Abstract
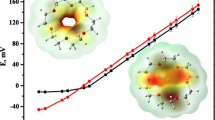
A new indole-containing 2,6-pyridinedicarbohydrazide P3 was synthesized and well characterized employing NMR, ESI+-MS, FT-IR, and elemental analyses. The synthesized compound was examined as an efficient fluorescent turn-off and colorimetric cation receptor. The P3 receptor exhibited a remarkable rapid color change from colorless to brown in the presence of Cu2+ cations. P3 displayed selective fluorescence quenching and a UV-vis redshift only in the presence of Cu2+ ions. Job’s plot, NMR titration, and ESI+-MS data were used to determine the complex’s 1:2 stoichiometry between P3 and Cu2+. Fluorescence titration was used to calculate the association constant (Ka) as 2.9–3.5 × 1011 M− 2 and the limit of detection (LOD) as 4.2 × 10− 9 M. P3-based test strips were developed, which might be used as a simple and effective Cu2+ test kit. DFT calculations were also performed to optimize the structures of the P3 and P3 + Cu2+ complex. This design will likely provide another avenue to develop chemosensors incorporating a functional group on the upper rim of the 2,6-pyridinedicarbohydrazide platform.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to [According to Mazandaran University’s policies that all analysis devices are not connected to the Internet, the output of all devices is printed as a sheet or available on CD.] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, W., Alharthy, R.D., Zubair, M., Ahmed, M., Hameed, A., Rafique, S.: Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 11, 17006 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94616-4
Hamdan, A.M., Abd-El-Mageed, H., Ghanem, N.: Biological treatment of hazardous heavy metals by Streptomyces rochei ANH for sustainable water management in agriculture. Sci. Rep. 11, 9314 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88843-y
Franz, K.J., Metzler-Nolte, N., Introduction: Metals in Medicine. Chem. Rev. 119, 727–729 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00685
Carter, P., Young, K.M., Palmer, A.E.: Fluorescent sensors for Measuring Metal Ions in Living Systems. Chem. Rev. 114, 4564–4601 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400546e
Mohanty, P., Behura, R., Bhardwaj, V., Dash, P.P., Sahoo, S., Jali, B.: Recent advancement on chromo-fluorogenic sensing of aluminum(III) with Schiff bases. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 34, e00166 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2022.e00166
Bhardwaj, V., Nurchi, V., Sahoo, S.: Mercury Toxicity and Detection using chromo-fluorogenic chemosensors. Pharmaceuticals. 14, 123 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020123
Turski, M.L., Thiele, D.J.: New roles for copper metabolism in cell proliferation, signaling, and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 717–721 (2009)
Li, Y., Ji, Y.-X., Song, L.-J., Zhang, Y., Li, Z.-C., Yang, L., et al.: A novel BF2–curcumin-based fluorescent chemosensor for detection of Cu2 + in aqueous solution and living cells. Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 5169–5180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3416-y
Bhardwaj, V., Patel, D., Majeed, S.A., Hameed, A.S., Aatif, A.M., Sk, A., et al.: Probing Biothiols using a red-emitting Pyridoxal Derivative by adopting copper(II) Displacement Approach and Cell Imaging. Chem. Biodivers. 19 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202200425
Bertini, I., Rosato, A.: Menkes disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 89 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7439-6
Gaggelli, E., Kozlowski, H., Valensin, D., Valensin, G.: Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative Disorders (Alzheimer’s, Prion, and Parkinson’s Diseases and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Chem. Rev. 106, 1995–2044 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040410w
Hung, Y.H., Bush, A.I., Cherny, R.A.: Copper in the brain and Alzheimer’s disease. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 15, 61–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-009-0600-y
Tapiero, H., Townsend, D.M., Tew, K.D.: Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Copp. Biomed Pharmacother. 57, 386–398 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0753-3322(03)00012-x
Vulpe, C., Levinson, B., Whitney, S., Packman, S., Gitschier, J.: Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper–transporting ATPase. Nat. Genet. 3, 7–13 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0193-7
Lee, J.C., Gray, H.B., Winkler, J.R.: Copper(II) binding to α-Synuclein, the Parkinson’s protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 6898–6899 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja711415b
Chen, Y., Tang, T., Chen, Y., Xu, D.: Novel 1,8-naphthalimide dye for multichannel sensing of H + and. Cu2+ Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 2379–2393 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-017-3235-6
Kaiafa, G.D., Saouli, Z., Diamantidis, M.D., Kontoninas, Z., Voulgaridou, V., Raptaki, M., et al.: Copper levels in patients with hematological malignancies. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 23, 738–741 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2012.07.009
Rakesh, P., Singh, H.B., Butcher, R.J.: Isolation and molecular structures of novel organotellurium(iv) halides, oxyhalide, and mixed halide. Dalt Trans. 41, 10707–10714 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT30645J
Shi, M., Kwon, H.S., Peng, Z., Elder, A., Yang, H.: Effects of Surface Chemistry on the generation of reactive oxygen species by copper nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 6, 2157–2164 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300445d
Gao, G., Hao, C., Ding, C., Zheng, X., Liu, L., Xie, P., et al.: A near-infrared colorimetric and fluorometric chemodosimeter for Cu2 + based on a bis-spirocyclic rhodamine and its application in imagings. Res. Chem. Intermed. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-022-04920-5
Liu, J.-M., Zheng, Q.-Y., Chen, C.-F., Huang, Z.-T.: The design of a highly selective fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu(II) within wide pH region and a molecular switch controlled by pH. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 51, 165–171 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-004-6445-7
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Guo, F., Wang, Y., Xie, P.: A new naked-eye fluorescent chemosensor for Cu(II) and its practical applications. Res. Chem. Intermed. 47, 3515–3528 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-021-04489-5
Yang, Y., Gao, C.-Y., Li, T., Chen, J.A., Tetraphenylethene-Based: Cu2+. ChemistrySelect. 1, 4577–4581 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201600883 Rhodamine Hydrazone Chemosensor for Colorimetric and Reversible Detection of
Kumar, M., Nagendra Babu, J., Bhalla, V.: Fluorescent chemosensor for Cu2 + ion based on iminoanthryl appended calix[4]arene. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 66, 139–145 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-009-9670-2
Hosseinzadeh, R., Domehri, E., Tajbakhsh, M., Bekhradnia, A.: New fluorescent sensor based on a calix[4]arene bearing two triazole–coumarin units for copper ions: Application for Cu2 + detection in human blood serum. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 93, 245–252 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0872-3
Thangaraj, A., Bhardwaj, V., Sahoo, S.K.: A multi-analyte selective dansyl derivative for the fluorescence detection of Cu(ii) and cysteine. Photochem. Photobiol Sci. 18, 1533–1539 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9pp00080a
Bhardwaj, V., Sk, A., Sahoo, S.: Pyridoxal derived red-emitting aggregates for the ratiometric sensing of pH and copper(II). Opt. Mater. (Amst). 136, 113414 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113414
Tajbakhsh, M., Chalmardi, G.B., Bekhradnia, A., Hosseinzadeh, R., Hasani, N., Amiri, M.A.: A new fluorene-based Schiff-base as fluorescent chemosensor for selective detection of Cr3 + and Al3+. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 189, 22–31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.08.007
Savran, T., Karuk Elmas, S.N., Aydin, D., Arslan, S., Arslan, F.N., Yilmaz, I.: Design of multiple-target chemoprobe: “naked-eye” colorimetric recognition of Fe3 + and off–on fluorogenic detection for Hg2 + and its on-site applications. Res. Chem. Intermed. 48, 1003–1023 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-021-04648-8
Inoue, K., Aikawa, S., Fukushima, Y.: Colorimetric chemosensor based on a carminic acid and Pb2 + complex for selective detection of cysteine over homocysteine and glutathione in aqueous solution. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 90, 105–110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-017-0772-y
Zhou, Q., Qian, L., Pan, Q., Si, G., Qi, Z., Zheng, Y., et al.: A novel chemosensor for Fe3 + based on open–closed-loop mechanism and imaging in living cells. Res. Chem. Intermed. 46, 533–545 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03965-3
Fanna, D.J., Lima, L.M.P., Craze, A.R., Trinchi, A., Wei, G., Reynolds, J.K., et al.: Determination of Cu2 + in drinking water using a hydroxyjulolidine-dihydroperimidine colorimetric sensor. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 94, 141–154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0862-5
Chalmardi, G.B., Tajbakhsh, M., Hasani, N., Bekhradnia, A.: A new Schiff-base as fluorescent chemosensor for selective detection of Cr3+: An experimental and theoretical study. Tetrahedron. 74, 2251–2260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2018.03.046
Lee, S.C., Lee, M., Suh, B., Lee, J., Kim, C.: A bithiophene-based Ratiometric fluorescent sensor for sensing Cd2+. ChemistrySelect. 6, 8397–8401 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202102503
Bhardwaj, V., Hindocha, L., Ashok Kumar, S.K., Sahoo, S.K.: An aggregation-induced emissive pyridoxal derived tetradentate Schiff base for the fluorescence turn-off sensing of copper(ii) in an aqueous medium. New. J. Chem. 46, 3248–3257 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ05523B
Duke, R.M., O’Brien, J.E., McCabe, T., Gunnlaugsson, T.: Colorimetric sensing of anions in aqueous solution using a charge neutral, cleft-like, amidothiourea receptor: Tilting the balance between hydrogen bonding and deprotonation in anion recognition. Org. Biomol. Chem. 6, 4089–4092 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/B807579D
Li, J., Gu, Q., Heng, H., Wang, Z., Jin, H., He, J.: Rare-earth hydroxide nanosheets based ratio fluorescence nanoprobe for dipicolinic acid detection. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 272, 120969 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.120969
Narula, A., Rao, C.P.: Fluorophoric conjugate of N-Alkyl Naphthalimide in Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate as a tunable and sustainable sensing system: Differential Sensing of Zn2 + and Al3 + and the application of its Zn2 + complex in detecting Dipicolinic Acid, a component of Anthrax Bact. J. Phys. Chem. C. 123, 21271–21280 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b05349
Chopra, S., Singh, N., Thangarasu, P., Bhardwaj, V.K., Kaur, N.: Fluorescent organic nanoparticles as chemosensor for nanomolar detection of cs + in aqueous medium. Dye Pigment. 106, 45–50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2014.02.024
Lee, S., Yuen, K.K.Y., Jolliffe, K.A., Yoon, J.: Fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for pyrophosphate. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 1749–1762 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00353E
Lee, H.G., Lee, J.H., Jang, S.P., Park, H.M., Kim, S.-J., Kim, Y., et al.: Zinc selective chemosensor based on pyridyl-amide fluorescence. Tetrahedron. 67, 8073–8078 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2011.08.049
Dorazco-González, A., Alamo, M.F., Godoy-Alcántar, C., Höpfl, H., Yatsimirsky, A.K.: Fluorescent anion sensing by bisquinolinium pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide receptors in water. RSC Adv. 4, 455–466 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA44363A
Rahimi, H., Hosseinzadeh, R., Tajbakhsh, M.: A new and efficient pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide-based fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensor for sensitive and selective recognition of Pb2 + and Cu2+. J. Photochem. Photobiol A Chem. 407, 113049 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.113049
Łukasik, N., Wagner-Wysiecka, E., Hubscher-Bruder, V., Michel, S., Bocheńska, M., Kamińska, B.: Naphthyl- vs. anthrylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxamides in cation binding studies. Synthesis and spectroscopic properties. Supramol Chem. 28, 673–685 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10610278.2015.1119830
Mohanasundaram, D., Bhaskar, R., Sankarganesh, M., Nehru, K., Gangatharan Vinoth Kumar, G., Rajesh, J.: A simple pyridine based fluorescent chemosensor for selective detection of copper ion. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 265, 120395 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120395
Amini, A., Rahimi, M., Behmadi, H., Nazari, M., Benson, V., Cheng, C., et al.: 2,6-Pyridinedicarbohydrazide-salicylal hydrazone-base derivative with high detection limit and binding constant for emissive ion chemosensing in aqueous solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol A Chem. 392, 112344 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112344
Yadav, N., Singh, A.K.: Dicarbohydrazide based chemosensors for copper and cyanide ions via a displacement approach. New. J. Chem. 42, 6023–6033 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ00230D
Chen, A.Y., Thomas, P.W., Stewart, A.C., Bergstrom, A., Cheng, Z., Miller, C., et al.: Dipicolinic acid derivatives as inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase-1. J. Med. Chem. 60, 7267–7283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00407
Fegade, U.A., Sahoo, S.K., Singh, A., Singh, N., Attarde, S.B., Kuwar, A.S.: A chemosensor showing discriminating fluorescent response for highly selective and nanomolar detection of Cu2 + and Zn2 + and its application in molecular logic gate. Anal. Chim. Acta. 872, 63–69 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.051
De Silva, A.P., Gunaratne, H.Q.N., Gunnlaugsson, T., Huxley, A.J.M., McCoy, C.P., Rademacher, J.T., et al.: Signaling recognition events with fluorescent sensors and switches. Chem. Rev. 97, 1515–1566 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr960386p
Huang, H., Li, H., Wang, A.-J., Zhong, S.-X., Fang, K.-M., Feng, J.-J.: Green synthesis of peptide-templated fluorescent copper nanoclusters for temperature sensing and cellular imaging. Analyst. 139, 6536–6541 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN01757A
Parker, C.A., Rees, W.T.: Correction of fluorescence spectra and measurement of fluorescence quantum efficiency. Analyst. 85, 587–600 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9608500587
Kaur, M., Cho, M.J., Choi, D.H.: A phenothiazine-based “naked-eye” fluorescent probe for the dual detection of Hg2 + and Cu2+: Application as a solid state sensor. Dye Pigment. 125, 1–7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2015.09.030
Bhattacharyya, A., Ghosh, S., Guchhait, N.: Highly sensitive and selective “naked eye” sensing of Cu(ii) by a novel amido–imine based receptor: A spectrophotometric and DFT study with practical application. RSC Adv. 6, 28194–28199 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA01269H
Sadia, M., Naz, R., Khan, J., Khan, R.: Synthesis and evaluation of a Schiff-Based fluorescent chemosensors for the selective and sensitive detection of Cu2 + in aqueous media with fluorescence Off-On responses. J. Fluoresc. 28, 1281–1294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-018-2278-4
Benesi, H.A., Hildebrand, J.H.: A Spectrophotometric Investigation of the Interaction of Iodine with aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 71, 2703–2707 (1949). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01176a030
Organization, W.H.: Safety IP on C. Guidelines for drinking-water Quality. Vol. 2, Health criteria and other supporting information n.d
Liu, S., Wang, Y.-M., Han, J.: Fluorescent chemosensors for copper(II) ion: Structure, mechanism and application. J. Photochem. Photobiol C Photochem. Rev. 32, 78–103 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2017.06.002
Mani, K.S., Rajamanikandan, R., Murugesapandian, B., Shankar, R., Sivaraman, G., Ilanchelian, M., et al.: Coumarin based hydrazone as an ICT-based fluorescence chemosensor for the detection of Cu2 + ions and the application in HeLa cells. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 214, 170–176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.02.020
Kumar, A., Kumar, V., Diwan, U., Upadhyay, K.K.: Highly sensitive and selective naked-eye detection of Cu2 + in aqueous medium by a ninhydrin–quinoxaline derivative. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 176, 420–427 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.089
Zheng, X., Lee, K.H., Liu, H., Park, S.-Y., Yoon, S.S., Lee, J.Y., et al.: A bis(pyridine-2-ylmethyl)amine-based selective and sensitive colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for Cu2+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 222, 28–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.053
Zhao, C., Liu, B., Bi, X., Liu, D., Pan, C., Wang, L., et al.: A novel flavonoid-based bioprobe for intracellular recognition of Cu2 + and its complex with Cu2 + for secondary sensing of pyrophosphate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 229, 131–137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.116
Kumar, R., Jain, H., Gahlyan, P., Joshi, A., Ramachandran, C.N.: A highly sensitive pyridine-dicarbohydrazide based chemosensor for colorimetric recognition of Cu2+, AMP2–, F – and AcO – ions. New. J. Chem. 42, 8567–8576 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ00918J
Fang, H., Huang, P.-C., Wu, F.-Y.: A highly sensitive fluorescent probe with different responses to Cu2 + and Zn2+. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 214, 233–238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.02.007
Zhang, X., Shen, L.-Y., Zhang, Q.-L., Yang, X.-J., Huang, Y.-L., Redshaw, C., et al.: A simple turn-off Schiff Base fluorescent sensor for copper (II) Ion and its application in Water Analysis. Mol. 26 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051233
Tang, L., Cai, M.: A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent sensor for Cu2 + and its complex for successive sensing of cyanide via Cu2 + displacement approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 173, 862–867 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.07.112
Liu, Y., Jiang, B., Zhao, L., Zhao, L., Wang, Q., Wang, C., et al.: A dansyl-based fluorescent probe for sensing Cu2 + in aqueous solution. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 261, 120009 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120009
Wei, J., Sun, H., Jiang, Y., Miao, B., Han, X., Zhao, Y., et al.: A novel 1,8-naphthalimide-based Cu2 + ion fluorescent probe and its bioimaging application. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 261, 120037 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120037
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this work from the Research Council of the University of Mazandaran is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
Partial financial support was received from the Research Council of the Univerity of Mazandaran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ali Zamani: Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation, Investigation, Writing - original draft. Yaghoub Sarrafi: Validation, Conceptualization, Investigation. Mahmood Tajbakhsh: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing - review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This is an observational study. The University of Mazandaran Research Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zamani, A., Sarrafi, Y., Rouzbahani, M.R. et al. A new pyridine-dicarbohydrazide-based turn-off fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensor for selective recognition of Cu2+. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 103, 277–288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-023-01193-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-023-01193-2