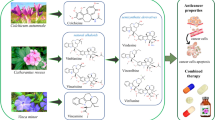
Abstract
Vinca alkaloids including vincristine, vinblastine, vindesine, and vinflunine are chemotherapeutic compounds commonly used to treat various cancers. Vinca alkaloids are one of the first microtubule-targeting agents to be produced and certified for the treatment of hematological and lymphatic neoplasms. Microtubule targeting agents like vincristine and vinblastine work by disrupting microtubule dynamics, causing mitotic arrest and cell death. The key issues facing vinca alkaloids applications include establishing an environment-friendly production technique based on microorganisms, as well as increasing bioavailability without causing harm to patient’s health. The low yield of these vinca alkaloids from the plant and the difficulty of meeting their huge colossal demand around the globe prompted researchers to create a variety of approaches. Endophytes could thus be selected to produce beneficial secondary metabolites required for the biosynthesis of vinca alkaloids. This review covers the significant aspects of these vital drugs, from their discovery to the present day, in a concise manner. In addition, we emphasize the major hurdles that must be overcome in the coming years to improve vinca alkaloid’s effectiveness.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Anjum N, Chandra R (2019) Endophytic bacteria of Catharanthus roseus as an alternative source of vindoline and application of response surface methodology to enhance its production. Arch Biol Sci 71(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS180802044A
Armand JP, Fumoleau P, Marty M, Variol P, Pinel MC, Picard M, Puozzo C (2001) Pharmacokinetics of vinflunine, a novel Vinca alkaloid, during the Phase I dose-escalation study. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 42:381
Arora RD, Menezes RG (2021) Vinca alkaloid toxicity. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Ashoka H, Hegde P, Madihalli C, Kumar A, Shettihalli A (2017) Isolation and detection of vinca alkaloids from endophytes isolated from Catharanthus roseus. Eur J Biomed Pharm Sci 4(10):675–683
Aslam J, Khan SH, Siddiqui ZH, Fatima Z, Maqsood M, Bhat MA, Sharma MP (2010) Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. An important drug: its applications and production. Pharm Glob (IJCP) 4(12):1–16
Ataei-Azimi A, Hashemloian BD, Ebrahimzadeh H, Majd A (2008) High in vitro production of anti-cancer indole alkaloids from periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) tissue culture. Afr J Biotechnol 7(16)
Ayob FW, Simarani K, Zainal Abidin N, Mohamad J (2017) First report on a novel Nigrospora sphaerica isolated from Catharanthus roseus plant with anticarcinogenic properties. Microb Biotechnol 10(4):926–932. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12603
Bandara CJ, Siriwardhana A, Karunaratne DN, Ratnayake Bandara BM, Wickramasinghe A, Krishnarajah SA, Karunaratne V (2021) Production of vincristine and vinblastine by the endophytic fungus Botryosphaeria laricina strain (CRS1) is dependent on stimulating factors present in Catharanthus roseus. J Nat Prod 11(2):221–230. https://doi.org/10.2174/2210315510666200108102735
Banyal A, Thakur V, Thakur R, Kumar P (2021) Endophytic microbial diversity: a new hope for the production of novel anti-tumor and anti-HIV agents as future therapeutics. Curr Microbiol 78(5):1699–1717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02359-2
Barnett CJ, Cullinan GJ, Gerzon K, Hoying RC, Jones WE, Newlon WM, Sweeney MJ (1978) Structure-activity relationships of dimeric Catharanthus roseus alkaloids. 1. Deacetyl vinblastine amide (vindesine) sulfate. J Med Chem 21(1):88–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00199a016
Barrios-Gonzalez J, Fernandez FJ, Tomasini A, Mejia A (2005) Secondary metabolites production by solid-state fermentation. Malays J Microbiol 1(1):1–6
Bellmunt J, Théodore C, Demkov T, Komyakov B, Sengelov L, Daugaard G, von der Maase H (2009) Phase III trial of vinflunine plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone after a platinum-containing regimen in patients with advanced transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelial tract. J Clin Oncol 27(27):4454–4461. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.20.5534
Bennouna J, Delord JP, Campone M, Nguyen L (2008) Vinflunine: a new microtubule inhibitor agent. Clin Cancer Res 14(6):1625–1632. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432
Bertrand S, Bohni N, Schnee S, Schumpp O, Gindro K, Wolfender JL (2014) Metabolite induction via microorganism co-culture: a potential way to enhance chemical diversity for drug discovery. Biotechnol Adv 32(6):1180–1204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.03.001
Bo G, Haiyan L, Lingqi Z (1998) Isolation of a fungus producing Vinblastine. J Yunnan Univ Nat Sci Ed 20(3):214–215
Bonfil RD, Russo DM, Binda MM, Delgado FM, Vincenti M (2002) Higher antitumor activity of vinflunine than vinorelbine against an orthotropic murine model of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Oncol 7(4):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1078-1439(02)00184-9
Bowman LC, Houghton JA, Houghton PJ (1986) GTP influences the binding of vincristine in human tumor cytosols. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 135(3):695–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(86)90984-8
Brogan C (2010) Alkaloids cancer treatments
Budman DR (1997) Vinorelbine (Navelbiner): a third-generation Vinca alkaloid. Cancer Invest 15(5):475–490. https://doi.org/10.3109/07357909709047587
Byrd RL, Rohrbaugh TM, Beverly Raney Jr R, Norris DG (1981) Transient cortical blindness secondary to vincristine therapy in childhood malignancies. Cancer 47(1):37–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)
Caputi L, Franke J, Farrow SC, Chung K, Payne RM, Nguyen TD, O’Connor SE (2018) Missing enzymes in the biosynthesis of the anticancer drug vinblastine in Madagascar periwinkle. Science 360(6394):1235–1239. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat4100
Chandra S (2012) Endophytic fungi: novel sources of anticancer lead molecules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(1):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4128-7
Chandra S, Chandra R (2011) Engineering secondary metabolite production in hairy roots. Phytochem Rev 10(3):371
Coderch C, Morreale A, Gago F (2012) Tubulin-based structure-affinity relationships for antimitotic Vinca alkaloids. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 12(3):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1002/vjch.201900087
Courdavault V, O’Connor SE, Oudin A, Besseau S, Papon N (2020) Towards the microbial production of plant-derived anticancer drugs. Trends Cancer 6(6):444–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2020.02.004
Craig SL, Jensen VB (2017) Animal models in cancer nanotechnology. Cancer nanotechnology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 45–69
Da Silva PP, Meijer L (2012) Search for natural substances with therapeutic activity: Pierre Potier (1934–2006). Med Sci 28(5):534–542. https://doi.org/10.1051/medsci/2012285020
Dandamudi S, Campbell RB (2007) The drug loading, cytotoxicity and tumor vascular targeting characteristics of magnetite in magnetic drug targeting. Biomaterials 28(31):4673–4683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.07.024
Datta A, Srivastava PS (1997) Variation in vinblastine production by Catharanthus roseus, during in vivo and in vitro differentiation. Phytochemistry 46(1):135–137
De Luca V, Marineau C, Brisson N (1989) Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA encoding a plant tryptophan decarboxylase: comparison with animal dopa decarboxylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86(8):2582–2586. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.8.2582
Dhyani P, Quispe C, Sharma E, Bahukhandi A, Sati P, Attri DC, Cho WC (2022) Anticancer potential of alkaloids: a key emphasis to colchicine, vinblastine, vincristine, vindesine, vinorelbine and vincamine. Cancer Cell Int 22(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02624-9
Domenech GH, Vogel CL (2001) A review of vinorelbine in the treatment of breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 2(2):113–128. https://doi.org/10.3816/CBC.2001.n.016
Duflos A, Kruczynski A, Barret JM (2002) Novel aspects of natural and modified vinca alkaloids. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 2(1):55–70. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568011023354452
Dumontet C, Sikic BI (1999) Mechanisms of action of and resistance to anti-tubulin agents: microtubule dynamics, drug transport, and cell death. J Clin Oncol 17(3):1061–1061. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1999.17.3.1061
Dyke RW, Nelson RL, Brade WP (1979) Vindesine a short review of preclinical and first clinical data. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2(4):229–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257185
Elmoslamy SH, Elkady MF, Rezk AH, Abdelfattah YR (2017) Applying taguchi design and large-scale strategy for mycosynthesis of nanosilver from endophytic Trichoderma harzianum SYA.F4 and its application against phytopathogens. Sci Rep 7:45297. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45297
El-Sayed ER (2021) Discovery of the anticancer drug vinblastine from the endophytic Alternaria alternata and yield improvement by gamma irradiation mutagenesis. J Appl Microbiol 131(6):2886–2898. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15169
El-Sayed M, Verpoorte R (2007) Catharanthus terpenoid indole alkaloids: biosynthesis and regulation. Phytochem Rev 6(2):277–305
Facchini PJ (2001) Alkaloid biosynthesis in plants: biochemistry, cell biology, molecular regulation, and metabolic engineering applications. Annu Rev Plant Biol 52(1):29–66. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.29
Facchini PJ, Huber-Allanach KL, Tari LW (2000) Plant aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylases: evolution, biochemistry, regulation, and metabolic engineering applications. Phytochemistry 54(2):121–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(00)00050-9
Fahy J, Duflos A, Ribet JP, Jaequesy JC, Berrier C, Jouannetaud MP, Zunino F (1997) Vinca alkaloids in superacidic media: a method for creating a new family of antitumor derivatives. J Am Chem Soc 119(36):8576–8577
Ferguson PJ, Cass CE (1985) Differential cellular retention of vincristine and vinblastine by cultured human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60/Cl cells: the basis of differential toxicity. Cancer Res 45(11 Pt 1):5480–5488
Ferguson PJ, Phillips JR, Selner M, Cass CE (1984) Differential activity of vincristine and vinblastine against cultured cells. Cancer Res 44(8):3307–3312
Galindo-Solís JM, Fernández FJ (2022) Endophytic fungal terpenoids: natural role and bioactivities. Microorganisms 10(2):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020339
Gidding CM, Kellie SJ, Kamps WA, De Graaf SN (1999) Vincristine revisited. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 29(3):267–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1040-8428(98)00023-7
Goa KL, Faulds D (1994) Vinorelbine. Drugs Aging 5(3):200–234. https://doi.org/10.2165/00002512-199405030-00006
Gregory RK, Smith IE (2000) Vinorelbine—a clinical review. Br J Cancer 82(12):1907–1913. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1203
Groger D (1985) Alkaloids derived from tryptophan. In: Mothes K, Schutte HR, Luckner M (ed) Biochemistry of Alkaloids. VEB Deutscher Verlag, Berlin, pp 272–313
Hill BT, Fiebig HH, Waud WR, Poupon MF, Colpaert F, Kruczynski A (1999) Superior in vivo experimental antitumor activity of vinflunine, relative to vinorelbine, in a panel of human tumor xenografts. Eur J Cancer 35(3):512–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00416-x
Himes RH (1991) Interactions of the Catharanthus (Vinca) alkaloids with tubulin and microtubules. Pharmacol Ther 51(2):257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-7258(91)90081-v
Hisiger S, Jolicoeur M (2007) Analysis of Catharanthus roseus alkaloids by HPLC. Phytochem Rev 6(2–3):207–234
Hong SB, Peebles CA, Shanks JV, San KY, Gibson SI (2006) Expression of the Arabidopsis feedback-insensitive anthranilate synthase holoenzyme and tryptophan decarboxylase genes in Catharanthus roseus hairy roots. J Biotechnol 122(1):28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.08.008
Houghton PJ, Houghton JA, Bowman LC, Hazelton BJ (1987) Therapeutic selectivity of vinca alkaloids: a role for guanosine 5’-triphosphate. Anticancer Drug Des 2(2):165–179
Ishikawa H, Colby DA, Seto S, Va P, Tam A, Kakei H, Boger DL (2009) Total synthesis of vinblastine, vincristine, related natural products, and key structural analogues. J Am Chem Soc 131(13):4904–4916. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja809842b
Jacobs DI, Snoeijer W, Hallard D, Verpoorte R (2004) The Catharanthus alkaloids: pharmacognosy and biotechnology. Curr Med Chem 11(5):607–628. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867043455846
Joel S (1995) The comparative clinical pharmacology of vincristine and vindesine: does vindesine offer any advantage in clinical use. Cancer Treat Rev 21(6):513–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-7372(95)90015-2
Johnson IS (1968) Historical background of Vinca alkaloid research and areas of future interest. Cancer Treat Rep 52(4):455–461
Johnson IS, Wright HF, Svoboda GH, Vlantis J (1960) Anti-tumor principles derived from Vinca rosea Linn I. Vinca leukoblastine and leurosine. Cancer Res 20(7):1016–1022
Johnson IS, Armstrong JG, Gorman M, Burnett JP (1963) The vinca alkaloids: a new class of oncolytic agents. Cancer Res 23(8 Part 1):1390–1427
Johnson SA, Harper P, Hortobagyi GN, Pouillart P (1996) Vinorelbine: an overview. Cancer Treat Rev 22(2):127–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0305-7372(96)90032-8
Jordan MA, Himes RH, Wilson L (1985) Comparison of the effects of vinblastine, vincristine, vindesine, and vinepidine on microtubule dynamics and cell proliferation in vitro. Cancer Res 45(6):2741–2747
Kruczynski A, Barret JM, Etiévant C, Colpaert F, Fahy J, Hill BT (1998a) Antimitotic and tubulin-interacting properties of vinflunine, a novel fluorinated Vinca alkaloid. Biochem Pharmacol 55(5):35–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(97)00505-4
Kruczynski A, Colpaert F, Tarayre JP, Mouillard P, Fahy J, Hill BT (1998b) Preclinical in vivo antitumor activity of vinflunine, a novel fluorinated Vinca alkaloid. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41(6):437–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050764
Kruczynski A, Etievant C, Chansard N, Cabrol N, Astruc J, Chazottes E, Hill BT (1998c) Induction of apoptosis by vinflunine, a novel fluorinated Vinca alkaloid. Ann Oncol 9:102–102
Kumar A (2016) Vincristine and vinblastine: a review. IJMPS 6:23–30
Kumar A, Patil D, Rajamohanan PR, Ahmad A (2013) Isolation, purification and characterization of vinblastine and vincristine from endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum isolated from Catharanthus roseus. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071805
Kumar P, Singh B, Thakur V, Thakur A, Thakur N, Pandey D, Chand D (2019) Hyper-production of taxol from Aspergillus fumigatus, an endophytic fungus isolated from Taxus sp. of the Northern Himalayan region. Biotechnol Rep 24:e00395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00395
Kusari S, Singh S, Jayabaskaran C (2014) Biotechnological potential of plant-associated endophytic fungi: hope versus hype. Trends Biotechnol 32(6):297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.03.009
Leete E (1961) Biogenesis of the Rauwolfia alkaloids—II: the incorporation of tryptophan into serpentine and reserpine. Tetrahedron 14(1–2):35–41
Levac D, Murata J, Kim WS, De Luca V (2008) Application of carborundum abrasion for investigating the leaf epidermis: molecular cloning of Catharanthus roseus 16-hydroxytabersonine-16-O-methyltransferase. Plant J 53(2):225–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03337.x
Lingqi Z, Bo G, Haiyan L, Songrong Z, Hua S, Su G, Rongcheng W (2000) Preliminary study on the isolation of endophytic fungus of Catharanthus roseus and its fermentation to produce products of therapeutic value. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 31(11):805–807
Liscombe DK, O’Connor SE (2011) A virus-induced gene silencing approach to understanding alkaloid metabolism in Catharanthus roseus. Phytochemistry 72(16):1969–1977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.07.001
Liscombe DK, Usera AR, O’Connor SE (2010) Homolog of tocopherol C methyltransferases catalyze N methylation in anticancer alkaloid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(44):18793–18798. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009003107
Liu J, Zhu J, Tang L, Wen W, Lv S, Yu R (2014) Enhancement of vindoline and vinblastine production in suspension-cultured cells of Catharanthus roseus by artemisinic acid elicitation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1432-z
Liu J, Cai J, Wang R, Yang S (2017) Transcriptional regulation and transport of terpenoid indole alkaloid in Catharanthus roseus: exploration of new research directions. Int J Mol Sci 18(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010053
Maqsood M, Abdul M (2017) Yeast extract elicitation increases vinblastine and vincristine yield in protoplast derived tissues and plantlets in Catharanthus roseus. Rev Bras Farmacogn 27:549–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2017.05.008
Martino E, Casamassima G, Castiglione S, Cellupica E, Pantalone S, Papagni F, Collina S (2018) Vinca alkaloids and analogues as anti-cancer agents: looking back, peering ahead. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett 28(17):2816–2826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.06.044
Maswadeh H, Demetzos C, Daliani I, Kyrikou I, Mavromoustakos T, Tsortos A, Nounesis G (2002) A molecular basis explanation of the dynamic and thermal effects of vinblastine sulfate upon di palmitoyl phosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1567:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-2736(02)00564-3
Mckay LI, Cidlowski JA (2003) Corticosteroids in the treatment of neoplasms. In: Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, Bast RC, Gansler TS, Holland JF and Frei E (ed) Cancer Medicine, 6th edn. BC Decker, Hamilton ON, Canada. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK13383/
Memelink J, Verpoorte R, Kijne JW (2001) Orcanization of jasmonate-responsive gene expression in alkaloid metabolism. Trends Plant Sci 6(5):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(01)01924-0
Mistry V, Darji S, Tiwari P, Sharma A (2022) Engineering Catharanthus roseus monoterpenoid indole alkaloid pathway in yeast. J Appl Microbiol 106(7):2337–2347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11883-5
Mollaamin F, Monajjemi M, Mehrzad J (2014) Molecular modelling investigation of an anti-cancer agent joint to SWCNT using theoretical methods. Fuller Nanotub Carbon Nanostruct 22(8):738–751. https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383X.2012.731582
Moreno PR, van der Heijden R, Verpoorte R (1995) Cell and tissue cultures of Catharanthus roseus: a literature survey. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 42(1):1–25
Moudi M, Go R, Yien CYS, Nazre M (2013) Vinca alkaloids. Int J Prev Med 4(11):1231
Munier F, Perentes E, Herbort CP, Uffer S, Biollaz J (1992) Selective loss of optic nerve β-tubulin in vincristine-induced blindness. Am J Med 93(2):232–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(92)90058-j
Ngan VK, Bellman K, Hill BT, Wilson L, Jordan MA (2001) Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by the semisynthetic Vinca alkaloids vinorelbine and its newer derivative vinflunine. Mol Pharmacol 60(1):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.60.1.225
Noble RL (1990) The discovery of the vinca alkaloids—chemotherapeutic agents against cancer. Biochem Cell Biol 68(12):1344–1351
O’Donnell PH, Guo WX, Reynolds CP, Maurer BJ (2002) N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide increases ceramide and is cytotoxic to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines, but not to non-malignant lymphocytes. Leukemia 16(5):902–910. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402485
Oudin A, Mahroug S, Courdavault V, Hervouet N, Zelwer C, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Burlat V (2007) Spatial distribution and hormonal regulation of gene products from methyl erythritol phosphate and monoterpene-secoiridoid pathways in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Mol Biol 65(1):13–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9190-7
Owellen RJ, Owens AH Jr, Donigian DW (1972) The binding of vincristine, vinblastine and colchicine to tubulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 47(4):685–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(72)90546-3
Owellen RJ, Donigian DW, Hartke CA, Hains FO (1977a) Correlation of biologic data with physico-chemical properties among the vinca alkaloids and their congeners. Biochem Pharmacol 26(13):1213–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(77)90108-3
Owellen RJ, Hartke CA, Hains FO (1977b) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of vinblastine in humans. Cancer Res 37(8 Part 1):2597–2602
Palem PPC, Kuriakose GC, Jayabaskaran C (2016) An endophytic fungus, Talaromyces radicus, isolated from Catharanthus roseus, produces vincristine and vinblastine, which induce apoptotic cell death. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0153111. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153111
Pandey SS, Singh S, Babu CV, Shanker K, Srivastava NK, Shukla AK, Kalra A (2016) Fungal endophytes of Catharanthus roseus enhance vindoline content by modulating structural and regulatory genes related to terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis. Sci Rep 6(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26583
Pandrangi SL, Chalumuri SS, Garimella S (2022) Emerging therapeutic efficacy of alkaloids as anticancer agents. Ann Romanian Soc Cell Biol 26(01):64–74
Parthasarathy R, Shanmuganathan R, Pugazhendhi A (2020) Vinblastine production by the endophytic fungus Curvularia verruculosa from the leaves of Catharanthus roseus and its in vitro cytotoxicity against HeLa cell line. Anal Biochem 593:113530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.113530
Pernot B, Gyan E, Maillot F, Hodges P, Ertault M, Ferreira-Maldent N (2018) Lymphomas diagnosed in an internal medicine department compared to lymphomas diagnosed in other departments: clinical and outcome differences. Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000013228
Pliankong P, Suksa-Ard P, Wannakrairoj S (2018) Chitosan elicitation for enhancing of vincristine and vinblastine accumulation in cell culture of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. J Agric Sci 10(12):287–293. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v10n12p287
Qu Y, Easson ME, Simionescu R, Hajicek J, Thamm AM, Salim V, De Luca V (2018) Solution of the multistep pathway for assembly of corynanthean, strychnos, iboga, and aspidosperma monoterpenoid indole alkaloids from 19E-geissoschizine. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(12):3180–3185. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719979115
Renault JH, Nuzillard JM, Le Crouérour G, Thépenier P, Zèches-Hanrot M, Le Men-Olivier L (1999) Isolation of indole alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus by centrifugal partition chromatography in the pH-zone refining mode. J Chromatogr A 849(2):421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(99)00495-1
Ripps H, Carr RE, Siegel IM, Greenstein VC (1984) Functional abnormalities in vincristine-induced night blindness. Investig Ophthalmol vis Sci 25(7):787–794
Rischer H, Orešič M, Seppänen-Laakso T, Katajamaa M, Lammertyn F, Ardiles-Diaz W, Goossens A (2006) Gene-to-metabolite networks for terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(14):5614–5619. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601027103
Roberts SC (2007) Production and engineering of terpenoids in plant cell culture. Nat Chem Biol 3(7):387–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2007.8
Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC (1991) The clinical pharmacology and use of anti-microtubule agents in cancer chemotherapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 52(1):35–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-7258(91)90086-2
Sahelian R (2011) Alkaloid substances in plants, information on vinca, ergot and ephedra alkaloid compounds
Scherlach K, Hertweck C (2009) Triggering cryptic natural product biosynthesis in microorganisms. Org Biomol Chem 7(9):1753–1760
Schutz FA, Bellmunt J, Rosenberg JE, Choueiri TK (2011) Vinflunine: drug safety evaluation of this novel synthetic vinca alkaloid. Expert Opin Drug Saf 10(4):645–653. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.2011.581660
Shams K, Nazif N, Azim N, Shafeek K, Missiry M, Ismail S, Nasr M (2009) Isolation and characterization of antineoplastic alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus L. Don. cultivated in Egypt. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajtcam.v6i2.57082
Sharma A, Verma P, Mathur A, Mathur AK (2018) Genetic engineering approach using early Vinca alkaloid biosynthesis genes led to increased tryptamine and terpenoid indole alkaloids biosynthesis in differentiating cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Protoplasma 255:425–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1151-7
Sharma A, Amin D, Sankaranarayanan A, Arora R, Mathur AK (2020) Present status of Catharanthus roseus monoterpenoid indole alkaloids engineering in homo-and heterologous systems. Biotechnol Lett 42(1):11–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02757-4
Sharma A, Tiwari P, Arora R, Sankaranarayanan A (2022) Madagascar periwinkle alkaloids: biosynthesis, ethnobotanical attributes, and pharmacological functions. S Afr J Bot 151:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2022.09.039
Sheard M, Kang M, Cabral D, Lee J, Castro L, Khankaldyyan V, Reynolds C (2007) Bone marrow-level oxygen tension enables enhanced and sustained growth of new pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402485
Siddiqui MJA, Ismail Z, Saidan NH (2011) Simultaneous determination of secondary metabolites from Vinca rosea plant extractives by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. Pharmacogn Mag 7(26):92. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.80662
Silvestri R (2013) New prospects for vinblastine analogues as anticancer agents. J Med Chem 56(3):625–627
Singer WD, Himes RH (1992) Cellular uptake and tubulin binding properties of four Vinca alkaloids. Biochem Pharmacol 43(3):545–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(92)90577-6
Song KM, Park SW, Hong WH, Lee H, Kwak SS, Liu JR (1992) Isolation of vindoline from Catharanthus roseus by supercritical fluid extraction. Biotechnol Prog 8(6):583–586. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp00018a018
Sottomayor M, Barceló AR (2006) The Vinca alkaloids: from biosynthesis and accumulation in plant cells, to uptake, activity and metabolism in animal cells. Stud Nat Prod Chem 33:813–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1572-5995(06)80041-4
Stadler M, Schulz B (2009) High energy biofuel from endophytic fungi? Trends Plant Sci 14(7):353–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.05.001
St-Pierre B, De Luca V (1995) A cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase catalyzes the first step in the conversion of tabersonine to vindoline in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol 109(1):131–139. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.1.131
St-Pierre B, Laflamme P, Alarco AM, Luca E (1998) The terminal O-acetyltransferase involved in vindoline biosynthesis defines a new class of proteins responsible for coenzyme A-dependent acyl transfer. Plant J 14(6):703–713. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00174.x
St-Pierre B, Vazquez-Flota FA, De Luca V (1999) Multicellular compartmentation of Catharanthus roseus alkaloid biosynthesis predicts intercellular translocation of a pathway intermediate. Plant Cell 11(5):887–900. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.5.887
Tatsis EC, Carqueijeiro I, de Bernonville TD, Franke J, Dang TT, Oudin A, O’Connor SE (2017) A three enzyme system to generate the Strychnos alkaloid scaffold from a central biosynthetic intermediate. Nat Commun 8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00154-x
Thimmaiah KN, Sethi VS (1985) Chemical characterization of the degradation products of vinblastine dihydrogen sulfate. Cancer Res 45(11 Part 1):5382–5385
Tonk D, Mujib A, Maqsood M, Ali M, Zafar N (2016) Aspergillus flavus fungus elicitation improves vincristine and vinblastine yield by augmenting callus biomass growth in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 126(2):291–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-0998-1
Van Tellingen O, Beijnen JH, Nooijen WJ, Bult A (1993) Plasma pharmacokinetics of vinblastine and the investigational Vinca alkaloid N-(deacetyl-O-4-vinblastoyl-23)-L-ethyl isoleucinate in mice as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Cancer Res 53(9):2061–2065
Vazquez-Flota F, De Carolis E, Alarco AM, De Luca V (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of desacetoxyvindoline-4-hydroxylase, a 2-oxoglutarate dependent-dioxygenase involved in the biosynthesis of vindoline in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Plant Mol Biol 34(6):935–948. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005894001516
Venugopalan A, Srivastava S (2015) Endophytes as in vitro production platforms of high value plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 33(6):873–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.07.004
Verma P, Mathur AK, Srivastava A, Mathur A (2012) Emerging trends in research on spatial and temporal organization of terpenoid indole alkaloid pathway in Catharanthus roseus: a literature update. Protoplasma 249(2):255–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0291-4
Vu PTB, Bui AL, Nguyen NN, Quach PND (2022) In vitro growth and content of vincristine and vinblastine of Catharanthus roseus L. hairy roots in response to precursors and elicitors. Plant Sci Today 9(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.14719/pst.1337
WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, 20th List (2017)
Wink M, Alfermann AW, Franke R, Wetterauer B, Distl M, Windhövel J, Ripplinger P (2005) Sustainable bio production of phytochemicals by plant in vitro cultures: anticancer agents. Plant Genet Resour 3(2):90–100
Yan L, Zhao H, Zhao X, Xu X, Di Y, Jiang C, Jin M (2018) Production of bio products by endophytic fungi: chemical ecology, biotechnological applications, bottlenecks, and solutions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(15):6279–6298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9101-7
Yang X, Zhang L, Guo B, Guo S (1994) Preliminary study of a vincristine-producing endophytic fungus isolated from leaves of Catharanthus roseus. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs
Yokoshima S, Ueda T, Kobayashi S, Sato A, Kuboyama T, Tokuyama H, Fukuyama T (2002) Stereo controlled total synthesis of (+)-vinblastine. J Am Chem Soc 124(10):2137–2139. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0177049
Zafari D, Leylaiee S, Tajick MA (2019) Isolation and identification of vinblastine from the fungus of Chaetomium globosum Cr95 isolated from Catharanthus roseus plant. BJM 8(32):1–14. https://doi.org/10.22108/BJM.2018.107927.1095
Zaferanloo B, Virkar A, Mahon PJ, Palombo EA (2013) Endophytes from an Australian native plant are a promising source of industrially useful enzymes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(2):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1187-y
Zhou X, Xu Z, Li A, Zhang Z, Xu S (2018) Double-sides sticking mechanism of vinblastine interacting with α, β-tubulin to get activity against cancer cells. J Biomol Struct Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2018.1539412
Zhu J, Wang M, Wen W, Yu R (2015) Biosynthesis and regulation of terpenoid indole alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus. Pharmacogn Rev 9(17):24–28. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.156323
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Prof. Prem Kumar Khosla, Chancellor, Shoolini University of Biotechnology and Management Sciences, Solan, Himachal Pradesh, India, and the School of Biotechnology here for providing the laboratory and technical facilities in the field of secondary metabolite production. All the structures have been adopted from PubChem, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, and modified for the creation of the images.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB and PK were involved in conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—reviewing and editing, and validation; ST was responsible for data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—reviewing and editing, and validation; AS and SKSP contributed to data curation, formal analysis, and validation; and IC took part in data curation and formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical statement
This article does not have any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors mutually agreed that the work should be published in the 3 Biotech.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Banyal, A., Tiwari, S., Sharma, A. et al. Vinca alkaloids as a potential cancer therapeutics: recent update and future challenges. 3 Biotech 13, 211 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03636-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03636-6