Abstract
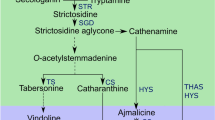
The monoterpene indole alkaloids (MIAs) from Madagascar periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) are secondary metabolites of high interest due to their therapeutical values. Secologanin, the monoterpenoid moiety incorporated into MIAs, is derived from the plastidial methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway. Here, we have cloned a cDNA encoding hydroxymethylbutenyl diphosphate synthase (HDS), a MEP pathway enzyme, and generated antibodies to investigate the distribution of transcripts and protein in MIA-producing aerial tissues. Consistent with our earlier work, transcripts for the genes encoding the so-called early steps in monoterpenoid biosynthesis (ESMB) enzymes (HDS, others MEP pathway enzymes and geraniol 10-hydroxylase) were preferentially co-localized to internal phloem associated parenchyma (IPAP) cells. By contrast, transcripts for the enzyme catalysing the last biosynthetic step to secologanin, secologanin synthase, were found in the epidermis. A coordinated response of ESMB genes was also observed in cell cultures stimulated to synthesise MIAs by hormone treatment, whereas no changes in SLS expression were detected under the same experimental conditions. Immunocytolabelling studies with the HDS-specific serum demonstrated the localisation of HDS to the plastid stroma and revealed that HDS proteins were most abundant in IPAP cells but could also be found in other cell types, including epidermal and mesophyll cells. Besides showing the existence of post-transcriptional mechanisms regulating the levels of HDS in C. roseus cells, our results support that intercellular translocation likely plays an important role during monoterpene-secoiridoid assembly.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DXS:
-
1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase
- DXR:
-
1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase
- ESMB:
-
Early steps in monoterpenoid biosynthesis
- G10H:
-
Geraniol 10-hydroxylase
- HDS:
-
Hydroxymethylbutenyl 4-diphosphate synthase
- HMBPP:
-
Hydroxymethylbutenyl 4-diphosphate
- IM:
-
Inducing medium
- IPAP:
-
Internal phloem associated parenchyma
- MECS:
-
2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-diphosphate synthase
- MeJa:
-
Methyljasmonate
- MEP:
-
Methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate
- MIA:
-
Monoterpene indole alkaloid
- MM:
-
Maintenance medium
- PM:
-
Production medium
- SLS:
-
Secologanin synthase
- STR:
-
Strictosidine synthase
- T16H:
-
Tabersonine 16-hydroxylase
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
References
Adam KP, Thiel R, Zapp J (1999) Incorporation of 1-[1-C-13]deoxy-d-xylulose in chamomile sesquiterpenes. Arch Biochem Biophys 369:127–132
Aerts RJ, Gisi D, De Carolis E, De Luca V, Baumann TW (1994) Methyl jasmonate vapor increases the developmentally controlled synthesis of alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus and Cinchona seedlings. Plant J 5:635–643
Araki N, Kusumi K, Masamoto K, Niwa Y, Iba K (2000) Temperature-sensitive Arabidopsis mutant defective in 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase within the plastid non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. Physiol Plant 108:19–24
Arigoni D, Sagner S, Latzel C, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Zenk MH (1997) Terpenoid biosynthesis from 1-deoxy-d-xylulose in higher plants by intramolecular skeletal rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10600–10605
Botella-Pavia P, Besumbes O, Phillips MA, Carretero-Paulet L, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2004) Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants: evidence for a key role of hydroxymethylbutenyl diphosphate reductase in controlling the supply of plastidial isoprenoid precursors. Plant J 40:188–199
Bouvier F, Suire C, d’Harlingue A, Backhaus RA, Camara B (2000) Molecular cloning of geranyl diphosphate synthase and compartmentation of monoterpenes synthesis in plant cells. Plant J 24:241–252
Brinkmann U, Mattes RE, Buckel P (1989) High-level expression of recombinant genes in Escherichia coli is dependent on the availability of the dnaY gene product. Gene 85:109–114
Burlat V, Ambert K, Ruel K, Joseleau JP (1997) Relationship between the nature of lignin and the morphology of degradation performed by white-rot fungi. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:645–654
Burlat V, Kwon M, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2001) Dirigent proteins and dirigent sites in lignifying tissues. Phytochemistry 57:883–897
Burlat V, Oudin A, Courtois M, Rideau M, St-Pierre B (2004) Co-expression of three MEP pathway genes and geraniol 10-hydroxylase in internal phloem parenchyma of Catharanthus roseus implicates multicellular translocation of intermediates during the biosynthesis of monoterpene indole alkaloids and isoprenoid-derived primary metabolites. Plant J 38:131–141
Campos N, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Sauret-Güeto S, Gallego F, Lois LM, Boronat A (2001a) Escherichia coli engineered to synthesize isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate from mevalonate: a novel system for the genetic analysis of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis. Biochem J 353:59–67
Campos N, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Seeman M, Rohmer M, Boronat A (2001b) Identification of gcpE as a novel gene of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 488:170–173
Carretero-Paulet L, Ahumada I, Cunillera N, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Ferrer A, Boronat A, Campos N (2002) Expression and molecular analysis of the arabidopsis DXR gene encoding 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, the first committed enzyme of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway. Plant Physiol 129:1581–1591
Chahed K, Oudin A, Guivarc’h N, Hamdi S, Chénieux JC, Rideau M, Clastre M (2000) 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase from periwinkle: cDNA identification and induced gene expression in terpenoid indole alkaloid-producing cells. Plant Physiol Biochem 38:559–566
Chatel G, Montiel G, Pré M, Memelink J, Thiersault M, Saint-Pierre B, Doireau P, Gantet P (2003) CrMYC1, a Catharanthus roseus elicitor- and jasmonate-responsive bHLH transcription factor that binds the G-box element of the strictosidine synthase gene promoter. J Exp Bot 54:2587–2588
Collu G, Unver N, Peltenburg-Looman AMG, van der Heijden R, Verpoorte R, Memelink J (2001) Geraniol 10-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 508:215–220
Contin A, van der Heijden R, Lefeber AWM, Verpoorte R (1998) The iridoid glucoside secologanin is derived from the novel triose phosphate/pyruvate pathway in Catharanthus cell culture. FEBS Lett 434:413–416
Courdavault V, Thiersault M, Courtois M, Gantet P, Oudin A, Doireau P, St-Pierre B, Giglioli-Guivarc’h N (2005a) CaaX-prenyltransferases are essential for expression of genes involved in the early stages of monoterpenoid biosynthetic pathway in Catharanthus roseus cells. Plant Mol Biol 57:855–870
Courdavault V, Burlat V, St-Pierre B, Giglioli-Guivarc’h N (2005b) Characterisation of CaaX-prenyltransferases in Catharanthus roseus: relationships with the expression of genes involved in the early stages of monoterpenoid biosynthetic pathway. Plant Sci 168:1097–1107
Décendit A, Liu D, Ouelhazi L, Doireau P, Mérillon JM, Rideau M (1992) Cytokinin-enhanced accumulation of indole alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus cell cultures-The factors affecting the cytokinin response. Plant Cell Rep 11:400–403
Décendit A, Petit G, Andreu F, Doireau P, Mérillon JM, Rideau M (1993). Putative sites of cytokinin action during their enhancing effect on indole alkaloid accumulation in periwinkle cell suspensions. Plant Cell Rep 12:710–712
Eisenreich W, Rohdich F, Bacher A (2001) Deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway to terpenoids. Trends Plant Sci 6:78–84
Estevez JM, Cantero A, Romero C, Kawaide H, Jimenez LF, Kuzuyama T, Seto H, Kamiya Y, Leon P (2000) Analysis of the expression of CLA1, a gene that encodes the 1-deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate synthase of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Phys 124:95–103
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gantet P, Imbault N, Thiersault M, Doireau P (1998) Necessity of a functional octadecanoic pathway for indole alkaloid synthesis by Catharanthus roseus cell suspensions cultured in an auxin-starved medium. Plant Cell Physiol 39:220–225
Geerlings A, Ibanez MM, Memelink J, van der Heijden R, Verpoorte R (2000). Molecular cloning and analysis of strictosidine beta-d-glucosidase, an enzyme in terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. J Biol Chem 275:3051–3056
Giglioli-Guivarc’h N, Courdavault V, Oudin A, Crèche J, St-Pierre B (2006) Madagascar periwinkle, an attractive model for studying the control of the biosynthesis of terpenoid derivative compounds. In: Teixeira Da Silva JA (ed) Floriculture, Ornamental and Plant Biology, Vol. II. Global Science Books
Guevara-Garcia A, San Roman C, Arroyo A, Cortes ME, Gutiérrez-Nava MdL, Leon P (2005) Characterization of the Arabidopsis clb6 mutant illustrates the importance of posttranslational regulation of the methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway. Plant Cell 17:628–643
Gutiérrez-Nava MdL, Gillmor CS, Jiménez LF, Guevara-García A, León P (2004) CHLOROPLAST BIOGENESIS Genes Act Cell and Noncell Autonomously in Early Chloroplast Development. Plant Physiol 135:471–482
Irmler S, Schröder G, St-Pierre B, Crouch NP, Hotze M, Schmidt J, Strack D, Matern U, Schröder J (2000) Indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus: new enzyme activities and identification of cytochrome P450 CYP72A1 as secologanin synthase. Plant J 24:797–804
Itoh H, Tanaka-Ueguchi M, Kawaide H, Chen X, Kamiya Y, Matsuoka M (1999) The gene encoding tobacco gibberellin 3β-hydroxylase is expressed at the site of GA action during stem elongation and flower organ development. Plant J 20:15–24
Kasahara H, Hanada A, Kuzuyama T, Takagi M, Kamiya Y, Yamaguchi S (2002) Contribution of the mevalonate and methylerythritol phosphate pathways to the biosynthesis of gibberellins in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:45188–45194
Kutchan TM (2005) A role for intra- and intercellular translocation in natural product biosynthesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:292–300
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Levêque D, Wihlm J, Jehl F (1996). Pharmacology of Catharanthus alkaloids. Bull Cancer 83:176–186
Lichtenthaler HK, Schwender J, Disch A, Rohmer M (1997) Biosynthesis of isoprenoids in higher plant chloroplasts proceeds via a mevalonate-independent pathway. FEBS Lett 400:271–274
Lichtenthaler HK (1999) The 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:47–65
Mahroug S, Burlat V, St-Pierre B (2006a). Cellular and sub-cellular organization of the monoterpenoid indole alkaloid pathway in Catharanthus roseus. Phytochem Rev (in press). DOI 10.1007/s11101–006–9017–1
Mahroug S, Courdavault V, Thiersault M, St-Pierre B, Burlat V (2006b). Epidermis is a pivotal site of at least four secondary metabolic pathways in Catharanthus roseus aerial organs. Planta 223:1191–1200
Menke F, Champion A, Kijne J, Memelink J (1999a) A novel jasmonate- and elicitor-responsive element in the periwinkle secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene Str interacts with a jasmonate- and elicitor-inducible AP2-domain transcription factor, ORCA2. EMBO J 18:4455–4463
Menke F, Parchamnn S, Mueller MJ, Kijne J, Memelink J (1999b) Involvement of the octadenoid pathway and protein phosphorylation in fungal elicitor-induced expression of terpenoid indole alkaloid biostynthetic genes in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol 119:1289–1296
Murata J, De Luca V (2005) Localization of tabersonine 16-hydroxylase and 16-OH tabersonine-16-O-methyltransferase to leaf epidermal cells defines them as a major site of precursor biosynthesis in the vindoline pathway in Catharanthus roseus. Plant J 44:581–594
Nagata N, Suzuki M, Yoshida S, Muranaka T (2002) Mevalonic acid partially restores chloroplast and etioplast development in Arabidopsis lacking the non-mevalonate pathway. Planta 216:345–350
Oudin A, Courtois M, Rideau M, Clastre M (2007) The iridoid pathway in Catharanthus roseus alkaloid biosynthesis Phytochem Rev (in press). DOI 10.1007/s11101–006–9054–9
Oudin A, Hamdi S, Ouélhazi L, Chénieux JC, Rideau M, Clastre M (1999) Induction of a novel cytochrome P450 (CYP96 family) in periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) cells induced for terpenoid indole alkaloid production. Plant Sci 149:105–113
Papon N, Bremer J, Vansiri A, Andreu F, Rideau M, Crèche J (2005) Cytokinin and ethylene control indole alkaloid production at the level of the MEP/terpenoid pathway in Catharanthus roseus suspension cells. Planta Med 71:572–574
Querol J, Campos N, Imperial S, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2002) Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana GCPE protein involved in plastid isoprenoid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 514:343–346
Rischer H, Oresic M, Seppanen-Laakso T, Katajamaa M, Lammertyn F, Ardiles-Diaz W, Van Montagu MC, Inzé D, Oksman-Caldentev KM, Goossens A (2006) Gene-to-metabolite networks for terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5614–5619
Rodríguez-Concepción M (2006) Early steps in isoprenoid biosynthesis: Multilevel regulation of the supply of common precursors in plant cells. Phytochem Rev 5:1–15
Rodríguez-Concepción M, Boronat A (2002) Elucidation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoids biosynthesis in bacteria and plastids. A metabolic milestone achieved through genomics. Plant Physiol 130:1079–1089
Rodríguez-Concepción M, Querol J, Lois LM, Imperial S, Boronat A (2003) Bioinformatic and molecular analysis of hydroxymethylbutenyl diphosphate synthase (GCPE) gene expression during carotenoid accumulation in ripening tomato fruit. Planta 217:476–482
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Habour, NY
Sauret-Güeto S, Botella-Pavia P, Flores-Perez U, Martinez-Garcia JF, San Roman C, Leon P, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2006) Plastid cues post-transcriptionally regulate the accumulation of key enzymes of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:75–84
Seemann M, Wegner P, Schunemann V, Bui BT, Wolff M, Marquet A, Trautwein AX, Rohmer M (2005) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in chloroplasts via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway: the (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase (GcpE) from Arabidopsis thaliana is a [4Fe-4S] protein. J Biol Inorg Chem 10:131–137
Silverstone AL, Chang CW, Krol E, Sun TP (1997) Developmental regulation of the gibberellin biosynthetic gene GA1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 12:9–19
St-Pierre B, Vazquez-Flota FA, De Luca V (1999) Multicellular compartmentation of Catharanthus roseus alkaloid biosynthesis predicts intercellular translocation of a pathway intermediate. Plant Cell 11:887–900
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Ac Res 22:4673–4680
Van der Fits L, Memelink J (2000) ORCA3, a jasmonate-responsive transcriptional regulator of plant primary and secondary metabolism. Science 289:295–297
Van der Heijden R, Jacobs D, Snoeijer W, Hallard D, Verpoorte R (2004) The Catharanthus Alkaloids: Pharmacognosy and Biotechnology. Curr Med Chem 11:607–628
Veau B, Courtois M, Oudin A, Chénieux JC, Rideau M, Clastre M (2000) Cloning and expression of cDNAs encoding two enzymes of the MEP pathway in Catharanthus roseus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1517:159–163
Yahia A, Kevers C, Gaspar T, Chénieux JC, Rideau M, Crèche J (1998) Cytokinins and ethylene stimulate indole alkaloids accumulation in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus by two distinct mechanisms. Plant Sci 133:9–15
Yamaguchi S, Kamiya Y, Sun TP (2001) Distinct cell-specific expression patterns of early and late gibberellin biosynthetic genes during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J 28:443–453
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Ministère de l’Education Nationale, de la Recherche et de la Technologie (MENRT, France), by Biotechnocentre, by the Conseil Régional du Centre, by the Ligue contre le Cancer (comité d’Indre et Loire and comité de l’Indre) and by the Spanish Ministerio de Educacion y Ciencia and FEDER (grant BIO2005–00367 to MR-C). We thank Dr. J. Memelink (University of Leiden, the Netherlands) who kindly provided C. roseus G10H cDNA and the oriented cDNA library, and Dr. N. Campos (Universitat de Barcelona) for the EcAB3-3 strain. We also thank Dr. B. Arbeille and the staff of the Electron Microscopy Platform (CHU Bretonneau, Tours, France) for providing excellent working conditions for ultramicrotomy and TEM studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oudin, A., Mahroug, S., Courdavault, V. et al. Spatial distribution and hormonal regulation of gene products from methyl erythritol phosphate and monoterpene-secoiridoid pathways in Catharanthus roseus . Plant Mol Biol 65, 13–30 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9190-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9190-7