Abstract
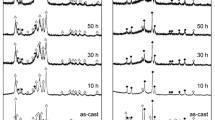
Mg2Ni-type Mg20−xYxNi10 (x = 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4) electrode alloys were fabricated by vacuum induction melting. Subsequently, the as-cast alloys were mechanically milled on a planetary-type ball mill. The effects of milling time and Y content on the microstructures and electrochemical performances of the alloys were investigated in detail. The results show that nanocrystalline and amorphous structure can be successfully obtained through mechanical milling. The substitution of Y for Mg facilitates the glass forming of the Mg2Ni-type alloy and significantly enhances the electrochemical characteristics of the alloy electrodes. Moreover, the discharge capacity of Y-free alloy monotonously grows with the milling time prolonging, while that of the Y-substituted alloys has the maximum values in the same case. The milling time of obtaining the greatest discharge capacity markedly decreases with Y content increasing. The electrochemical kinetics of the alloys, including high rate discharge ability (HRD), diffusion coefficient (D), limiting current density (IL) and charge transfer rate, monotonously increase with milling time extending.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dibandjo P, Zlotea C, Gadiou R, Ghimbeu CM, Cuevas F, Latroche M, Leroy E, Vix-Guterl C. Hydrogen storage in hybrid nanostructured carbon/palladium materials: influence of particle size and surface chemistry. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2013;38(2):952.
Meng ZS, Lu RF, Rao DW, Kan E, Xiao CY, Deng KM. Catenated metal-organic frameworks: promising hydrogen purification materials and high hydrogen storage medium with further lithium doping. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2013;38(23):9811.
Jorge AM Jr, Prokofiev E, Ferreira de Lima G, Rauch E, Veron M, Botta WJ, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG. An investigation of hydrogen storage in a magnesium-based alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2013;38(20):8306.
Xie DH, Li P, Zeng CX, Sun JW, Qu XH. Effect of substitution of Nd for Mg on the hydrogen storage properties of Mg2Ni alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2009;478(1–2):96.
Wang H, Zhang J, Liu JW, Ouyang LZ, Zhu M. Improving hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 by addition of alkali hydroxides. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2013;38(20):10932.
Zhu YF, Yang C, Zhu JY, Li LQ. Structural and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Mg2Ni-based alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2011;509(17):5309.
Anik M, Akay I, Topcu S. Effect of electroless nickel coating on the electrochemical hydrogen storage characteristics of Al and Zr including Mg-based alloys. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2009;34(13):5449.
Liu ZP, Yang SQ, Li Y, Liu JJ, Ma MZ, Han SM. Phase structure and electrochemical performances of Co-free La–Mg–Ni-based alloys with Nd/Sm partial substitution for La. Rare Met. 2014;33(6):674.
Kim JW, Ahn JP, Jin SA, Lee SH, Chung HS, Shim JH, Cho YW, Oh KH. Microstructural evolution of NbF5-doped MgH2 exhibiting fast hydrogen sorption kinetics. J Power Sources. 2008;178(1):373.
Rivoirard S, de Rango P, Fruchart D, Charbonnier J, Vempaire D. Catalytic effect of additives on the hydrogen absorption properties of nano-crystalline MgH2(X) composites. J Alloys Compd. 2003;356–357:622.
Wang Y, Qiao SZ, Wang X. Electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of ball-milled NdMg12 alloy with Ni powders. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2008;33(3):1023.
Hima Kumar L, Viswanathan B, Srinivasa Murthy S. Hydrogen absorption by Mg2Ni prepared by polyol reduction. J Alloys Compd. 2008;461(1–2):72.
Ebrahimi-Purkani A, Kashani-Bozorg SF. Nanocrystalline Mg2Ni-based powders produced by high-energy ball milling and subsequent annealing. J Alloys Compd. 2008;456(1–2):211.
Dornheim M, Doppiu S, Barkhordarian G, Boesenberg U, Klassen T, Gutfleisch O, Bormann R. Hydrogen storage in magnesium-based hydrides and hydride composites. Scr Mater. 2007;56(10):841.
Teresiak A, Gebert A, Savyak M, Uhlemann M, Mickel C, Mattern N. In situ high temperature XRD studies of the thermal behaviour of the rapidly quenched Mg77Ni18Y5 alloy under hydrogen. J Alloys Compd. 2005;398(1–2):156.
Ruggeri S, Roué L, Huot J, Schulz R, Aymard L, Tarascon JM. Properties of mechanically alloyed Mg–Ni–Ti ternary hydrogen storage alloys for Ni-MH batteries. J Power Sources. 2002;112(2):547.
Aono K, Orimo S, Fujii H. Structural and hydriding properties of MgYNi4: a new intermetallic compound with C15b-type Laves phase structure. J Alloys Compd. 2000;309(1–2):L1.
Zhang YH, Yang T, Shang HW, Zhao C, Xu C, Zhao DL. The electrochemical hydrogen storage characteristics of as-spun nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg20Ni10−xMx (M = Cu Co, Mn; x = 0–4) alloys. Rare Met. 2014;33(6):663.
Zhang YH, Li C, Cai Y, Hu F, Liu ZC, Guo SH. Highly improved electrochemical hydrogen storage performances of the Nd–Cu–added Mg2Ni-type alloys by melt spinning. J Alloys Compd. 2014;584:81.
Niua H, Northwood DO. Enhanced electrochemical properties of ball-milled Mg2Ni electrodes. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2002;27(1):69.
Tanaka K, Kanda Y, Furuhashi M, Saito K, Kuroda K, Saka H. Improvement of hydrogen storage properties of melt-spun Mg–Ni–RE alloys by nanocrystallization. J Alloys Compd. 1999;293–295:521.
Spassov T, Lyubenova L, Köster U, Baró MD. Mg–Ni–RE nanocrystalline alloys for hydrogen storage. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;375–377:794.
Cui N, Luan B, Zhao HJ, Liu HK, Dou SX. Effects of yttrium additions on the electrode performance of magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloys. J Alloys Compd. 1996;233(1–2):236.
Endo D, Sakaki K, Akiba E. Formation of lattice strain in MmNi4.30−xCoxAl0.30Mn0.40 (x = 0, 0.75) during hydrogenation. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2007;32(17):4202.
Zuttel A, Meli F, Schtapbach I. AB2 and AB5 metal hydride electrodes: a phenomenological model for the cycle life. J Alloys Compd. 1993;200(1–2):157.
Zaluski L, Zaluska A, Strom-Olesen JO. Nanocrystalline metal hydrides. J Alloys Compd. 1997;253–254:70.
Simičić MV, Zdujić M, Dimitrijević R, Nikolić-Bujanović L, Popović NH. Hydrogen absorption and electrochemical properties of Mg2Ni-type alloys synthesized by mechanical alloying. J Power Sources. 2006;158(1):730.
Ren HP, Zhang YH, Li BW, Zhao DL, Guo SH, Wang XL. Influence of the substitution of La for Mg on the microstructure and hydrogen storage characteristics of Mg20−xLaxNi10 (x = 0–6) alloys. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2009;34(3):1429.
Gasiorowski A, Iwasieczko W, Skoryna D, Drulis H, Jurczyk M. Hydriding properties of nanocrystalline Mg2−xMxNi alloys synthesized by mechanical alloying (M = Mn, Al). J Alloys Compd. 2004;364(1–2):283.
Wang ZM, Zhou HY, Gu ZF, Cheng G, Yu AB. Preparation of Mg2−xRExNi (RE = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Y) alloys and their electrochemical characteristics. J Alloys Compd. 2004;381(1–2):234.
Zhao XY, Ding Y, Ma LQ, Wang LY, Yang M, Shen XD. Electrochemical properties of MmNi3.8Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.2 hydrogen storage alloy modified with nanocrystalline nickel. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2008;33(22):6727.
Kuriyama N, Sakai T, Miyamura H, Uehara I, Ishikawa H, Iwasaki T. Electrochemical impedance and deterioration behavior of metal hydride electrodes. J Alloys Compd. 1993;202(1–2):183.
Zheng G, Popov BN, White RE. Electrochemical determination of the diffusion coefficient of hydrogen through an LaNi4.25Al0.75 electrode in alkaline aqueous solution. J Electrochem Soc. 1995;142(8):2695.
Ratnakumar BV, Witham C, Bowman RC Jr, Hightower A, Fultz B. Electrochemical studies on LaNi5−xSnx metal hydride alloys. J Electrochem Soc. 1996;143(8):2578.
Wu Y, Han W, Zhou SX, Lototsky MV, Solberg JK, Yartys VA. Microstructure and hydrogenation behavior of ball-milled and melt-spun Mg–10Ni–2 Mm alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2008;466(1–2):176.
Jafarian M, Azizi O, Gobal F, Mahjani MG. Kinetics and electrocatalytic behavior of nanocrystalline CoNiFe alloy in hydrogen evolution reaction. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2007;32(12):1686.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Nos. 51161015 and 51371094) and the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metals and Materials (No. 2011-ZD06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YH., Song, XP., Zhang, PL. et al. Structure and electrochemical performances of Mg20−xYxNi10 (x = 0–4) alloys prepared by mechanical milling. Rare Met. 38, 954–964 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0727-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0727-2