Abstract—
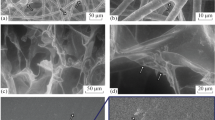
One of the most important aspects of regenerative medicine is the selection of the scaffold—the biological skeleton of the tissue-engineering structure. To reproduce the structure and properties of damaged tissue and maintain the cell adhesion and proliferation, it is optimal to use scafflds obtained by decellularization of native organs with subsequent recellularization of various cell lines. Using the methods of environmental scanning electron microscopy and scanning pulsed ultrasound microscopy, the microstructure of native and decellularized matrixes of dermal tissues was determined.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
B. A. Paramonov, Ya. O. Poremskii, and V. G. Yablonskii, Burns (Spetslit, St. Petersburg, 2000) [in Russian].
M. Yu. Aleksashin, Skor. Med. Pomoshch’ 7, 221 (2006).
V. V. Azolov and G. I. Dmitriev, Surgical Treatment of Burn Effects (NNIITO, Nizh. Novgorod, 1995) [in Russian].
K. M. Krylov, Rehabilitation of Burn Victims, The School-Book (OGK, St. Petersburg, 2002), No. 8 [in Russian].
J. P. Barret, Brit. Med. J. 329, 274 (2004).
V. P. Deikalo and A. N. Tolstik, Nov. Khirurg., No. 5, 577 (2015).
D. G. Papaskiri, N. A. Efimenko, A. A. Makharashvili, et al., Transplantologiya, Nos. 3–4, 68 (2018).
J. P. Barret, Brit. Med. J. 329, 274 (2004).
Z. J. Xin, Z. Qin, N. Y. Wen, et al., Burns 36, 1296 (2010).
A. A. Alekseev, M. G. Krutikov, and A. M. Rakhaev, Ann. Khirurg., No. 1, 59 (2001).
S. F. Badylak, Anat. Rec. B New Anat. 287, 36 (2005).
A. Atala, J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 1, 83 (2007).
A. Atala, S. B. Bauer, S. Soker, J. J. Yoo, and A. B. Retik, Lancet 367, 1241 (2006).
A. Kanematsu, S. Yamamoto, M. Ozekiet, et al., Biomaterials 25, 4513 (2004).
S. F. Badylak, D. Taylor, and K. Uygun, Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 13, 27 (2011).
M. T. Conconi, P. de Coppi, S. Bellini, et al., Biomaterials 26, 2567 (2005).
T. W. Gilbert, J. Cell. Biochem. 113, 2217 (2012).
E. A. Gubareva, S. Sjöqvist, I. V. Gilevich, et al., Biomaterials, No. 77, 320 (2016).
P. M. Baptista, G. Orlo, S.-H. Mirmalek-Sani, et al., in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference of Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,2009, p. 6526.
H. C. Ott, T. S. Matthiesen, S. K. Goh, et al., Nat. Med. 14, 213 (2008).
P. B. Milan, A. Pazoukid, M. T. Joghataeia, et al., Methods (San Diego, CA) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.07.005
J.-C. Luo, W. Chen, X.-H. Chen, et al., Biomaterials 32, 706 (2011).
Q. Zhang, J. A. Johnson, L. W. Dunne, et al., Acta Biomater. 35, 166 (2016).
S. Wu, Y. Liu, S. Bharadwaj, A. Atala, and Y. Zhang, Biomaterials 32, 1317 (2011).
B. Mendoza-Novelo, E. E. Avila, J. V. Cauich-Rodriguez, et al., Acta Biomater. 7, 1241 (2011).
L. Muscariello, F. Rosso, G. Marino, et al., J. Cell Physiol. 205, 328 (2005).
B. Ruozi, G. Tosi, E. Leo, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. C 27, 802 (2007).
D. J. Stokes, S. M. Rea, A. E. Porter, et al., Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 711, 113 (2002).
J. Chen, M. A. Birch, and S. J. Bull, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21, 277 (2010).
C. Maia-Brigagão and W. de Souza, Micron 43, 494 (2012).
A. Bridier, T. Meylheuc, and R. Briandet, Micron 48, 65 (2013).
A. M. Gatti, J. Kirkpatrick, A. Gambarelli, et al., J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 19, 1515 (2008).
A. H. Morris, J. Chang, and T. R. Kyriakides, Biores. Open Access 5, 177 (2016).
E. Morokov, E. Khramtsova, E. Kuevda, et al., Artif. Organs 43, 1104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/aor.13516
E. Khramtsova, E. Morokov, E. Lukanina, et al., Polym. Eng. Sci. 57, 697 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24617
Funding
The study work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 17-13-01376) on the topic “Visualization of Adhesion and Proliferation of Stromal and Epithelial Cells on Various Types of Matrices based on Biocompatible Polymers.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamyshinsky, R.A., Antipova, K.G., Kuevda, E.V. et al. Determination of the Microstructure of Decellularized Dermal Scaffolds. Nanotechnol Russia 14, 362–366 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019040074
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019040074