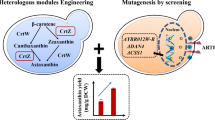
Abstract
(2S)-Naringenin, a dihydro-flavonoid, serves as a crucial precursor for flavonoid synthesis due to its extensive medicinal values and physiological functions. A pathway for the synthesis of (2S)-naringenin from glucose has previously been constructed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through metabolic engineering. However, this synthetic pathway of (2S)-naringenin is lengthy, and the genes involved in the competitive pathway remain unknown, posing challenges in significantly enhancing (2S)-naringenin production through metabolic modification. To address this issue, a novel high-throughput screening (HTS) method based on color reaction combined with a random mutagenesis method called atmospheric room temperature plasma (ARTP), was established in this study. Through this approach, a mutant (B7-D9) with a higher titer of (2S)-naringenin was obtained from 9600 mutants. Notably, the titer was enhanced by 52.3% and 19.8% in shake flask and 5 L bioreactor respectively. This study demonstrates the successful establishment of an efficient HTS method that can be applied to screen for high-titer producers of (2S)-naringenin, thereby greatly improving screening efficiency and providing new insights and solutions for similar product screenings.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data presented in this study is available from the correspoding author upon reasonable request.
References
Akhter S, Arman MSI, Tayab MA, Islam MN, Xiao J (2022) Recent advances in the biosynthesis, bioavailability, toxicology, pharmacology, and controlled release of citrus neohesperidin. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 23:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2149466
Cai M, Wu Y, Qi H, He J, Wu Z, Xu H, Qiao M (2021) Improving the level of the tyrosine biosynthesis pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through HTZ1 Knockout and Atmospheric and Room Temperature Plasma (ARTP) Mutagenesis. ACS Synth Biol 10(1):49–62. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00448
Cai J, Wen H, Zhou H, Zhang D, Lan D, Liu S, Li C, Dai X, Song T, Wang X, He Y, He Z, Tan J, Zhang J (2023) Naringenin: a flavanone with anti-inflammatory and anti-infective properties. Biomed Pharmacother 164:114990–115006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114990
Cao S, Zhou X, Jin W, Wang F, Tu R, Han S, Chen H, Chen C, Xie G-J, Ma F (2017) Improving of lipid productivity of the oleaginous microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa via atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP). Bioresour Technol 244(2):1400–1406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.039
Chengcheng S, Guangjian L, Hongbiao L, Yunbin L, Shiqin Y, Jingwen Z (2021) Enhancing flavan-3-ol biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Agric Food Chem 69(43):12763–12772. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04489
Frydman A, Liberman R, Huhman DV, Carmeli-Weissberg M, Sapir-Mir M, Ophir R, Sumner LW, Eyal Y (2013) The molecular and enzymatic basis of bitter/non-bitter flavor of citrus fruit: evolution of branch-forming rhamnosyl-transferases under domestication. Plant J 73(1):166–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12030
Gao S, Zhou H, Zhou J, Chen J (2020) Promoter-Library-Based Pathway Optimization for Efficient (2S)-Naringenin [roduction from p-Coumaric Acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Agric Food Chem 68(25):6884–6891. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01130
Hartmann M, Schneider TR, Pfeil A, Heinrich G, Lipscomb WN, Braus GH (2003) Evolution of feedback-inhibited beta/alpha barrel isoenzymes by gene duplication and a single mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(3):862–867. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0337566100
Hassing E-J, de Groot PA, Marquenie VR, Pronk JT, Daran J-MG (2019) Connecting central carbon and aromatic amino acid metabolisms to improve de novo 2-phenylethanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 56:165–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.09.011
Jiang G, Yang Z, Wang Y, Yao M, Chen Y, Xiao W, Yuan Y (2020) Enhanced astaxanthin production in yeast via combined mutagenesis and evolution. Biochem Eng J 156:107519–107528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2020.107519
Juca MM, Sales Cysne Filho FM, de Almeida JC, Mesquita DdS, de Moraes Barriga JR, Cilene Ferreira DK, Barbosa TM, Vasconcelos LC, Almeida Moreira Leal LK, Ribeiro Honorio Junior JE, Mendes Vasconcelos SM (2020) Flavonoids: biological activities and therapeutic potential. Biochem Eng J 34(5):692–705. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1493588
Kalra S, Peyser R, Ho J, Babbin C, Bohan N, Cortes A, Erley J, Fatima M, Flinn J, Horwitz E, Hsu R, Lee W, Lu V, Narch A, Navas D, Kalu I, Ouanemalay E, Ross S, Sowole F, Specht E, Woo J, Yu K, Coolon JD (2023) Genome-wide gene expression responses to experimental manipulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae repressor activator protein 1 (Rap1) expression level. Genomics 115(3):110625–110635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110625
Kawai K, Kanesaki Y, Yoshikawa H, Hirasawa T (2019) Identification of metabolic engineering targets for improving glycerol assimilation ability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on adaptive laboratory evolution and transcriptome analysis. J Biosci Bioeng 128(2):162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.02.001
Koopman F, Beekwilder J, Crimi B, van Houwelingen A, Hall RD, Bosch D, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT, Daran J-M (2012) De novo production of the flavonoid naringenin in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 11:155–169. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-11-155
Kopustinskiene DM, Jakstas V, Savickas A, Bernatoniene J (2020) Flavonoids as anticancer agents. Nutrients 12(2):457–457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020457
Lee DYW, Zhang W-Y, Karnati VVR (2003) Total synthesis of puerarin, an isoflavone C-glycoside. Tetrahedron Lett 44(36):6857–6859. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(03)01715-5
Li M, Kildegaard KR, Chen Y, Rodriguez A, Borodina I, Nielsen J (2015) De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 32:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.08.007
Li H, Gao S, Zhang S, Zeng W, Zhou J (2021) Effects of metabolic pathway gene copy numbers on the biosynthesis of (2S)-naringenin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 325:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.11.009
Li H, Lyv Y, Zhou S, Yu S, Zhou J (2022a) Microbial cell factories for the production of flavonoids–barriers and opportunities. Bioresour Technol 360:127538–127549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127538
Li H, Ma W, Lyv Y, Gao S, Zhou J (2022b) Glycosylation modification enhances (2S)-Naringenin Production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ACS Synth Biol 11(7):2339–2347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.2c00065
Lim HG, Jang S, Jang S, Seo SW, Jung GY (2018) Design and optimization of genetically encoded biosensors for high-throughput screening of chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 54:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2018.01.011
Liu W, Zhang B, Jiang R (2017) Improving acetyl-CoA biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via the overexpression of pantothenate kinase and PDH bypass. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0726-z
Liu Q, Yu T, Li X, Chen Y, Campbell K, Nielsen J, Chen Y (2019) Rewiring carbon metabolism in yeast for high level production of aromatic chemicals. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12961-5
Lu M, Liu S, Zhao L, Pei J (2023) Screening β-glucosidase and α-rhamnosidase for biotransformation of naringin to naringenin by the one-pot enzymatic cascade. Enzyme Microb Technol 167:110239–110248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2023.110239
Luo Z, Zeng W, Du G, Liu S, Fang F, Zhou J, Chen J (2017) A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing pyruvate production in Candida glabrata by random mutagenesis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40(5):693–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1734-x
Luwen Z, Jiawei T, Meiqing F, Shaoxin C (2023) Engineering methyltransferase and sulfoxide synthase for high-yield production of ergothioneine. J Agric Food Chem 71(1):671–679. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07859
Meng C, Peng B (2023) Establishment of a high-throughput screening platform to screen Schizochytrium sp. with a high yield of DHA. Algal Res 74:103201–103212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2023.103201
Meng L, Gao X, Liu X, Sun M, Yan H, Li A, Yang Y, Bai Z (2021) Enhancement of heterologous protein production in Corynebacterium glutamicum via atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis and high-throughput screening. J Biotechnol 339:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.07.010
Ottenheim C, Nawrath M, Wu JC (2018) Microbial mutagenesis by atmospheric and room-temperature plasma (ARTP): the latest development. Bioresour Bioprocess 5:12–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-018-0200-1
Pais P, Oliveira J, Almeida V, Yilmaz M, Monteiro PT, Teixeira MC (2021) Transcriptome-wide differences between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii: clues on host survival and probiotic activity based on promoter sequence variability. Genomics 113(2):530–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.11.034
Pandey RP, Parajuli P, Koffas MAG, Sohng JK (2016) Microbial production of natural and non-natural flavonoids: pathway engineering, directed evolution and systems/synthetic biology. Biotechnol Adv 34(5):634–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.02.012
Park SR, Yoon JA, Paik JH, Park JW, Jung WS, Ban Y-H, Kim EJ, Yoo YJ, Han AR, Yoon YJ (2009) Engineering of plant-specific phenylpropanoids biosynthesis in Streptomyces venezuelae. J Biotechnol 141(3–4):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.03.013
Park SY, Yang D, Ha SH, Lee SY (2018) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the production of natural compounds. Adv Biosyst 8(1):589069–589084. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.201700190
Salehi B, Fokou PVT, Sharifi-Rad M, Zucca P, Pezzani R, Martins N, Sharifi-Rad J (2019) The therapeutic potential of naringenin: a review of clinical trials. Pharmaceuticals 12(1):11–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12010011
Siddiqui MS, Thodey K, Trenchard I, Smolke CD (2012) Advancing secondary metabolite biosynthesis in yeast with synthetic biology tools. FEMS Yeast Res 12(2):144–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2011.00774.x
Suastegui M, Guo W, Feng X, Shao Z (2016) Investigating strain dependency in the production of aromatic compounds in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 113(12):2676–2685. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26037
Tang D-M, Zhu C-F, Zhong S-A, Zhou M-D (2011) Extraction of naringin from pomelo peels as dihydrochalcone’s precursor. J Sep Sci 34(1):113–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201000475
Wang Q, Yang J, Zhang X-m, Zhou L, Liao X-L, Yang B (2015) Practical synthesis of naringenin. J Chem Res 8:455–457. https://doi.org/10.3184/174751915x14379994045537
Wei W, Zhang P, Shang Y, Zhou Y, Ye B-C (2020) Metabolically engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for the biosynthesis of naringenin from a mixture of glucose and xylose. Bioresour Technol 314:123726–123735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123726
Yun J, Zabed HM, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Zhao M, Qi X (2022) Improving tolerance and 1,3-propanediol production of Clostridium butyricum using physical mutagenesis, adaptive evolution and genome shuffling. Bioresour Technol 363:127967–127974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127967
Zhang X, Zhang X-F, Li H-P, Wang L-Y, Zhang C, Xing X-H, Bao C-Y (2014) Atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) as a new powerful mutagenesis tool. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(12):5387–5396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5755-y
Zhang X, Zhang C, Zhou Q-Q, Zhang X-F, Wang L-Y, Chang H-B, Li H-P, Oda Y, Xing X-H (2015) Quantitative evaluation of DNA damage and mutation rate by atmospheric and room-temperature plasma (ARTP) and conventional mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(13):5639–5646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6678-y
Zhou G, Tian X, Lin Y, Zhang S, Chu J (2019) Rational high-throughput system for screening of high sophorolipids-producing strains of Candida bombicola. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42(4):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-02062-w
Zhou S, Hao T, Zhou J (2020) Fermentation and metabolic pathway optimization to De Novo synthesize (2S)-naringenin in Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol 30(10):1574–1582. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.2008.08005
Zhou K, Yu C, Liang N, Xiao W, Wang Y, Yao M, Yuan Y (2023) Adaptive evolution and metabolic engineering boost lycopene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via enhanced precursors supply and utilization. J Agric Food Chem 71(8):3821–3831. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c08579
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32021005), and the Starry Night Science Fund of Zhejiang University Shanghai Institute for Advanced Study (Grant No. SN-ZJU-SIAS-0013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q. G. and S. G. designed the study and wrote the manuscript. Q. G., W. Z., and J. Z. critically revised the manuscript. Q. G. performed the experiments and analyzed the results. J. Z. designed and supervised the project. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Gao, S., Zeng, W. et al. Enhancing (2S)-naringenin production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by high-throughput screening method based on ARTP mutagenesis. 3 Biotech 14, 85 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03892-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03892-6