O’Donoughue LS, Bureau TE, 2001. Inter-MITE polymorphism (IMP): a high through-put transposon-based genome mapping and finger-printing approach. Theor Appl Genet 102: 773–781.
Chavanne F, Zhang DX, Liaud MF, Cerff R, 1998. Structure and evolution of Cyclops: a novel giant retrotransposon of theTy3/Gypsy family highly amplified in pea and other legume species. Plant Mol Biol 37: 363–375.
Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, 1995. PCR Strategies. Academic Press.
Iwamoto M, Nagashima H, Nagamine T, Higo T, Higo K, 1999. p-SINE-like intron of the CatA catalase homologs and phylogenetic relationships amongAagenome, Oryza and related species. Theor Appl Genet 98: 853–861.
Jing RC, Knox MR, Lee JM,Vershinin AV, Ambrose M, Ellis THN, Flavell AJ, 2005. Insertional polymorphism and antiquity of PDR1 retrotransposon insertions inPisum species. Genetics 171: 741–752.
Kalendar R, Grob T, Regina M, Suoniemi A, Schulam A, 1999. IRAP and REMAP: two new retrotransposon-based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theor Appl Genet 98: 704–711.
Kalendar R, Tanskanen J, Immonen S, Nevo E, Schulman AH, 2000. Genome evolution of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) by BARE-1 retrotransposon dynamics in response to sharp microclimatic divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 6603–6607.
Kazazian HH, 2004. Mobile elements: drivers of genome evolution. Science 303: 1626–1632.
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL, 1999. Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33: 479–532.
Loridon K, McPhee K, Morin J, Dubreuil P, Pilet-Nayel ML, Aubert G, etal. 2005. Microsatellite marker polymorphism and mapping in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theor Appl Genet 111: 1022–1031.
Macas J, Koblizkova A, Neumann P, 2005. Characterization of Stowaway MITEs in pea (Pisum sativum L.) and identification of their potential master elements. Genome 48: 831–839.
Manninen O, Kalendar R, Robinson J, Schulman AH, 2000. Application of BAR/M retrotransposon markers to the mapping of a major resistance gene for net blotch in barley. Mol Gen Genet 264: 325–334.
McCouch SR, Chen X, Panaud O, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, 1997. Microsatellite marker development, mapping and application in rice genetics and breeding. Plant Mol Biol 35: 89–99.
Morgante M, Olivieri AM, 1993. PCR-amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. The Plant J 3: 175–182.
Nei M, Li WH, 1979. Mathematical model for studing genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 5269–5273.
Neumann P, Nouzova M, Macas J, 2001. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of repetitive DNA in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Genome 44: 716–728.
Neumann P, Pozarkova D, Koblizkova A, Macas J, 2005. PIGY, a new plant envelope-class LTR retrotransposon. Mol Genet Genomics 273: 43–53.
Neumann P, Pozarkova D, Macas J, 2003. Highly abundant pea LTR retrotransposonOgre is constitutively transcribed and partially spliced. Plant Mol Biol 53: 399–410.
Pearce SR, Knox M, Ellis THN, Flavell AJ, Kumar A, 2000. PeaTy1-copia group retrotransposons: transpositional activity and use as markers to study genetic diversity inPisum. Mol Gen Genet 263: 898–907.
Rohlf M, 2000. NTSYS-pc: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.1, Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York, USA.
Samec P, Posvec J, Stejskal V, Nasinec V, Griga M, 1998. Cultivar identification and relationships inPisum sativum L. based on RAPD and isozymes. Biol Plant 41: 39–48.
Shedlock AM, Okada N, 2000. SINE insertions: powerful tools for molecular systematics. BioEssays 22: 148–160.
Schulman AH, Flavell AJ, Ellis THN, 2004. The application of LTR retrotransposons as molecular markers in plants. In: Method in Molecular Biology 260: 145–175.
Simioniuc D, Uptmoor R, Friedt W, Ordon F, 2002. Genetic diversity and relationships among pea cultivars revealed by RAPDs and AFLPs. Plant Breeding 121: 429–435.
Taŕan B, Zhang C, Warkentin T, Tullu A, Vandenberg A, 2005. Genetic diversity among varieties and wild species accessions of pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on molecular markers, and morphological and physiological characters. Genome 48: 257–272.
Tatout C, Warwick S, Lenoir A, Deragon JM, 1999. SINE insertions as clade markers for wild crucifer species. Mol Biol Evol 16: 1614–1621.
UPOV-BMT: BMT/36/10. 2002. Progress report of the 36th session of the technical committee, the technical working parties and working group on biochemical and molecular techniques and DNA-profiling in particular. Geneva.
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, et al. 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Waugh R, McLean K, Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A, Thomas WT, Powell W, 1997. Genetic distribution of Bare-1 like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphism (S-SAP). Mol Gen Genet 253: 687–694.
Weising K, Nybom H, Wolf K, Kahl G, eds. 2005. DNA fingerprinting in plants: Principles, methods and applications 2nd edn. CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, USA.
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV, 1990. DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 6531–6535.
Zietkiewitz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D, 1989. Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR) anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20: 176–173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smýkal, P. Development of an efficient retrotransposon-based fingerprinting method for rapid pea variety identification. J Appl Genet 47, 221–230 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03194627
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03194627