Abstract
The plant matter, lignocellulosic biomass, is a renewable and inexpensive abundant natural resource in the world. The development of inexhaustible energy rehabilitated from agricultural waste is an alternative for fossil fuel to reduce CO2 emission and prevent global warming. The amount of waste generated has a direct correlation with the human population. Thus, the waste generated by the community is being added to the environment as the municipal, agricultural waste, and waste produced from forest-based industries. Moreover, there are high possibilities of having environment-friendly valuable bio-based products, including biofuels, biogas, enzymes, and biochar from biomass without competing with the food supply chain. However, only a few or limited kinds of products are produced industrially. This review highlights the significance of lignocellulosic biomass. It describes the different valuable products like biochemicals, biochar, enzymes, single-cell protein, dye dispersant, and bioplastic from lignocellulosic biomass, emphasizing their applications briefly. Besides, this review also highlights the pretreatment of biomass, mainly focusing on biological pretreatment. Natural biomass utilization would lead to solving the energy shortage, food security issues, and obstacles for developing technological solutions in agriculture, agro-processing, and other related manufacturing sectors.
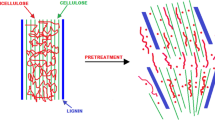
Graphic Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Dashtban, M., Schraft, H., Qin, W.: Fungal bioconversion of lignocellulosic residues, opportunities and perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 5, 578–595 (2009)
Saini, A., Aggarwal, N.K., Sharma, A., Yadav, A.: Actinomycetes: a source of lignocellulolytic enzymes. Enzyme Res. 2015, 1–15 (2015)
Sabiiti, E.N.: Utilizing agricultural waste to enhance food security and conserve the environment. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 11, 1–9 (2011)
Ezcurra, A.I., De-Zarate, O., Dhin, P.V., Lacaux, J.P.: Cereal waste burning pollution observed in the town of Vitoria (northern Spain). Atmos. Environ. 35, 1377–1386 (2001)
Sanchez, C.: Lignocellulosic residues: biodegradation and bioconversion by fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 27, 185–194 (2009)
Kumar, A., Gautam, A., Dutt, D.: Biotechnological transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into industrial products: an overview. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 7, 149–168 (2016)
Iqbal, H.M.N., Kyazze, G., Keshavarz, T.: Advances in valorization of lignocellulosic materials by biotechnology: an overview. BioResources. 8, 3157–3176 (2013)
Gupta, V.K., Kubicek, C.P., Berrin, J.G., Wilson, D.W., Couturier, M., Berlin, A., Filho, E.X.F., Ezeji, T.: Fungal enzymes for bio-products from sustainable and waste biomass. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41, 633–645 (2015)
Soccol, C.R., Faraco, V., Karp, S.G., Vandenberghe, L.P.S., Thomaz-Soccol, V., Woiciechowski, A.L., Pandey, A.: Lignocellulosic Bioethanol: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Biofuels: Alternative Feedstocks and Conversion Process for the Production of Liquid and Gaseous Biofuels, 2nd edn, pp. 331–354. Academic press / Elsevier Inc, New York (2019)
Isikgor, F.H., Becer, C.R.: Lignocellulosic biomass: a sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers. Polym. Chem. 6, 4497–4559 (2015)
Rancourt, Y., Neumeyer, C., Zou, N.: Results from 2015 Bio-Products Production and Development Survey. A report by statistics Canada, Ottawa (2017)
Biotechnology Innovation Organization: Advancing the bio-based economy: Renewable chemical biorefinery commercialization, progress and market opportunities, 2016 and beyond. http://www.bio.org/sites/default/files/BIO_Advancing _the _Biobased _Economy _2016.pdf (2016)
Cherubini, F.: The biorefinery concept: using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energ. Convers. Manage. 51, 1412–1421 (2010)
Huber, G.W.: Breaking the Chemical and Engineering Barriers to Lignocellulosic Biofuels: Next Generation Hydrocarbon Biorefineries, pp. 23–25. National Science Foundation, New York (2008)
Larson, E.: Biofuel Production Technologies: Status, Prospects and Implications for Trade and Development, p. 41. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, Geneva (2008)
De Jong, E., Higson, A., Walsh, P., Wellissch, M.: Bio-based chemicals, value added products from biorefineries. In: IEA Bioenergy task 42 report. https://www.ieabioenergy.com/wpcontent/uploads/2013/10/Task-42-Biobased-Chemicals value-added-products-from biorefineries.pdf (2013)
Saritha, M., Arora, A.: Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic substrates for enhanced delignification and enzymatic digestibility. Indian J. Microbiol. 52, 122–130 (2012)
Zhou, C.H., Xia, X., Lin, C.X., Tonga, D.S., Beltraminib, J.: Catalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to fine chemicals and fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 5588–5617 (2011)
Alonso, D.M., Wettstein, S.G., Dumesic, J.A.: Gamma-valerolactone, a sustainable platform molecule derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 15, 584–595 (2013)
Melero, J.A., Iglesias, J., Garcia, A.: Biomass as renewable feedstock in standard refinery units. Feasibility, opportunities and challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 7393–7420 (2012)
Rajendran, K., Drielak, E., Varma, V.S., Muthusamy, S., Kumar, G.: Updates on the pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks for bioenergy production–a review. Biomass Conver. Biorefin. 8, 471–483 (2017)
Saha, B.C.: Enzymes as Biocatalysts for Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass to Fermentable Sugars, in Handbook of Industrial Biocatalysis, C.R.C. Press, pp. 1–12 (2005)
Stocker, M.: Biofuels and biomass-to-biofuels in the biorefinery: catalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass using porous materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47, 9200–9211 (2008)
Doran-Peterson, J., Cook, D.M., Brandon, S.K.: Microbial conversion of sugars from plant biomass to lactic acid or ethanol. Plant J. 54, 582–592 (2008)
Edwards, M.C., Henriksen, E.D., Yomano, L.P., Gardner, B.C., Sharma, L.N., Ingram, L.O., Peterson, J.D.: Addition of genes for Cellobiase and Pectinolytic activity in Escherichia coli for fuel ethanol production from pectin-rich Lignocellulosic biomass. App. Environ. Microbio. 77, 5184–5191 (2011)
Mohen, D.: Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 11, 266–277 (2008)
Scheller, H.V., Ulvskov, P.: Hemicelluloses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 61, 263–289 (2010)
Bajpai, P.: Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuel production: Structure of lignocellulosic biomass, pp 17–70. Springer eBooks (2016)
Vassilev, S.V., Baxter, D., Andersen, L.K., Vassileva, C.G., Morgan, T.J.: An overview of the organic and inorganic phase composition of biomass. Fuel. 94, 1–33 (2012)
Agbor, V.B., Cicek, N., Sparling, R., Berlin, A., Levin, D.B.: Biomass pretreatment: fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol. Adv. 29, 675–685 (2011)
Morais, S., Morag, E., Barak, Y., Goldman, D., Hadar, Y., Lamed, R., Shoham, Y., Wilson, D.B., Bayer, E.A.: Deconstruction of lignocellulose into soluble sugars by native and designer cellulosomes. Microbiology. 3, 1–11 (2012)
Gardner, K., Blackwell, J.: The structure of native cellulose. Biopolymers. 13, 1975–2001 (1974)
Li, X., Hua-jun-Yang, H., Roy, B., Wang, D., Yue, W., Jiang, L., Park, E.Y., Miao, Y.: The most stirring technology in future: Cellulase enzyme and biomass utilization. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 8, 2418–2422 (2009)
VanderHart, D.L., Atalla, R.H.: Studies of microstructure in native celluloses using solid-state carbon-13 N.M.R. Macromolecules. 17, 1465–1472 (1984)
Kuhad, R.C., Singh, A., Eriksson, K.E.L.: Microorganisms and enzymes involved in the degradation of plant fiber cell walls. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 57, 45–125 (1997)
Klemm, D., Heublein, B., Fink, H.P., Bohn, A.: Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 3358–3393 (2005)
Sorieul, M., Dickson, A., Hill, S.J., Pearson, H.: Plant fibre: molecular structure and biomechanical properties, of a complex living material, influencing its deconstruction towards a biobased composite. Materials. 9, 1–36 (2016)
Saha, B.C.: Hemicellulose bioconversion. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30, 279–291 (2003)
Pérez, J., Muñoz-Dorado, J., De-la-Rubia, T., Martínez, J.: Biodegradation and biological treatments of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin: an overview. Int. Microbiol. 5, 53–63 (2002)
Xiao, C., Anderson, C.T.: Roles of pectin in biomass yield and processing for biofuels. Frontiers in plant sci. 4(67) (2013)
Liaotrakoon, W., Van Buggenhout, S., Christiaens, S., Houben, K., De Clercq, N., Dewettinck, K., Hendrickx, M.E.: An explorative study on the cell wall polysaccharides in the pulp and peel of dragon fruits (Hylocereus spp.). European Food Res. Technol. 237, 341–351 (2013)
Taboada, E., Fisher, P., Jara, R., Zúñiga, E., Gidekel, M., Cabrera, J.C., Pereira, E., Gutierrez-Moraga, A., Villalonga, R., Cabrera, G.: Isolation and characterization of pectic substances from murta (Ugni molinae Turcz) fruits. Food Chem. 123, 669–678 (2010)
Abid, M., Cheikhrouhou, S., Renard, C.M., Bureau, S., Cuvelier, G., Attia, H., Ayadi, M.A.: Characterization of pectins extracted from pomegranate peel and their gelling properties. Food Chem. 215, 318–325 (2017)
Saulnier, L., Thibault, J.F.: Extraction and characterization of pectic substances from pulp of grape berries. Carbohydr. Polym. 7, 329–343 (1987)
Kulkarni, S.G., Vijayanand, P.: Effect of extraction conditions on the quality characteristics of pectin from passion fruit peel (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa L.). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 43, 1026–1031 (2010)
Femenia, A., Garcia-Conesa, M., Simal, S., Rosselló, C.: Characterisation of the cell walls of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica L.) fruit tissues. Carbohydr. Polym. 35, 169–177 (1998)
Boluda-Aguilar, M., García-Vidal, L., del Pilar González-Castañeda, F., López-Gómez, A.: Mandarin peel wastes pretreatment with steam explosion for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 3506–3513 (2010)
Hilz, H., Bakx, E.J., Schols, H.A., Voragen, A.G.: Cell wall polysaccharides in black currants and bilberries—characterisation in berries, juice, and press cake. Carbohydr. Polym. 59, 477–488 (2005)
Liang, R.H., Chen, J., Liu, W., Liu, C.M., Yu, W., Yuan, M., Zhou, X.Q.: Extraction, characterization and spontaneous gel-forming property of pectin from creeping fig (Ficus pumila Linn.) seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 76–83 (2012)
Ridley, B.L., O’Neill, M., Mohen, D.: Pectins: structure, biosynthesis, and oligogalacturonide-related signaling. Phytochem. 57, 929–967 (2001)
Coetzee, B., Schols, H.A., Wolfaardt, F.: Determination of pectin content of eucalyptus wood. Holzforschung. 65, 327–331 (2011)
Edwards, M.C., Doran-Peterson, J.: Pectin-rich biomass as feedstock for fuel ethanol production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 95, 565–575 (2012)
Marcus, S.E., Verhertbruggen, Y., Herve, C., Ordaz-Ortiz, J.J., Farkas, V., Pedersen, H.L., Willats, W.G., Knox, J.P.: Pectic homogalacturonan masks abundant sets of xyloglucan epitopes in plant cell walls. BMC Plant Biol. 8, 60 (2008)
Willats, W.G., Mccartney, L., Mackie, W., Knox, J.P.: Pectin: cell biology and prospects for functional analysis. Plant Mol. Biol. 47, 9–27 (2001)
Pedrolli, D.B., Monteiro, A.C., Gomes, E., Carmona, E.C.: Pectin and pectinases: production, characterization and industrial application of microbial pectinolytic enzymes. Open Biotechnol. J. 3, 9–18 (2009)
Chen, J., Liu, W., Liu, C.M., Li, T., Liang, R.H., Luo, S.J.: Pectin modifications: a review. Critical reviews in food sci. nutri. 55, 1684–1698 (2015)
Sharma, H.K., Xu, C., Qin, W.: Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and bioproducts: an overview. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 10, 235–251 (2019)
Chaturvedi, V., Verma, P.: An overview of key pretreatment processes employed for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass into biofuels and value-added products. 3 Biotech. 3, 415–431 (2013)
Puligundla, P., Oh, S.E., Mok, C.: Microwave-assisted pretreatment technologies for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to sugars and ethanol: a review. Carbon Letters (Carbon Lett.). 17, 1–10 (2016)
Tu, W.C., Hallett, J.P.: Recent advances in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Current opinion Green Sustainable Chem. 20, 11–17 (2019)
Kuhad, R.C., Singh, A.: Lignocellulose Biotechnology: Future Prospects, Pp 400. I.K. International Ltd, New Delhi (2007)
Kuhad, R.C., Gupta, R., Singh, A.: Microbial celluloses and their industrial applications. Enzymes Res. 2011, 1–10 (2011)
Mtui, G.Y.S.: Lignocellulolytic enzymes from tropical fungi: types, substrates and applications- review. Scientific Res. Essays. 15, 1544–1555 (2012)
Agrawal, R., Semwal, S., Kumar, R., Mathur, A., Gupta, R.P., Tuli, D.K., Satlewal, A.: Synergistic enzyme cocktail to enhance hydrolysis of steam exploded wheat straw at pilot scale. Front. Energy Res. 6, 122 (2018)
Henrissat, B., Davies, G.: Structural and sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 7, 637–644 (1997)
Beguin, P., Aubert, J.P.: The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 13, 25–58 (1994)
Lynd, L.R., Weimer, P.J., van Zyl, W.H., Pretorius, I.S.: Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 66, 506–577 (2002)
Bhat, M.K., Bhat, S.: Cellulose degrading enzymes and their potential industrial applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 15, 583–620 (1997)
Maki, M., Leung, K.T., Qin, W.: The prospects of cellulase-producing bacteria for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 5, 500–516 (2009)
Adsul, M., Sandhu, S.K., Singhania, R.R., Gupta, R., Puri, S.K., Mathur, A.: Designing a cellulolytic enzyme cocktail for the efficient and economical conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to biofuels. Enzyme Microbial Technol. 133, 109442 (2020)
Sajith, S., Priji, P., Sreedevi, S., Benjamin, S.: An overview on fungal cellulases with an industrial perspective. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 6, 1–13 (2016)
Sweeney, M.D., Xu, F.: Biomass converting enzymes as industrial biocatalysts for fuels and chemicals: recent developments. Catalysts. 2, 244–263 (2012)
Walia, A., Guleria, S., Mehta, P., Chauhan, A., Parkash, J.: Microbial xylanases and their industrial application in pulp and paper biobleaching: a review. 3 Biotech. 7, 11 (2017)
Chauhan, P.S., Puri, N., Sharma, P., Gupta, N.: Mannanases: microbial sources, production, properties and potential biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 93, 1817–1830 (2012)
Dekker, R.F.H.: Biodegradation of the hemicelluloses. In: Higuchi, T. (ed.) Biosynthesis and Biodegradation of Wood Components, pp. 505–533. Academic Press, New York (1985)
Niladevi, K.N.: Ligninolytic Enzymes, in: Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilization, pp. 397–414. Springer, Dordrecht (2009)
Sokan-Adeaga, A.A., Ana, G.R.E.E., Sokan-Adeaga, M.A., Sokan-Adeaga, E.D.: Lignocelluloses: an economical and ecological resource for bio-ethanol production – a review. Intl. J. Natural Resour. Ecology and Management. 1, 128–144 (2016)
Hofrichter, M.: Lignin conversion by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Enzyme Microbio. Technol. 30, 454–466 (2002)
Tian, J.H., Pourcher, A.M., Bouchez, T., Gelhaye, E., Peu, P.: Occurrence of lignin degradation genotypes and phenotypes among prokaryotes- review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 9527–9544 (2014)
Heinzkill, M., Bech, L., Halkier, T., Schneider, P., Anke, T.: Characterization of laccases and peroxidases from wood-rotting fungi (family Coprinaceae). Appl. Environ. Microbio. 64, 1601–1606 (1998)
Huang, X.F., Santhanam, N., Badri, D.V., Hunter, W.J., Manter, D.K., Decker, S.R., Vivanco, J.M., Reardon, K.F.: Isolation and characterization of lignin-degrading bacteria from rainforest soils. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 110, 1616–1626 (2013)
Fisher, A.B., Fong, S.S.: Lignin biodegradation and industrial implications. AIMS Bioeng. 1, 92–112 (2014)
Singh, R., Kumar, M., Mittal, A., Mehta, P.K.: Microbial enzymes: industrial progress in 21st century. 3 Biotech. 6, 1–15 (2016)
Maciel, M.J., Silva, A.C., Ribeiro, H.C.T.: Industrial and biotechnological applications of ligninolytic enzymes of the basidiomycota: a review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 13, 14–15 (2010)
Placido, J., Capareda, S.: Ligninolytic enzymes: a biotechnological alternative for bioethanol production. Biores. Bioprocess. 2, 1–12 (2015)
Lobos, S., Larram, J., Salas, L., Cullen, D., Vicuna, R.: Isoenzymes of manganese dependent peroxidase and laccase produced by the lignin degrading basidiomycete Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Microbio. 14, 2691–2698 (1994)
Hammel, K.E., Cullen, D.: Role of fungal peroxidases in biological ligninolysis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 11, 349–355 (2008)
Kashyap, D.R., Vohra, P.K., Chopra, S., Tewari, R.: Applications of pectinases in the commercial sector: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 77, 215–227 (2001)
Jayani, R.S., Saxena, S., Gupta, R.: Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: a review. Process Biochem. 40, 2931–2944 (2005)
Garg, G., Singh, A., Kaur, A., Singh, R., Kaur, J., Mahajan, R.: Microbial pectinases: an ecofriendly tool of nature for industries. 3 Biotech. 6, 47 (2016)
Geetha, M., Saranraj, P., Mahalakshmi, S., Reetha, D.: Screening of pectinase producing bacteria and fungi for its pectinolytic activity using fruit waste. Int. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. Sci. 1, 30–42 (2012)
Pandey, A., Selvakumar, P., Soccol, C.R., Nigam, P.: Solid-state fermentation for the production of industrial enzymes. Curr. Sci. 77, 149–162 (2009)
Grethlein, H.E., Converse, A.O.: Common aspects of acid prehydrolysis and steam explosion for pretreating wood. Bioresour. Technol. 36, 77–82 (1991)
Howard, R.L., Abotsi, E., Jansen-van-Rensburg, E.L., Howard, S.R.: Lignocellulose biotechnology: issues of bioconversion and enzyme production. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2, 602–619 (2003)
Cho, E.J., Trinh, L.T.P., Song, Y., Lee, Y.G., Bae, H.J.: Bioconversion of biomass waste into high value chemicals. Bioresour. Technol. 298, 122386 (2020)
Garcia, A., Gandini, A., Labidi, J., Belgacem, N., Bras, J.: Industrial and crop wastes: a new source for nanocellulose biorefinery. Ind. Crop. Prod. 93, 26–38 (2016)
Liu, X., Duan, X., Wei, W., Wang, S., Ni, B.J.: Photocatalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to valuable products. Green Chem. 21, 4266–4289 (2019)
Kobayashi, F.A.: Synthesis and utilization of sugar compounds derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 15, 1740–1763 (2013)
Werpy, T.A., Petersen, G.: Top value-added chemicals from biomass: I. Results of screening for potential candidates from sugars and synthesis gas. National Renewable Energy Lab United States (2004). https://doi.org/10.2172/15008859
Bozell, J.J., Petersen, G.R.: Technology development for the production of biobased products from biorefinery carbohydrates-the U.S. Department of Energy’s "top 10" revisited. Green Chem. 12, 539–554 (2010)
Luque, R., Clark, J.H., Yoshida, K.: Gai, PL: efficient aqueous hydrogenation of biomass platform molecules using supported metal nanoparticles on Starbons. Chem. Comm. 45, 5305–5307 (2009)
Delhomme, C., Weuster-Botz, D., Kuhn, F.E.: Succinic acid from renewable resources as a C4 building-block chemical-a review of the catalytic possibilities in aqueous media. Green Chem. 11, 13–26 (2009)
Nhuan, P.N., Kleff, S., Schwegmann, S.: Review succinic acid: technology development and commercialization. Fermentation. 3, 1–14 (2017)
Mäki-Arvela, P., Simakova, L.I., Salmi, T., Murzin, D.Y.: Production of lactic acid/lactates from biomass and their catalytic transformations to commodities. Chem. Rev. 114, 1909–1971 (2014)
Kahlich, D., Wiechern, U., Lindner, J.: Propylene Oxide, In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, (Ed.). Wiley-VCH (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/14356007.a22_239.pub2
Alsaheb, R.A.A., Aladdin, A., Othman, N.Z., Malek, R.A., Leng, O.M., Aziz, R., El Enshasy, H.A.: Lactic acid applications in pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 7, 729–735 (2015)
Nee; Nigam, P.S.: Chapter 3: Production of Organic Acids from Agro-Industrial Residues, Book Biotechnology for Agro Industries, pp. 38–58. Springer, New Delhi (2009)
Fernandes, D.R., Rocha, A.S., Mai, E.F., Mota, C.J.A., Teixeira, D.S.A.: Levulinic acid esterification with ethanol to ethyl levulinate production over solid acid catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: General. 425-426, 199–204 (2012)
Bozell, J.J., Moens, L., Elliott, D.C., Wang, Y., Neuenscwander, G.G., Fitzpatrick, S.W., Bilski, R.J., Jarnefeld, J.L.: Production of levulinic acid and use as a platform chemical for derived products. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 28, 227–239 (2000)
Dutta, S., De, S., Saha, B.: A brief summary of the synthesis of polyester building-block chemicals and biofuels from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ChemPlusChem. 77, 259–272 (2012)
Yan, K., Wu, G., Lafleur, T., Jarvis, C.: Production, properties and catalytic hydrogenation of furfural to fuel additives and value-added chemicals. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 38, 663–676 (2014)
Mariscal, R., Maireles-Torres, P., Ojeda, M., Sadaba, I., Lopez, G.M.: Furfural: a renewable and versatile platform molecule for the synthesis of chemicals and fuels. Energy Env. Sci. 9, 1144–1189 (2016)
Takkellapati, S., Li, T., Gonzalez, M.A.: An overview of biorefinery derived platform chemicals from a cellulose and hemicellulose biorefinery. Clean Techn. Environ. Policy. 20, 1615–1630 (2018)
Van-Putten, R.J., van der Waal, J.C., De Jong, E., Rasrendra, C.B., Heeres, H.J., De Vries, J.G.: Hydroxymethylfurfural: a versatile platform chemical made from renewable resources. Chem. Rev. 113, 1499–1597 (2013)
Bai, R., Zhang, H., Mei, F., Wang, S., Li, T., Gu, Y., Li, G.: One-pot synthesis of glycidol from glycerol and dimethyl carbonate over a highly efficient and easily available solid catalyst NaAlO2. Green Chem. 15, 2929–2934 (2013)
Almeida, J.R., Fávaro, L.C., Quirino, B.F.: Biodiesel biorefinery: opportunities and challenges for microbial production of fuels and chemicals from glycerol waste. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 5, 48 (2012)
Santacesaria, E., Tesser, R., Di Serio, M., Casale, L., Verde, D.: New process for producing Epichlorohydrin via glycerol chlorination. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 964–970 (2010)
Pappenberger, G., Hohmann, H.P.: Industrial production of L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and D-isoascorbic acid. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 143, 143–188 (2014)
Parker, J.D., Parker, J.O.: Nitrate therapy for stable angina pectoris. N. Engl. J. Med. 338, 520–531 (1998)
Zhang, J., Li, J., Wu, S.B., Liu, Y.: Advances in catalytic production and utilization of sorbitol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 11799–11815 (2013)
Star-Colibri: Strategic targets for 2020-collaboration initiative on biorefineries: Background information and biorefinery status, potential and Sustainability. https://edepot.wur.nl/158542 (2010). Accessed 18 Mar 2010
Lugani, Y., Oberoi, S., Sooch, B.S.: Xylitol: a sugar substitute for patients of diabetes mellitus. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6, 741–749 (2017)
Guo, X., Zhang, R., Li, Z., Dai, D., Li, C., Zhou, X.: A novel pathway construction in Candida tropicalis for direct xylitol conversion from corncob xylan. Bioresour. Technol. 128, 547–552 (2013)
Kim, S.: Evaluation of alkali-pretreated soybean straw for lignocellulosic bioethanol production. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 1–7 (2018)
Subramani, V., Gangwal, S.K.: A review of recent literature to search for an efficient catalytic process for the conversion of syngas to ethanol. Energy Fuel. 22, 814–839 (2008)
Wyman, C.E., Kumar, R., Cai, C.M.: Bioethanol from Lignocellulosic Biomass. U.C. Riverside (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2493-6_521-3
Abubackar, H.N., Veiga, M.C., Kennes, C.: Biological conversion of carbon monoxide: rich syngas or waste gases to bioethanol. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 5, 93–114 (2011)
Choi, D.W., Chipman, D.C., Bents, S.C., Brown, R.C.: A techno-economic analysis of polyhydroxyalkanoate and hydrogen production from syngas fermentation of gasified biomass. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 160, 1032–1046 (2010)
Misawa, N.: Pathway engineering of plants toward astaxanthin production. Plant Biotechnol. 26, 93–99 (2009)
Jaswir, I., Noviendri, D., Harini, R.F., Octavianti, F.: Carotenoids: sources, medicinal properties and their application in food and nutraceutical industry. J. Med. Plants Res. 5, 7119–7131 (2011)
Lou, S.N., Hsu, Y.S., Ho, C.T.: Flavonoid compositions and antioxidant activity of calamondin extracts prepared using different solvents. J. Food and drug Analysis. 22, 290–295 (2014)
Bradshaw, H.D., Schemske, D.W.: Allele substitution at a flower colour locus produces a pollinator shift in monkeyflowers. Nature. 426, 176–178 (2003)
Saini, A., Panesar, P.S., Bera, M.B.: Valorization of fruits and vegetables waste through green extraction of bioactive compounds and their nanoemulsions based delivery system. Biores. Bioprocess. 6, 1–12 (2019)
Minatel, O., Borges, C.V., Ferreira, M.I., Gomez, H.A.G., Chen, C.Y.O., Lima, G.P.P.: Phenolics compounds: Functional properties, impact of processing and bioavailability- In Phenolic compounds- biological activity (2017). https://doi.org/10.5772/66368
Wang, C., Kelley, S.S., Venditti, R.A.: Lignin-based thermoplastic materials. ChemSusChem. 9, 770–783 (2016)
Potočnik, J.: Renewable energy sources and the realities of setting an energy agenda. Science. 315, 810–811 (2007)
Scacchi, C.C.O., Gonzalez-Garcia, S., Caserini, S., Rigamonti, L.: Greenhouse gases emissions and energy use of wheat grain-based bioethanol fuel blends. Sci. Total Environ. 21, 5010–5018 (2010)
Wang, S., Dai, G., Yang, H., Luo, Z.: Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis mechanism: a state-of-the-art review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 62, 33–86 (2017)
Rosenbaum, M., He, Z., Angenent, L.T.: Light energy to bioelectricity: photosynthetic microbial fuel cells. Current Opinion in Biotechnol. 21, 259–264 (2010)
Velasquez-Orta, S.B., Curtis, T.P., Logan, B.E.: Energy from algae using microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 103, 1068–1076 (2009)
Rashid, N., Cui, Y.F., Rehman, M.S.U., Han, J.I.: Enhanced electricity generation by using algae biomass and activated sludge in microbial fuel cell. Sci. Total Environ. 456-457, 91–97 (2013)
Ren, Z., Ward, T.E., Regan, J.M.: Electricity production from cellulose in a microbial fuel cell using a defined binary culture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 4781–4786 (2007)
Gujjala, L.K., Kumar, S.J., Talukdar, B., Dash, A., Kumar, S., Sherpa, K.C., Banerjee, R.: Biodiesel from oleaginous microbes: opportunities and challenges. Biofuels. 10, 45–59 (2019)
Yousuf, A.: Biodiesel from lignocellulosic biomass–prospects and challenges. Waste Manag. 32, 2061–2067 (2012)
Thushari, I., Babel, S.: Biodiesel production from waste palm cooking oil using solid acid catalyst derived from coconut meal residue. Waste Biomass Valor. 11, 4941–4956 (2020)
Vanarasi, P., Singh, P., Auer, M., Adams, P.D., Simmons, B.A., Singh, S.: Survey of renewable chemicals produced from lignocellulosic biomass during ionic liquid pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 6, 1–9 (2013)
Agrawal, A., Kaushik, N., Biswas, S.: Derivatives and applications of lignin – an insight – review article. The Scitech. 1, 2348–2311 (2014)
Bozell, J.J., Holladay, J.E., Johnson, D., White, D.F.: Top Value-Added Candidates from Biomass, Volume II: Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Biorefinery Lignin, pp. 48–77. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Springfield (2007)
Ritala, A., Häkkinen, S.T., Toivari, M., Wiebe, M.G.: Single cell protein—state-of-the-art, industrial landscape and patents 2001-2016. Front. Microbiol. 8, 2009 (2017)
Mondal, A.K., Sengupta, S., Bhowal, J., Bhattacharya, D.K.: Utilization of fruit wastes in producing single cell protein. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1, 430–438 (2012)
Anupama, R.P.: Value-added food: single cell protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 18, 445–479 (2000)
Turnbull, W.H., Leeds, A.R., Edwards, G.D.: Mycoprotein reduces blood lipids in free-living subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55, 415–419 (1992)
NSF.: Breaking the chemical and engineering barriers to lignocellulosic biofuels: Next generation hydrocarbon biorefineries. Ed. George W. Huber, University of Massachusetts Amherst, pp 180. National Science Foundation, Chemical, Bioengineering, Environmental, and Transport Systems Division, Washington DC (2008)
Meyer, S., Glaser, B., Quicker, P.: Technical, economical, and climate-related aspects of biochar production technologies: a literature review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 9473–9483 (2011)
Srinivasan, P., Sarmah, K.A., Smernik, R., Das, O., Farid, M., Gao, W.: A feasibility study of agricultural and sewage biomass as biochar, bioenergy and biocomposites feedstock: production, characterization and potential applications. Sci. Total Environ. 512-513, 495–505 (2015)
Xiao, X., Chen, B., Chen, Z., Zhu, L., Schnoor, L.J.: Insight into multiple and multilevel structures of biochars and their potential environmental applications: a critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 5027–5047 (2018)
Yang, D.J., Li, H., Qin, Y.L., Zhong, R.S., Bai, M.X., Qiu, X.Q.: Structure and properties of sodium lignosulfonate with different molecular weight used as dye dispersant. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 36, 532–539 (2015)
Qin, Y., Lin, X., Lu, Y., Wu, S., Yang, D., Qiu, X., Fang, Y., Wang, T.: Preparation of a low reducing effect sulfonatd alkali lignin and application as dye dispersant. Polymers. 10, 982 (2018)
Qiu, X., Yu, J., Yang, J., Mo, W., Qian, Y.: Whitening sulfonated alkali lignin via H2O2/UV radiation and its application as dye dispersant. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 1055–1060 (2018)
Bacakova, L., Pajorova, J., Bacakova, M., Skogberg, A., Kallio, P., Kolarova, K., Svorcik, V.: Versatile application of nanocellulose: from industry to skin tissue engineering and wound healing. Nanomaterials. 9, 1–39 (2019)
de Souza, A.P., Grandis, A., Leite, D.C., Buckeridge, M.S.: Sugarcane as a bioenergy source: history, performance, and perspectives for second-generation bioethanol. Bioenergy Res. 7, 24–35 (2014)
Emaga, T.H., Robert, C., Ronkart, S.N., Wathelet, B., Paquot, M.: Dietary fibre components and pectin chemical features of peels during ripening in banana and plantain varieties. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 4346–4354 (2008)
Rabemanolontsoa, H., Saka, S.: Comparative study on chemical composition of various biomass species. RSC Adv. 3, 3946–3956 (2013)
Bhushan, S., Kalia, K., Sharma, M., Singh, B., Ahuja, P.S.: Processing of apple pomace for bioactive molecules. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 28, 285–296 (2008)
Banerjee, J., Singh, R., Vijayaraghavan, R., MacFarlane, D., Patti, A.F., Arora, A.: Bioactives from fruit processing wastes: green approaches to valuable chemicals. Food Chem. 225, 10–22 (2017)
Zheng, Y.X., Wang, Y.L., Pan, J., Zhang, J.R., Dai, Y., Chen, K.Y.: Semi-continuous production of high-activity pectinases by immobilized Rhizopus oryzae using tobacco wastewater as substrate and their utilization in the hydrolysis of pectin-containing lignocellulosic biomass at high solid content. Biores.Technol. 241, 1138–1144 (2017)
Wang, J., Chio, C., Chen, X., Su, E., Cao, F., Jin, Y., Qin, W.: Efficient saccharification of agave biomass using Aspergillus niger produced low-cost enzyme cocktail with hyperactive pectinase activity. Bioresour. Technol. 272, 26–33 (2019)
Di-Blasi, C., Branca, C., Galgano, A.: Biomass screening for the production of furfural via thermal decomposition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 2658–2671 (2010)
Thite, V.S., Nerurkar, A.S.: Physicochemical characterization of pectinase activity from Bacillus spp. and their accessory role in synergism with crude xylanase and commercial cellulase in enzyme cocktail mediated saccharification of agrowaste biomass. J. applied microbio. 124, 1147–1163 (2018)
Rahimi, S., Hasanloo, T.: The effect of temperature and pH on biomass and bioactive compound production in Silybum marianum hairy root cultures. Res. J. Pharmacognosy. 3, 53–59 (2016)
Lee, M.J., Son, K.H., Oh, M.M.: Increase in biomass and bioactive compounds in lettuce under various ratios of red to far-red LED light supplemented with blue LED light. Horticul. Environ. Biotechnol. 57, 139–147 (2016)
Nitsos, C., Matsakas, L., Triantafyllidis, K., Rova, U., Christakopoulos, P.: Investigation of different pretreatment methods of Mediterranean-type ecosystem agricultural residues: characterisation of pretreatment products, high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis and bioethanol production. Biofuels. 9, 545–558 (2018)
Schmidt, L.M., Mthembu, L.D., Reddy, P., Deenadayalu, N., Kaltschmitt, M., Smirnova, I.: Levulinic acid production integrated into a sugarcane bagasse based biorefinery using thermal-enzymatic pretreatment. Indus. crops products. 99, 172–178 (2017)
Tao, P., Zhang, Y., Wu, Z., Liao, X., Nie, S.: Enzymatic pretreatment for cellulose nanofibrils isolation from bagasse pulp: transition of cellulose crystal structure. Carbohydr. Polym. 214, 1–7 (2019)
Funding
No funding was provided for this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS did the major contribution in writing the manuscript, A.L.M.K. did proofread, and all authors have helped in writing and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrestha, S., Kognou, A.L.M., Zhang, J. et al. Different Facets of Lignocellulosic Biomass Including Pectin and Its Perspectives. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 4805–4823 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01305-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01305-w