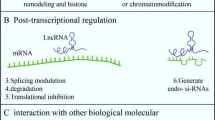
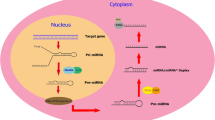
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder. PD is characterized by progressive loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) region of brain tissue followed by the α-synuclein-based Lewy bodies’ formation. These conditions are manifested by various motor and non-motor symptoms such as resting tremor, limb rigidity, bradykinesia and posture instability, cognitive impairment, sleep disorders, and emotional and memory dysfunctions. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are closely related to protein-coding genes and are involved in various biological processes. Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) lncRNA is involved in different pathways, including alternative splicing, transcriptional regulation, and post-transcriptional regulation, and also interacts with RNAs as a miRNA sponge. MALAT1 is highly expressed in brain tissues and several lines of evidence suggested it is probably involved in synapse generation and other neurophysiological pathways. This narrative review discussed all aspects of MALAT1-associated mechanisms involved in the PD pathogenesis, i.e., perturbed α-synuclein homeostasis, apoptosis and autophagy, and neuro-inflammation. Lastly, the possible applications of MALAT1 as a diagnostic biomarker and its importance to developing therapeutic strategies were highlighted. The literature search was conducted using neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disorders, Parkinson’s disease, lncRNA, and MALAT1 as search items in Google Scholar, Web of Knowledge, PubMed, and Scopus up to December 2021.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 July 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02961-w
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- AMP:
-
Adenosine monophosphate
- ASO:
-
Specific antisense oligonucleotide
- CSF:
-
Cerebro-spinal fluid
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DAPK1:
-
Death-associated protein kinase1
- EZH2:
-
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- GPNMB:
-
Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- HTR2A:
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- lncRNA:
-
Long ncRNA
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LRRK2:
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2
- MALAT1:
-
Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1
- mascRNA:
-
MALAT1-associated small cytoplasmic RNA
- MPP+ :
-
Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl–4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine
- N2a:
-
Neuro 2A
- nc-RNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- NEAT2:
-
Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 2
- NRF2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- NLGN1:
-
Neuroligin1
- NLR:
-
NOD-like receptor
- NLRP3:
-
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3
- NS:
-
Nervous system
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung cancer
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PRC2:
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SAA3:
-
Serum amyloid A3
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SNCA:
-
Alpha-synuclein
- sncRNA:
-
Small ncRNA
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SynCAM1:
-
Synaptic cell adhesion molecule1
- TH+ :
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase positive
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Xin C, Liu J (2021) Long Non-coding RNAs in Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 1–12
Rasheed M, Liang J, Wang C, Deng Y, Chen Z (2021) Epigenetic regulation of neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 22(9):4956
Taghizadeh E, Gheibihayat SM, Taheri F, Afshani SM, Farahani N, Saberi A (2021) LncRNAs as putative biomarkers and therapeutic targets for Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 42(10):4007–4015
Tang Y, Meng L, Wan C-M, Liu Z-H, Liao W-H, Yan X-X et al (2017) Identifying the presence of Parkinson’s disease using low-frequency fluctuations in BOLD signals. Neurosci Lett 645:1–6
Hirsch L, Jette N, Frolkis A, Steeves T, Pringsheim T (2016) The incidence of Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 46(4):292–300
Rezaei O, Nateghinia S, Estiar MA, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2021) Assessment of the role of non-coding RNAs in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 173914
Recasens A, Perier C, Sue CM (2016) Role of microRNAs in the regulation of α-synuclein expression: a systematic review. Front Mol Neurosci 9:128
Beitz JM (2014) Parkinson’s disease: a review. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 6(6):65–74
Devos D, Moreau C, Dujardin K, Cabantchik I, Defebvre L, Bordet R (2013) New pharmacological options for treating advanced Parkinson’s disease. Clin Ther 35(10):1640–1652
Lv Q, Wang Z, Zhong Z (2020) Huang W (2020) Role of long noncoding RNAs in Parkinson’s disease: putative biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Parkinson’s Disease 2020
Lim SY, Lang AE (2010) The nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease—an overview. Mov Disord 25(S1):S123–S130
Wood LD, Neumiller JJ, Setter SM, Dobbins EK (2010) Clinical review of treatment options for select nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 8(4):294–315
Bonifati V (2014) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease–state of the art, 2013. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20:S23–S28
Renani PG, Taheri F, Rostami D, Farahani N, Abdolkarimi H, Abdollahi E et al (2019) Involvement of aberrant regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease and epigenetic-based therapies. J Cell Physiol 234(11):19307–19319
Koros C, Simitsi A, Stefanis L (2017) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease: genotype–phenotype correlations. Int Rev Neurobiol 132:197–231
Hipp MS, Kasturi P, Hartl FU (2019) The proteostasis network and its decline in ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(7):421–435
Nair VD, Ge Y (2016) Alterations of miRNAs reveal a dysregulated molecular regulatory network in Parkinson’s disease striatum. Neurosci Lett 629:99–104
Lyu Y, Bai L, Qin C (2019) Long noncoding RNAs in neurodevelopment and Parkinson’s disease. Animal models and experimental medicine 2(4):239–251
Andican G, Konukoglu D, Bozluolcay M, Bayülkem K, Firtiına S, Burcak G (2012) Plasma oxidative and inflammatory markers in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Belg 112(2):155–159
Capurro A, Bodea L-G, Schaefer P, Luthi-Carter R, Perreau VM (2015) Computational deconvolution of genome wide expression data from Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease brain tissues using population-specific expression analysis. Front Neurosci 8:441
Schapira AH (2013) Recent developments in biomarkers in Parkinson disease. Curr Opin Neurol 26(4):395
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin K-J (2017) The long noncoding RNA Malat1: its physiological and pathophysiological functions. RNA Biol 14(12):1705–1714
Yin K-J, Hamblin M, Chen YE (2014) Non-coding RNAs in cerebral endothelial pathophysiology: emerging roles in stroke. Neurochem Int 77:9–16
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U, Sahu A, Hosono Y et al (2015) The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet 47(3):199–208
Barres BA (2008) The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron 60(3):430–440
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2009) Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10(3):155–159
Xie C, Yuan J, Li H, Li M, Zhao G, Bu D et al (2014) NONCODEv4: exploring the world of long non-coding RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D98–D103
Fatica A, Bozzoni I (2014) Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet 15(1):7–21
Shen J, Siegel AB, Remotti H, Wang Q, Shen Y, Santella RM (2015) Exploration of deregulated long non-coding RNAs in association with hepatocarcinogenesis and survival. Cancers 7(3):1847–1862
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M et al (2011) A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147(2):358–369
Grote P, Herrmann BG (2015) Long noncoding RNAs in organogenesis: making the difference. Trends Genet 31(6):329–335
Menon DU, Meller VH (2015) Identification of the Drosophila X chromosome: the long and short of it. RNA Biol 12(10):1088–1093
Kanduri C (2016) Long noncoding RNAs: lessons from genomic imprinting. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1859(1):102–11
Bhartiya D, Kapoor S, Jalali S, Sati S, Kaushik K, Sachidanandan C et al (2012) Conceptual approaches for lncRNA drug discovery and future strategies. Expert Opin Drug Discov 7(6):503–513
Brown JA, Kinzig CG, DeGregorio SJ, Steitz JA (2016) Methyltransferase-like protein 16 binds the 3′-terminal triple helix of MALAT1 long noncoding RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(49):14013–14018
Brown JA, Kinzig CG, DeGregorio SJ, Steitz JA (2016) Hoogsteen-position pyrimidines promote the stability and function of the MALAT1 RNA triple helix. RNA 22(5):743–749
Yang Y, Li Y, Yang H, Guo J, Li N (2021) Circulating microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Front Mol Neurosci 14
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Sunkin SM, Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2008) Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(2):716–721
Khorkova O, Hsiao J, Wahlestedt C (2015) Basic biology and therapeutic implications of lncRNA. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 87:15–24
Rinn JL, Chang HY (2012) Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 81:145–166
Majidinia M, Mihanfar A, Rahbarghazi R, Nourazarian A, Bagca B, Avci ÇB (2016) The roles of non-coding RNAs in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Biol Rep 43(11):1193–1204
Soreq L, Guffanti A, Salomonis N, Simchovitz A, Israel Z, Bergman H et al (2014) Long non-coding RNA and alternative splicing modulations in Parkinson’s leukocytes identified by RNA sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol 10(3):e1003517
Zhou Y, Gu C, Li J, Zhu L, Huang G, Dai J et al (2018) Aberrantly expressed long noncoding RNAs and genes in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 14:3219
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF (2012) Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in brain evolution, development, plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(8):528–541
Chakrabarti S, Mohanakumar KP (2016) Aging and neurodegeneration: a tangle of models and mechanisms. Aging Dis 7(2):111
Ghanam A, Xu Q, Ke S, Azhar M, Cheng Q, Song X (2017) Shining the light on senescence associated LncRNAs. Aging Dis 8(2):149
Ni Y, Huang H, Chen Y, Cao M, Zhou H, Zhang Y (2017) Investigation of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(2):329–338
Soreq L, Salomonis N, Guffanti A, Bergman H, Israel Z, Soreq H (2015) Whole transcriptome RNA sequencing data from blood leukocytes derived from Parkinson’s disease patients prior to and following deep brain stimulation treatment. Genomics Data 3:57–60
Bernard D, Prasanth KV, Tripathi V, Colasse S, Nakamura T, Xuan Z et al (2010) A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. EMBO J 29(18):3082–3093
Lipovich L, Dachet F, Cai J, Bagla S, Balan K, Jia H et al (2012) Activity-dependent human brain coding/noncoding gene regulatory networks. Genetics 192(3):1133–1148
Zhang T-H, Liang L-Z, Liu X-L, Wu J-N, Su K, Chen J-Y et al (2017) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 interacts with miR-124 and modulates tongue cancer growth by targeting JAG1 retraction in/10.3892/or.2018.6688. Oncol Rep 37(4):2087–2094
Hutchinson JN, Ensminger AW, Clemson CM, Lynch CR, Lawrence JB, Chess A (2007) A screen for nuclear transcripts identifies two linked noncoding RNAs associated with SC35 splicing domains. BMC Genomics 8(1):1–16
Tripathi V, Shen Z, Chakraborty A, Giri S, Freier SM, Wu X et al (2013) Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 controls cell cycle progression by regulating the expression of oncogenic transcription factor B-MYB. PLoS Genet 9(3):e1003368
Michalik KM, You X, Manavski Y, Doddaballapur A, Zörnig M, Braun T et al (2014) Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates endothelial cell function and vessel growth. Circ Res 114(9):1389–1397
Schmidt LH, Spieker T, Koschmieder S, Humberg J, Jungen D, Bulk E et al (2011) The long noncoding MALAT-1 RNA indicates a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and induces migration and tumor growth. J Thorac Oncol 6(12):1984–1992
Goyal B, Yadav SRM, Awasthee N, Gupta S, Kunnumakkara AB, Gupta SC (2021) Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 188502
Tano K, Mizuno R, Okada T, Rakwal R, Shibato J, Masuo Y et al (2010) MALAT-1 enhances cell motility of lung adenocarcinoma cells by influencing the expression of motility-related genes. FEBS Lett 584(22):4575–4580
Wilusz JE (2016) Long noncoding RNAs: re-writing dogmas of RNA processing and stability. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1859(1):128–138
Wilusz JE, Freier SM, Spector DL (2008) 3′ end processing of a long nuclear-retained noncoding RNA yields a tRNA-like cytoplasmic RNA. Cell 135(5):919–932
Macias S, Plass M, Stajuda A, Michlewski G, Eyras E, Cáceres JF (2012) DGCR8 HITS-CLIP reveals novel functions for the microprocessor. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19(8):760–766
Yu B, Shan G (2016) Functions of long noncoding RNAs in the nucleus. Nucleus 7(2):155–166
Eißmann M, Gutschner T, Hämmerle M, Günther S, Caudron-Herger M, Groß M et al (2012) Loss of the abundant nuclear non-coding RNA MALAT1 is compatible with life and development. RNA Biol 9(8):1076–1087
Sun Q, Hao Q, Prasanth KV (2018) Nuclear long noncoding RNAs: key regulators of gene expression. Trends Genet 34(2):142–157
Yao J, Wang XQ, Li YJ, Shan K, Yang H, Wang YNZ et al (2022) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates retinal neurodegeneration through CREB signaling. EMBO Mol Med 14(3):e15623
Kryger R, Fan L, Wilce PA, Jaquet V (2012) MALAT-1, a non protein-coding RNA is upregulated in the cerebellum, hippocampus and brain stem of human alcoholics. Alcohol 46(7):629–634
Theo F, Kraus J, Haider M, Spanner J, Steinmaurer M, Dietinger V et al (2017) Altered long noncoding RNA expression precedes the course of Parkinson’s disease–a preliminary report. Mol Neurobiol 54(4):2869
Zhang Q-S, Wang Z-H, Zhang J-L, Duan Y-L, Li G-F, Zheng D-L (2016) Beta-asarone protects against MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease via regulating long non-coding RNA MALAT1 and inhibiting α-synuclein protein expression. Biomed Pharmacother 83:153–159
Xia D, Sui R, Zhang Z (2019) Administration of resveratrol improved Parkinson’s disease-like phenotype by suppressing apoptosis of neurons via modulating the MALAT1/miR-129/SNCA signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 120(4):4942–4951
Bennett MC (2005) The role of α-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther 105(3):311–331
Dehay B, Bourdenx M, Gorry P, Przedborski S, Vila M, Hunot S et al (2015) Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol 14(8):855–866
Robinson JL, Lee EB, Xie SX, Rennert L, Suh E, Bredenberg C et al (2018) Neurodegenerative disease concomitant proteinopathies are prevalent, age-related and APOE4-associated. Brain 141(7):2181–2193
Bengoa-Vergniory N, Roberts RF, Wade-Martins R, Alegre-Abarrategui J (2017) Alpha-synuclein oligomers: a new hope. Acta Neuropathol 134(6):819–838
Vekrellis K, Xilouri M, Emmanouilidou E, Rideout HJ, Stefanis L (2011) Pathological roles of α-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 10(11):1015–1025
Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG, Saad M et al (2014) Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 46(9):989–993
Ghavami S, Shojaei S, Yeganeh B, Ande SR, Jangamreddy JR, Mehrpour M et al (2014) Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol 112:24–49
Xiong N, Xiong J, Jia M, Liu L, Zhang X, Chen Z et al (2013) The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease: rotenone-based modeling. Behav Brain Funct 9(1):1–12
Lynch-Day MA, Mao K, Wang K, Zhao M, Klionsky DJ (2012) The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(4):a009357
Zhang L, Dong Y, Xu X, Xu Z (2012) The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res 7(2):141
Gong X, Wang H, Ye Y, Shu Y, Deng Y, He X et al (2016) miR-124 regulates cell apoptosis and autophagy in dopaminergic neurons and protects them by regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Am J Transl Res 8(5):2127
Liu W, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Pan W, Zhao J, Xu Y (2017) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 contributes to cell apoptosis by sponging miR-124 in Parkinson disease. Cell Biosci 7(1):1–9
Lu Y, Gong Z, Jin X, Zhao P, Zhang Y, Wang Z (2020) LncRNA MALAT1 targeting miR-124-3p regulates DAPK1 expression contributes to cell apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biochem 121(12):4838–4848
Chen Q, Huang X, Li R (2018) lncRNA MALAT1/miR-205-5p axis regulates MPP+-induced cell apoptosis in MN9D cells by directly targeting LRRK2. Am J Transl Res 10(2):563
Zeng R, Luo D-X, Li H-P, Zhang Q-S, Lei S-S, Chen J-H (2019) MicroRNA-135b alleviates MPP+-mediated Parkinson’s disease in in vitro model through suppressing FoxO1-induced NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. J Clin Neurosci 65:125–133
Moloney EB, Moskites A, Ferrari EJ, Isacson O, Hallett PJ (2018) The glycoprotein GPNMB is selectively elevated in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s disease patients and increases after lysosomal stress. Neurobiol Dis 120:1–11
Murthy MN, Blauwendraat C, Guelfi S, Hardy J, Lewis PA, Trabzuni D (2017) Increased brain expression of GPNMB is associated with genome wide significant risk for Parkinson’s disease on chromosome 7p15. 3. Neurogenetics 18(3):121–33
Lv K, Liu Y, Zheng Y, Dai S, Yin P, Miao H (2021) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis via miR-135b-5p/GPNMB axis in Parkinson’s disease cell model. Biol Res 54
Ransohoff RM (2016) How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science 353(6301):777–783
Joshi N, Singh S (2018) Updates on immunity and inflammation in Parkinson disease pathology. J Neurosci Res 96(3):379–390
Kabra A, Sharma R, Kabra R, Baghel US (2018) Emerging and alternative therapies for Parkinson disease: an updated review. Curr Pharm Des 24(22):2573–2582
He Q, Wang Q, Yuan C, Wang Y (2017) Downregulation of miR-7116-5p in microglia by MPP+ sensitizes TNF-α production to induce dopaminergic neuron damage. Glia 65(8):1251–1263
Wang S, Yuan Y-H, Chen N-H, Wang H-B (2019) The mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis activation and their role in Parkinson’s disease. Int Immunopharmacol 67:458–464
Heward JA, Lindsay MA (2014) Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of the immune response. Trends Immunol 35(9):408–419
Puthanveetil P, Chen S, Feng B, Gautam A, Chakrabarti S (2015) Long non-coding RNA MALAT 1 regulates hyperglycaemia induced inflammatory process in the endothelial cells. J Cell Mol Med 19(6):1418–1425
Ding Y, Guo F, Zhu T, Li J, Gu D, Jiang W et al (2018) Mechanism of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury is mediated by the miR-146a/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 41(1):446–454
Cai L-J, Tu L, Huang X-M, Huang J, Qiu N, Xie G-H et al (2020) LncRNA MALAT1 facilitates inflammasome activation via epigenetic suppression of Nrf2 in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Brain 13(1):1–15
Yang H (2021) LncRNA MALAT1 potentiates inflammation disorder in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Immunogenet 48(5):419–428
Yoon J-H, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2013) Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA. J Mol Biol 425(19):3723–3730
Arun G, Diermeier S, Akerman M, Chang K-C, Wilkinson JE, Hearn S et al (2016) Differentiation of mammary tumors and reduction in metastasis upon Malat1 lncRNA loss. Genes Dev 30(1):34–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design, drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and approval of the final version. MA contributed in preparing table and writing the manuscript. MJ designed and contributed to the preparation of the figure and manuscript. MR revised the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This is a review article. There is not ethical approval applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicated.
Consent for Publication
This is a review article. There is no consent to publish applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abrishamdar, M., Jalali, M.S. & Rashno, M. MALAT1 lncRNA and Parkinson’s Disease: The role in the Pathophysiology and Significance for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Mol Neurobiol 59, 5253–5262 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02899-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02899-z