Abstract
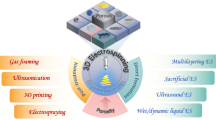
Electrospun nanofiber materials, with the advantages of large specific surface area, small pore size, high porosity, good channel connectivity, and ease of functional modification, have been widely used in various fields including environmental governance, safety protection, and tissue engineering. With the development of functional fiber materials, the construction of three-dimensional (3D) fiber materials with stable structures has become a critical challenge to expanding application and improving the performance of electrospun fibers. In recent years, researchers have carried out a lot of studies on the 3D reconstruction of electrospun fiber membranes and direct electrospinning of fiber sponges. Specifically, a variety of 3D fibrous sponges were constructed by the 3D reconstruction of electrospun fiber membranes, including embedded hydrogels, 3D printing, gas-foaming, and freeze-drying methods. Meanwhile, the direct electrospinning methods of 3D fibrous sponges have also been successfully developed, which are mainly divided into layer-by-layer stacking, liquid-assisted collection, 3D template collection, particle leaching, and humidity field regulation. Moreover, the applications of these fibrous sponges in many fields have been explored, such as sound absorption, warmth retention, thermal insulation, air filtration, adsorption/separation, and tissue engineering. These research works provide new ideas and methods for the fabrication of 3D fiber materials. Herein, the electrospinning technology and principle were briefly introduced, the representative progress of 3D fiber sponges in recent years was summarized, and their future development prospected.
Graphical Abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma W, Zhang Y, Pan S, Cheng Y, Shao Z, Xiang H, Chen G, Zhu L, Weng W, Bai H, Zhu M. Smart fibers for energy conversion and storage. Chem Soc Rev 2021;50:7009.
Chang H, Luo J, Gulgunje PV, Kumar S. Structural and functional fibers. Annu Rev Mater Res 2017;47:331.
Priyanka P, Dixit A, Mali HS. High strength kevlar fiber reinforced advanced textile composites. Iran Polym J 2019;28:621.
Shi Q, Sun J, Hou C, Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang H. Advanced functional fiber and smart textile. Adv Fiber Mater 2019;1:3.
Baye B, Tesfaye T. The new generation fibers: a review of high performance and specialty fibers. Polym Bull 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03966-6 .
Saito N, Aoki K, Usui Y, Shimizu M, Hara K, Narita N, Ogihara N, Nakamura K, Ishigaki N, Kato H, Haniu H, Taruta S, Kim YA, Endo M. Application of carbon fibers to biomaterials: a new era of nano-level control of carbon fibers after 30-years of development. Chem Soc Rev 2011;40:3824.
Joshi M, Butola BS, Saha K. Advances in topical drug delivery system: micro to nanofibrous structures. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2014;14:853.
Kenry, Lim CT. Nanofiber technology: current status and emerging developments. Prog Polym Sci 2017;70:1.
Kim BS, Kim IS. Recent nanofiber technologies. Polym Rev 2011;51:235.
Zhou X, Wang Y, Gong C, Liu B, Wei G. Production, structural design, functional control, and broad applications of carbon nanofiber-based nanomaterials: a comprehensive review. Chem Eng J 2020;402:126189.
Matsumoto H, Tanioka A. Functionality in electrospun nanofibrous membranes based on fiber’s size, surface area, and molecular orientation. Membranes 2011;1:249.
Toriello M, Afsari M, Shon HK, Tijing LD. Progress on the fabrication and application of electrospun nanofiber composites. Membranes 2020;10:204.
Stout DA. Recent advancements in carbon nanofiber and carbon nanotube applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Design 2015;21:2037.
Parveen S, Rana S, Fangueiro R. A review on nanomaterial dispersion, microstructure, and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube and nanofiber reinforced cementitious composites. J Nanomater 2013;2013:710175.
Wang X, Ding B, Sun G, Wang M, Yu J. Electro-spinning/netting: a strategy for the fabrication of three-dimensional polymer nano-fiber/nets. Prog Mater Sci 2013;58:1173.
Garg T, Rath G, Goyal AK. Biomaterials-based nanofiber scaffold: targeted and controlled carrier for cell and drug delivery. J Drug Target 2015;23:202.
Sundaramurthi D, Krishnan UM, Sethuraman S. Electrospun nanofibers as scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Polym Rev 2014;54:348.
Xue J, Wu T, Dai Y, Xia Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev 2019;119:5298.
Liao X, Dulle M, de Souza e Silva JM, Wehrspohn RB, Agarwal S, Foerster S, Hou H, Smith P, Greiner A. High strength in combination with high toughness in robust and sustainable polymeric materials. Science 2019;366:1376.
Xue J, Xie J, Liu W, Xia Y. Electrospun nanofibers: new concepts, materials, and applications. Accounts Chem Res 1976;2017:50.
Inagaki M, Yang Y, Kang F. Carbon nanofibers prepared via electrospinning. Adv Mater 2012;24:2547.
Fadil F, Affandi NDN, Misnon MI, Bonnia NN, Harun AM, Alam MK. Review on electrospun nanofiber-applied products. Polymers 2021;13:2087.
Sun B, Long YZ, Zhang HD, Li MM, Duvail JL, Jiang XY, Yin HL. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog Polym Sci 2014;39:862.
Chen Y, Dong X, Shafiq M, Myles G, Radacsi N, Mo X. Recent advancements on three-dimensional electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv Fiber Mater 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00170-7 .
Xu T, Ding Y, Liang Z, Sun H, Zheng F, Zhu Z, Zhao Y, Fong H. Three-dimensional monolithic porous structures assembled from fragmented electrospun nanofiber mats/membranes: methods, properties, and applications. Prog Mater Sci 2020;112:100656.
Han S, Nie K, Li J, Sun Q, Wang X, Li X, Li Q. 3D electrospun nanofiber-based scaffolds: from preparations and properties to tissue regeneration applications. Stem Cells Int 2021;2021:8790143.
Cao LT, Fu QX, Si Y, Ding B, Yu JY. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos Commun 2018;10:25.
Cao L, Shan H, Zong D, Yu X, Yin X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Fire-resistant and hierarchically structured elastic ceramic nanofibrous aerogels for efficient low-frequency noise reduction. Nano Lett 2022;22:1609.
Si Y, Wang X, Dou L, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight and fire-resistant ceramic nanofibrous aerogels with temperature-invariant superelasticity. Sci Adv 2018;4:eaas8925.
Cheng X, Liu Y, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Direct synthesis of highly stretchable ceramic nanofibrous aerogels via 3D reaction electrospinning. Nat Commun 2022;13:2637.
Fu Q, Si Y, Duan C, Yan Z, Liu L, Yu J, Ding B. Highly carboxylated, cellular structured, and underwater superelastic nanofibrous aerogels for efficient protein separation. Adv Funct Mater 2019;29:1808234.
Si Y, Fu Q, Wang X, Zhu J, Yu J, Sun G, Ding B. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015;9:3791.
Huang C, Soenen SJ, Rejman J, Lucas B, Braeckmans K, Demeester J, De Smedt SC. Stimuli-responsive electrospun fibers and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 2011;40:2417.
Zhang B, Kang F, Tarascon J, Kim J. Recent advances in electrospun carbon nanofibers and their application in electrochemical energy storage. Prog Mater Sci 2016;76:319.
Luo CJ, Stoyanov SD, Stride E, Pelan E, Edirisinghe M. Electrospinning versus fibre production methods: from specifics to technological convergence. Chem Soc Rev 2012;41:4708.
Li D, Xia YN. Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Adv Mater 2004;16:1151.
Taylor GI. Disintegration of water drops in an electric field. Proc R Soc Lond A 1964;280:383.
Reneker DH, Yarin AL. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008;49:2387.
Reneker DH, Yarin A, Zussman E, Koombhongse S, Kataphinan W. Nanofiber manufacturing: toward better process control. In: Reneker DH, Fong H, editors. Polymeric nanofibers. Washington: American Chemical Society; 2006. p. 7–20.
Shin YM, Hohman MM, Brenner MP, Rutledge GC. Experimental characterization of electrospinning: the electrically forced jet and instabilities. Polymer 2001;42:9955.
Agarwal S, Greiner A, Wendorff JH. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog Polym Sci 2013;38:963.
Yoon J, Yang H, Lee B, Yu W. Recent progress in coaxial electrospinning: new parameters, various structures, and wide applications. Adv Mater 2018;30:1704765.
Rahmati M, Mills DK, Urbanska AM, Saeb MR, Venugopal JR, Ramakrishna S, Mozafari M. Electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Prog Mater Sci 2021;117:100721.
Shi S, Si Y, Han Y, Wu T, Iqbal MI, Fei B, Li RKY, Hu J, Qu J. Recent progress in protective membranes fabricated via electrospinning: advanced materials, biomimetic structures, and functional applications. Adv Mater 2022;34:2107938.
Taylor GI. Electrically driven jets. Proc Roy Soc Lond A 1969;313:453.
He JH, Wu Y, Zuo WW. Critical length of straight jet in electrospinning. Polymer 2005;46:12637.
Lin JY, Ding B, Yu JY, Wu GC, Yang JM, Sun G. Effect of porous structure of electrospun fibers on their specific surface area: theoretical analysis and experimental verification. Int J Nonlinear Sci Num 2010;11:523.
Lin JY, Cai Y, Wang XF, Ding B, Yu JY, Wang MR. Fabrication of biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces inspired by lotus leaf and silver ragwort leaf. Nanoscale 2011;3:1258.
Fashandi H, Karimi M. Pore formation in polystyrene fiber by superimposing temperature and relative humidity of electrospinning atmosphere. Polymer 2012;53:5832.
Chen X, Xu Y, Zhang W, Xu K, Ke Q, Jin X, Huang C. Online fabrication of ultralight, three-dimensional, and structurally stable ultrafine fibre assemblies with a double-porous feature. Nanoscale 2019;11:8185.
Lin J, Ding B, Yu J, Hsieh Y. Direct fabrication of highly nanoporous polystyrene fibers via electrospinning. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2010;2:521.
Lu P, Xia Y. Maneuvering the internal porosity and surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene yarns by controlling the solvent and relative humidity. Langmuir 2013;29:7070.
Cao L, Si Y, Yin X, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight and resilient electrospun fiber sponge with a lamellar corrugated microstructure for effective low-frequency sound absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:35333.
Zhang C, Yu S. Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: recent advances and future prospects. Chem Soc Rev 2014;43:4423.
Dias JR, Granja PL, Bartolo PJ. Advances in electrospun skin substitutes. Prog Mater Sci 2016;84:314.
Cooper CJ, Mohanty AK, Misra M. Electrospinning process and structure relationship of biobased poly(butylene succinate) for nanoporous fibers. ACS Omega 2018;3:5547.
Fu Q, Duan C, Yan Z, Li Y, Si Y, Liu L, Yu J, Ding B. Nanofiber-based hydrogels: controllable synthesis and multifunctional applications. Macromol Rapid Comm 2018;39:1800058.
Lu X, Si Y, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. In situ synthesis of mechanically robust, transparent nanofiber-reinforced hydrogels for highly sensitive multiple sensing. Adv Funct Mater 2021;31:2103117.
Xu W, Ma J, Jabbari E. Material properties and osteogenic differentiation of marrow stromal cells on fiber-reinforced laminated hydrogel nanocomposites. Acta Biomater 1992;2010:6.
An D, Ji Y, Chiu A, Lu YC, Song W, Zhai L, Qi L, Luo D, Ma M. Developing robust, hydrogel-based, nanofiber-enabled encapsulation devices (NEEDs) for cell therapies. Biomaterials 2015;37:40.
Si Y, Wang L, Wang X, Tang N, Yu J, Ding B. Ultrahigh-water-content, superelastic, and shape-memory nanofiber-assembled hydrogels exhibiting pressure-responsive conductivity. Adv Mater 2017;29:1700339.
Coburn J, Gibson M, Bandalini PA, Laird C, Mao HQ, Moroni L, Seliktar D, Elisseeff J. Biomimetics of the extracellular matrix: an integrated three-dimensional fiber-hydrogel composite for cartilage tissue engineering. Smart Struct Syst 2011;7:213.
Chen Y, Shafiq M, Liu M, Morsi Y, Mo X. Advanced fabrication for electrospun three-dimensional nanofiber aerogels and scaffolds. Bioact Mater 2020;5:963.
Chen W, Xu Y, Liu Y, Wang Z, Li Y, Jiang G, Mo X, Zhou G. Three-dimensional printed electrospun fiber-based scaffold for cartilage regeneration. Mater Design 2019;179:107886.
Chen W, Xu Y, Li Y, Jia L, Mo X, Jiang G, Zhou G. 3D printing electrospinning fiber-reinforced decellularized extracellular matrix for cartilage regeneration. Chem Eng J 2019;382:122986.
Lee S, Nowicki M, Harris B, Zhang LG. Fabrication of a highly aligned neural scaffold via a table top stereolithography 3D printing and electrospinning. Tissue Eng A 2017;23:491.
Yu Y, Hua S, Yang M, Fu Z, Teng S, Niu K, Zhao Q, Yi C. Fabrication and characterization of electrospinning/3D printing bone tissue engineering scaffold. RSC Adv 2016;6:110557.
Rampichová M, Kuželová EK, Filová E, Chvojka J, Šafk J, Pelcl M, Daňková J, Prosecká E, Buzgo M, Plencner M, Lukáš D, Amler E. Composite 3D printed scaffold with structured electrospun nanofibers promotes chondrocyte adhesion and infiltration. Cell Adhes Migr 2018;12:271.
Yuan H, Zhou Q, Li B, Bao M, Lou X, Zhang Y. Direct printing of patterned three-dimensional ultrafine fibrous scaffolds by stable jet electrospinning for cellular ingrowth. Biofabrication 2015;7:045004.
Yi B, Zhang H, Yu Z, Yuan H, Wang X, Zhang Y. Fabrication of high performance silk fibroin fibers via stable jet electrospinning for potential use in anisotropic tissue regeneration. J Mater Chem B 2018;6:3934.
Jin X, Al-Qatatsheh A, Subhani K, Salim NV. Biomimetic and flexible 3D carbon nanofiber networks with fire-resistant and high oil-sorption capabilities. Chem Eng J 2021;412:128635.
Zhao P, Cao MY, Gu HB, Gao Q, Xia N, He Y, Fu JZ. Research on the electrospun foaming process to fabricate three-dimensional tissue engineering scaffolds. J Appl Polym Sci 2018;135:46898.
Chen YJ, Jia ZH, Shafiq M, Xie XR, Xiao XH, Castro R, Rodrigues J, Wu JL, Zhou GD, Mo XM. Gas foaming of electrospun poly(L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofiber scaffolds to promote cellular infiltration and tissue regeneration. Colloid Surf B 2021;201:111637.
Zhang K, Bai X, Yuan Z, Cao X, Jiao X, Li Y, Qin Y, Wen Y, Zhang X. Layered nanofiber sponge with an improved capacity for promoting blood coagulation and wound healing. Biomaterials 2019;204:70.
Rao F, Yuan Z, Li M, Yu F, Fang X, Jiang B, Wen Y, Zhang P. Expanded 3D nanofibre sponge scaffolds by gas-foaming technique enhance peripheral nerve regeneration. Artif Cell Nanomed Biotechnol 2019;47:491.
Kim SE, Tiwari AP. Three dimensional polycaprolactone/cellulose scaffold containing calcium-based particles: a new platform for bone regeneration. Carbohyd Polym 2020;250:116880.
Joshi MK, Pant HR, Tiwari AP, Kim HJ, Park CH, Kim CS. Multi-layered macroporous three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold via a novel gas foaming technique. Chem Eng J 2015;275:79.
Jiang J, Carlson MA, Teusink MJ, Wang H, MacEwan MR, Xie J. Expanding two-dimensional electrospun nanofiber membranes in the third dimension by a modified gas-foaming technique. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2015;1:991.
Jiang J, Li Z, Wang H, Wang Y, Carlson MA, Teusink MJ, MacEwan MR, Gu L, Xie J. Expanded 3D nanofiber scaffolds: cell penetration, neovascularization, and host response. Adv Healthc Mater 2016;5:2993.
Jia ZH, Liu Y, Wang YY, Peng SY, Jia P, Zhang W, Tan XY. Gas-foaming three-dimensional electrospun nanofiber scaffold improved three-dimensional cartilage regeneration. Mater Res Express 2021;8:085403.
Karki HP, Kafle L, Ojha DP, Song JH, Kim HJ. Three-dimensional nanoporous polyacrylonitrile-based carbon scaffold for effective separation of oil from oil/water emulsion. Polymer 2018;153:597.
Karki HP, Kafle L, Kim HJ. Modification of 3D polyacrylonitrile composite fiber for potential oil-water mixture separation. Sep Purif Technol 2019;229:115840.
Yuan ZP, Li YS, Zhao D, Zhang KX, Wang F, Wang CT, Wen YQ. High efficiency 3D nanofiber sponge for bilirubin removal used in hemoperfusion. Colloid Surf B 2018;172:161.
Gao Q, Gu HB, Zhao P, Zhang CM, Cao MY, Fu J, He Y. Fabrication of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds with 3D controllable geometric shapes. Mater Des 2018;157:159.
Jing X, Li H, Mi H, Liu Y, Tan Y. Fabrication of fluffy shish-kebab structured nanofibers by electrospinning, CO2 escaping foaming and controlled crystallization for biomimetic tissue engineering scaffolds. Chem Eng J 2019;372:785.
Jiang J, Chen S, Wang H, Carlson MA, Gombart AF, Xie J. CO2-expanded nanofiber scaffolds maintain activity of encapsulated bioactive materials and promote cellular infiltration and positive host response. Acta Biomater 2018;68:237.
Dong X, Cao L, Si Y, Ding B, Deng H. Cellular structured CNTs@SiO2 nanofibrous aerogels with vertically aligned vessels for salt-resistant solar desalination. Adv Mater 2020;32:1908269.
Zhang M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Song J, Si Y, Yan J, Ma C, Liu Y, Yu J, Ding B. Conductive and elastic TiO2 nanofibrous aerogels: a new concept toward self-supported electrocatalysts with superior activity and durability. Angew Chem Int Ed 2020;59:2.
Zhang M, Zhang L, Huang S, Wang Y, Si Y, Ma C, Zhang P, Liu Y, Yu J, Ding B. 2D gallium molybdenum selenide grown on a hollow carbon nanofibrous aerogel for high-efficiency electroreduction of nitrogen: optimized basal plane activity via selenium vacancy modulation. Appl Catal B-Environ 2021;292:120175.
Liao Y, Song J, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Superelastic and photothermal RGO/Zr-doped TiO2 nanofibrous aerogels enable the rapid decomposition of chemical warfare agents. Nano Lett 2022;22:4368.
Zhang F, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Sub-nanoporous engineered fibrous aerogel molecular sieves with nanogating channels for reversible molecular separation. Small 2022;18:2202173.
Wang L, Qiu Y, Lv H, Si Y, Liu L, Zhang Q, Cao J, Yu J, Li X, Ding B. 3D superelastic scaffolds constructed from flexible inorganic nanofibers with self-fitting capability and tailorable gradient for bone regeneration. Adv Funct Mater 2019;29:1901407.
Dong X, Si Y, Chen C, Ding B, Deng H. Reed leaves inspired silica nanofibrous aerogels with parallel-arranged vessels for salt-resistant solar desalination. ACS Nano 2021;15:12256.
Si Y, Yu J, Tang X, Ge J, Ding B. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat Commun 2014;5:5802.
Dou L, Zhang X, Shan H, Cheng X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Interweaved cellular structured ceramic nanofibrous aerogels with superior bendability and compressibility. Adv Funct Mater 2020;30:2005928.
Li Y, Cao L, Yin X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Semi-interpenetrating polymer network biomimetic structure enables superelastic and thermostable nanofibrous aerogels for cascade filtration of PM2.5. Adv Funct Mater 2020;30:1910426.
Wang F, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Tailoring nanonets-engineered superflexible nanofibrous aerogels with hierarchical cage-like architecture enables renewable antimicrobial air filtration. Adv Funct Mater 2021;31:2107223.
Wang F, Dou L, Dai J, Li Y, Huang L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. In situ synthesis of biomimetic silica nanofibrous aerogels with temperature-invariant superelasticity over one million compressions. Angew Chem Int Ed 2020;59:8285.
Cao L, Si Y, Wu Y, Wang X, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight, superelastic and bendable lashing-structured nanofibrous aerogels for effective sound absorption. Nanoscale 2019;11:2289.
Wu H, Cai H, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight, superelastic, and washable nanofibrous sponges with rigid-flexible coupling architecture enable reusable warmth retention. Nano Lett 2022;22:830.
Cao L, Yu X, Yin X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Hierarchically maze-like structured nanofiber aerogels for effective low-frequency sound absorption. J Colloid Interf Sci 2021;597:21.
Dou L, Zhang X, Cheng X, Ma Z, Wang X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Hierarchical cellular structured ceramic nanofibrous aerogels with temperature-invariant superelasticity for thermal insulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:29056.
Liao Y, Yang F, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Nanoflake-engineered zirconic fibrous aerogels with parallel-arrayed conduits for fast nerve agent degradation. Nano Lett 2021;21:8839.
Wang F, Dai J, Huang L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Biomimetic and superelastic silica nanofibrous aerogels with rechargeable bactericidal function for antifouling water disinfection. ACS Nano 2020;14:8975.
Zhang M, Dai J, Huang S, Fang D, Liu Y, Yu J, Ding B, Greiner A. Pt/TiO2-x nanofibrous aerogel for effective nitrogen reduction: a simple strategy for simultaneous Pt formation and TiO2-x vacancy engineering. Chin Chem Lett 2022;33:1001.
Si Y, Wang X, Yan C, Yang L, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight biomass-derived carbonaceous nanofibrous aerogels with superelasticity and high pressure-sensitivity. Adv Mater 2016;28:9512.
Zong D, Cao L, Yin X, Si Y, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. Flexible ceramic nanofibrous sponges with hierarchically entangled graphene networks enable noise absorption. Nat Commun 2021;12:6599.
Ziai Y, Petronella F, Rinoldi C, Nakielski P, Zakrzewska A, Kowalewski TA, Augustyniak W, Li X, Calogero A, Sabala I, Ding B, De Sio L, Pierini F. Chameleon-inspired multifunctional plasmonic nanoplatforms for biosensing applications. NPG Asia Mater 2022;14:18.
Li Y, Wang J, Qian D, Chen L, Mo X, Wang L, Wang Y, Cui W. Electrospun fibrous sponge via short fiber for mimicking 3D ECM. J Nanobiotechnol 2021;19:131.
Soliman S, Pagliari S, Rinaldi A, Forte G, Fiaccavento R, Pagliari F, Franzese O, Minieri M, Di Nardo P, Licoccia S, Traversa E. Multiscale three-dimensional scaffolds for soft tissue engineering via multimodal electrospinning. Acta Biomater 2010;6:1227.
Pham QP, Sharma U, Mikos AG. Electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration. Biomacromol 2006;7:2796.
Han D, Gouma PI. Electrospun bioscaffolds that mimic the topology of extracellular matrix. Nanomedicine 2006;2:37.
Erisken C, Kalyon DM, Wang H. Functionally graded electrospun polycaprolactone and β-tricalcium phosphate nanocomposites for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2008;29:4065.
Kim G, Son J, Park S, Kim W. Hybrid process for fabricating 3D hierarchical scaffolds combining rapid prototyping and electrospinning. Macromol Rapid Comm 2008;29:1577.
Martins A, Chung S, Pedro AJ, Sousa RA, Marques AP, Reis RL, Neves NM. Hierarchical starch-based fibrous scaffold for bone tissue engineering applications. J Tissue Eng Regen M 2009;3:37.
Moroni L, Schotel R, Hamann D, de Wijn JR, van Blitterswijk CA. 3D fiber-deposited electrospun integrated scaffolds enhance cartilage tissue formation. Adv Funct Mater 2008;18:53.
Yang XC, Shah JD, Wang HJ. Nanofiber enabled layer-by-layer approach toward three-dimensional tissue formation. Tissue Eng A 2009;15:945.
Park SH, Kim TG, Kim HC, Yang DY, Park TG. Development of dual scale scaffolds via direct polymer melt deposition and electrospinning for applications in tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater 2008;4:1198.
Kim SJ, Jang DH, Park WH, Min BM. Fabrication and characterization of 3-dimensional PLGA nanofiber/microfiber composite scaffolds. Polymer 2010;51:1320.
Zhang X, Cheng X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Elastic and highly fatigue resistant ZrO2-SiO2 nanofibrous aerogel with low energy dissipation for thermal insulation. Chem Eng J 2022;433:133628.
Zhang X, Cheng X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. All-ceramic and elastic aerogels with nanofibrous-granular binary synergistic structure for thermal superinsulation. ACS Nano 2022;16:5487.
Zhang X, Wang F, Dou L, Cheng X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Ultrastrong, superelastic, and lamellar multiarch structured ZrO2-Al2O3 nanofibrous aerogels with high-temperature resistance over 1300 °C. ACS Nano 2020;14:15616.
Li SZ, Wu F, Zhang X, Han GT, Si Y, Yu JY, Ding B. Flexible Al2O3/ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes for thermal insulation. CrystEngComm 1859;2022:24.
Zhang X, Liu C, Zhang X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Super strong, shear resistant, and highly elastic lamellar structured ceramic nanofibrous aerogels for thermal insulation. J Mater Chem A 2021;9:27415.
Wang W, Itoh S, Konno K, Kikkawa T, Ichinose S, Sakai K, Ohkuma T, Watabe K. Effects of Schwann cell alignment along the oriented electrospun chitosan nanofibers on nerve regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A 2009;91A:994.
Shim IK, Suh WH, Lee SY, Lee SH, Heo SJ, Lee MC, Lee SJ. Chitosan nano-/microfibrous double-layered membrane with rolled-up three-dimensional structures for chondrocyte cultivation. J Biomed Mater Res A 2009;90A:595.
Teo WE, Liao S, Chan CK, Ramakrishna S. Remodeling of three-dimensional hierarchically organized nanofibrous assemblies. Curr Nanosci 2008;4:361.
Ki CS, Kim JW, Hyun JH, Lee KH, Hattori M, Rah DK, Park YH. Electrospun three-dimensional silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffold. J Appl Polym Sci 2007;106:3922.
Roy S, Kuddannaya S, Das T, Lee HY, Lim J, Hu X, Yoona YC, Kim J. A novel approach for fabricating highly tunable and fluffy bioinspired 3D poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) fiber scaffolds. Nanoscale 2017;9:7081.
Hong S, Kim G. Fabrication of size-controlled three-dimensional structures consisting of electrohydrodynamically produced polycaprolactone micro/nanofibers. Appl Phys A Mater 2011;103:1009.
Jing X, Li H, Mi HY, Liu YJ, Tan YM. Fabrication of three-dimensional fluffy nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering via electrospinning and CO2 escaping foaming. Ind Eng Chem Res 2019;58:9412.
Smit E, Buttner U, Sanderson RD. Continuous yarns from electrospun fibers. Polymer 2005;46:2419.
Teo WE, Gopal R, Ramaseshan R, Fujihara K, Ramakrishna S. A dynamic liquid support system for continuous electrospun yarn fabrication. Polymer 2007;48:3400.
Gang EH, Ki CS, Kim JW, Lee J, Cha BG, Lee KH, Park YH. Highly porous three-dimensional poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) microfibrous scaffold prepared by electrospinning method: a comparison study with other PLGA type scaffolds on its biological evaluation. Fiber Polym 2012;13:685.
Yokoyama Y, Hattori S, Yoshikawa C, Yasuda Y, Koyama H, Takato T, Kobayashi H. Novel wet electrospinning system for fabrication of spongiform nanofiber 3-dimensional fabric. Mater Lett 2009;63:754.
Kasuga T, Obata A, Maeda H, Ota Y, Yao X, Oribe K. Siloxane-poly(lactic acid)-vaterite composites with 3D cotton-like structure. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2012;23:2349.
Chakrapani VY, Kumar T, Raj DK, Kumary TV. Electrospun 3D composite scaffolds for craniofacial critical size defects. J Mater Sci 2017;28:119.
Lin YZ, Zhong LB, Dou S, Shao ZD, Liu Q, Zheng YM. Facile synthesis of electrospun carbon nanofiber/graphene oxide composite aerogels for high efficiency oils absorption. Environ Int 2019;128:37.
Jin L, Wang T, Feng ZQ, Zhu ML, Leach MK, Naim YI, Jiang Q. Fabrication and characterization of a novel fluffy polypyrrole fibrous scaffold designed for 3D cell culture. J Mater Chem 2012;22:18321.
Yoon CK, Park BK, Lee WI. Characteristics of micro-glass bead/PLA porous composite prepared by electrospinning. Adv Compos Mater 2018;27:183.
Zhang D, Chang J. Electrospinning of three-dimensional nanofibrous tubes with controllable architectures. Nano Lett 2008;8:3283.
Park KY, Ramaraj B, Choi WS, Yoon KR. Fabrication and metallization of 3D electrospun nanofiberous architecture with gold and silver coating for applications related to electrochemical supercapacitors. Mater Chem Phys 2013;142:600.
Chang GQ, Zhu XF, Li AK, Kan WW, Warren R, Zhao RG, Wang XL, Xue G, Shen JY, Lin LW. Formation and self-assembly of 3D nanofibrous networks based on oppositely charged jets. Mater Design 2016;97:126.
Jin L, Feng ZQ, Wang T, Ren ZZ, Ma SS, Wu JH, Sun DP. A novel fluffy hydroxylapatite fiber scaffold with deep interconnected pores designed for three-dimensional cell culture. J Mater Chem B 2014;2:129.
Kim TG, Chung HJ, Park TG. Macroporous and nanofibrous hyaluronic acid/collagen hybrid scaffold fabricated by concurrent electrospinning and deposition/leaching of salt particles. Acta Biomater 2008;4:1611.
Schneider OD, Weber F, Brunner TJ, Loher S, Ehrbar M, Schmidlin PR, Stark WJ. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of flexible, cottonwool-like nanocomposites as bone substitute material for complex defects. Acta Biomater 2009;5:1775.
Hwang TI, Maharjan B, Tiwari AP, Lee S, Joshi MK, Park CH, Kim CS. Facile fabrication of spongy nanofibrous scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Mater Lett 2018;219:119.
Lee S, Joshi MK, Tiwari AP, Maharjan B, Kim KS, Yun YH, Park CH, Kim CS. Lactic acid assisted fabrication of bioactive three-dimensional PLLA/β-TCP fibrous scaffold for biomedical application. Chem Eng J 2018;347:771.
Choi W, Lee S, Kim SH, Jang JH. Polydopamine inter-fiber networks: new strategy for producing rigid, sticky, 3D fluffy electrospun fibrous polycaprolactone sponges. Macromol Biosci 2016;16:824.
Cheng M, Qin Z, Hu S, Yu H, Zhu M. Use of electrospinning to directly fabricate three-dimensional nanofiber stacks of cellulose acetate under high relative humidity condition. Cellulose 2017;24:219.
Kim JI, Lee JC, Kim MJ, Park CH, Kim CS. The impact of humidity on the generation and morphology of the 3D cotton-like nanofibrous piezoelectric scaffold via an electrospinning method. Mater Lett 2019;236:510.
Wu H, Zhao L, Si Y, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight and superelastic fibrous sponges with effective heat preservation and photo-thermal conversion for personal cold protection. Compos Commun 2021;25:100766.
Feng Y, Zong D, Hou Y, Yin X, Zhang S, Duan L, Si Y, Jia Y, Ding B. Gradient structured micro/nanofibrous sponges with superior compressibility and stretchability for broadband sound absorption. J Colloid Interf Sci 2021;593:59.
Xu H, Wang S, Gong X, Yang M, Liu X, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. Superelastic, ultralight, and washable electrospun fibrous sponges for effective warmth retention. Compos Commun 2022;29:101024.
Zong D, Cao L, Li Y, Yin X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Interlocked dual-network and superelastic electrospun fibrous sponges for efficient low-frequency noise absorption. Small Str 2020;1:2000004.
Zhao L, Wu H, Jiao W, Yin X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Superelastic, lightweight, and flame-retardant 3D fibrous sponge fabricated by one-step electrospinning for heat retention. Compos Commun 2021;25:100681.
Zhang R, Gong X, Wang S, Tian Y, Liu Y, Zhang S, Yu J, Ding B. Superelastic and fire-retardant nano-/microfibrous sponges for high-efficiency warmth retention. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:58027.
Zheng Z, Wu H, Si Y, Jia Y, Ding B. Stretchable and resilient fibrous sponges tailored by interlocking double-network for warmth retention. Compos Commun 2021;27:100788.
Wu H, Li Y, Zhao L, Wang S, Tian Y, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Stretchable and superelastic fibrous sponges tailored by “stiff-soft” bicomponent electrospun fibers for warmth retention. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020;12:27562.
Kalauni K, Pawar SJ. A review on the taxonomy, factors associated with sound absorption and theoretical modeling of porous sound absorbing materials. J Porous Mat 2019;26:1795.
Tang XN, Yan X. Acoustic energy absorption properties of fibrous materials: a review. Composites A 2017;101:360.
Wu H, Zhao L, Zhang S, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Ultralight and mechanically robust fibrous sponges tailored by semi-interpenetrating polymer networks for warmth retention. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:18165.
Dou L, Cheng X, Zhang X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Temperature-invariant superelastic, fatigue resistant, and binary-network structured silica nanofibrous aerogels for thermal superinsulation. J Mater Chem A 2020;8:7775.
Dou L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Semi-template based, biomimetic-architectured, and mechanically robust ceramic nanofibrous aerogels for thermal insulation. Nano Res 2022;15:5581.
Li Y, Yin X, Yu J, Ding B. Electrospun nanofibers for high-performance air filtration. Compos Commun 2019;15:6.
Li Y, Cao L, Yin X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Ultrafine, self-crimp, and electret nano-wool for low-resistance and high-efficiency protective filter media against PM0.3. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2020;578:565.
Qian ZC, Wang Z, Chen Y, Tong SR, Ge MF, Zhao N, Xu J. Superelastic and ultralight polyimide aerogels as thermal insulators and particulate air filters. J Mater Chem A 2018;6:828.
Zhang J, Zhang F, Song J, Liu L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Electrospun flexible nanofibrous membranes for oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A 2019;7:20075.
Zhang J, Liu L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes: an effective arsenal for the purification of emulsified oily wastewater. Adv Funct Mater 2020;30:2002192.
Zhang J, Liu L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Rational design of electrospun nanofibrous materials for oil/water emulsion separation. Mat Chem Front 2021;5:97.
Lee S, Kim B, Kim SH, Kim E, Jang JH. Superhydrophobic, reversibly elastic, moldable, and electrospun (SupREME) fibers with multimodal functions: from oil absorbents to local drug delivery adjuvants. Adv Funct Mater 2017;27:1702310.
Fu Q, Liu L, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B. Shapeable, underwater superelastic, and highly phosphorylated nanofibrous aerogels for large-capacity and high-throughput protein separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:44874.
Jang JH, Castano O, Kim HW. Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 2009;61:1065.
Dong Y, Zheng Y, Zhang K, Yao Y, Wang L, Li X, Yu J, Ding B. Electrospun nanofibrous materials for wound healing. Adv Fiber Mater 2020;2:212.
Wang L, Qiu Y, Guo Y, Si Y, Liu L, Cao J, Yu J, Li X, Zhang Q, Ding B. Smart, elastic, and nanofiber-based 3D scaffolds with self-deploying capability for osteoporotic bone regeneration. Nano Lett 2019;19:9112.
Wang J, Cheng Y, Wang H, Wang Y, Zhang K, Fan C, Wang H, Mo X. Biomimetic and hierarchical nerve conduits from multifunctional nanofibers for guided peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater 2020;117:180.
Chen Y, Xu W, Shafiq M, Tang J, Hao J, Xie X, Yuan Z, Xiao X, Liu Y, Mo X. Three-dimensional porous gas-foamed electrospun nanofiber scaffold for cartilage regeneration. J Colloid Interf Sci 2021;603:94.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2021YFE0105100), the Natural Science Foundation of China (51873031 and 52103050), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (21ZR1402600 and 21ZR1401800), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (CUSF-DH-D-2020040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, D., Zhang, X., Yin, X. et al. Electrospun Fibrous Sponges: Principle, Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4, 1434–1462 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00202-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00202-2