Abstract
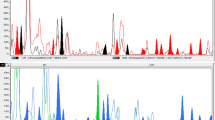
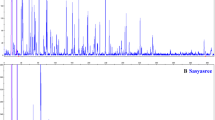
The sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) technique, aimed for the amplification of open reading frames (ORFs), vis-â-vis that of the amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLP) were used to analyze the genetic variation and relationships among forty Musa accessions; which include commercial cultivars and wild species of interest for the genetic enhancement of Musa. A total of 403 SRAP and 837 AFLP amplicons were generated by 10 SRAP and 15 AFLP primer combinations, of which 353 and 787 bands were polymorphic, respectively. Both cluster analysis of unweighted pair-grouping method with arithmetic averages (UPGMA) and principal coordinate (PCO) analysis separated the forty accessions into their recognized sections (Eumusa, Australimusa, Callimusa and Rhodochlamys) and species. The percentage of polymorphism amongst sections and species and the relationships within Eumusa species and subspecies varied between the two marker systems. In addition to its practical simplicity, SRAP exhibited approximately threefold more specific and unique bands than AFLP, 37 and 13%, respectively. SRAP markers are demonstrated here to be proficient tools for discriminating amongst M. acuminata, M. balbisiana and M. schizocarpa in the Eumusa section, as well as between plantains and cooking bananas within triploid cultivars.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFLP:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- SRAP:
-
Sequence related amplified polymorphism
References
Bakry, F., Careel, F., Jenny, C., & Horry, J. P. (2009). Genetic improvement of banana. In S. M. Jain & P. M. Priyadarshan (Eds.), Breeding plantation tree crops: tropical species (pp. 3–50). New York: Springer Science and Business Media.
Roux, N., Baurens, F. C., Doležel, J., Hribová, E., Heslop-Harrison, J. S., Town, C., et al. (2008). Genomics of banana and plantain (Musa spp.), major staple crops in the tropics. In P. Moore & R. Ming (Eds.), Genomics of tropical crop plants. Plant genetics and genomics, crops and models (Vol. 1, pp. 83–111). New York: Springer.
Loh, J. P., Kiew, R., Set, O., Gan, L. H., & Gan, Y. Y. (2000). Amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting of 16 banana cultivars (Musa cvs.). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 17, 360–366.
Wong, C., Kiew, R., Loh, J. P., Gan, L. H., Lee, S. K., Ohn, S., et al. (2001). Genetic diversity of the wild banana Musa acuminata Colla in Malaysia as evidenced by AFLP. Annals of Botany, 88, 1017–1025.
Ude, G., Pillay, M., Ogundiwin, E., & Tenkouano, A. (2003). Genetic diversity in an African plantain core collection using AFLP and RAPD markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 107, 248–255.
El-Khishin, D. A., Belatus, E. L., Abd El-Hamid, A., & Radwan, K. H. (2009). Molecular charactarization of banana cultivars (Musa spp.) from Egypt using AFLP. Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 5, 272–279.
Crouch, H. K., Crouch, J. H., Madsen, S., Vuylsteke, D., & Ortiz, R. (2000). Comparative analysis of phenotypic and genotypic diversity among plantain landraces (Musa spp., AAB group). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 101, 1056–1065.
Ferreira, C. F., Silva, S. O., Sobrinho, N. P. D., Damascena, S. C. S., Alves, F. S. A. O., & da Pereira Paz, O. (2004). Molecular characterization of banana (AA) diploids with contasting levels of black and yellow sigatoka resistance. American Journal of Applied Sciences, 1, 276–278.
Crouch, J. H., Crouch, H. K., Constandt, H., Van Gysel, A., Breyne, P., Van Montagu, M., et al. (1999). Comparison of PCR-based molecular marker analyses of Musa breeding populations. Molecular Breeding, 5, 233–244.
Careel, F., de Gonzalez Leon, D., Lagoda, P., Lanaud, C., Jenny, C., Horry, Tezenas., et al. (2002). Ascertaining maternal and paternal lineage within Musa by chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA RFLP analysis. Genome, 45, 679–692.
Nwakanma, D. C., Pillay, M., & Okoli, B. E. (2003). PCR-RFLP of the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers (ITS) provides markers for the A and B genomes in Musa L. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 108, 154–159.
Risterucci, A. M., Hippolyte, I., Perrier, X., Xia, L., Caig, V., Evers, M., et al. (2009). Development and assessment of diversity arrays technology for high-throughput DNA analyses in Musa. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 119, 1093–1103. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1111-5.
Li, G., & Quiros, C. F. (2001). Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 103, 455–461.
Ferriol, M., Pico, B., & Nuez, F. (2003). Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 107, 271–282.
Valdez-Ojeda, R., Hernandez-Stefanoni, J. L., Aguilar-Espinosa, M., Ortiz, R., Quiros, C. F., & Rivera-Madrid, R. (2008). Assessing morphological and genetic variation in Annatto (Bixa orellana L.) by sequence-related amplified polimorphism and cluster analysis. HortScience, 43, 2013–2017.
Suman, A., Kimbeng, C. A., Edme, S. J., & Veremis, J. (2008). Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers for assessing genetic relationships and diversity in sugarcane germplasm collections. Plant Genetic Resources: Characterization and Utilization, 6, 222–231.
Zaefizadeh, M., & Goliev, R. (2009). Diversity and relationships among durum wheat landraces (subconvars) by SRAP and phenotypic marker polymorphism. Research Journal of Biological Sciences, 4, 960–966.
Phothipan, S., Silayoi, B., Wanichkul, K., & Apisitwanich, S. (2005). Genetic relationship among banana in AA, AAB and B groups using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) techniques. Kasetsart Journal (Natural Science), 39, 703–710.
Dellaporta, S. L., Wood, J., & Hicks, J. B. (1983). A plant DNA mini-preparation: Version II. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 1, 19–21.
Stulnig, T. M., & Amberger, A. (1994). Exposing contaminating phenol in nucleic acid preparations. BioTechniques, 16, 403–404.
Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Hornes, M., et al. (1995). AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Research, 23, 4407–4414.
Wong, C., Kiew, R., Argent, G., Ohn, S., Lee, S. K., & Gan, Y. Y. (2002). Assessment of the validity of the sections in Musa (Musaceae) using AFLP. Annals of Botany, 90, 231–238.
Ude, G., Pillay, M., Nwakanma, A., & Tenkouano, A. (2002). Analysis of genetic diversity and selectional relationships in Musa using AFLP markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 104, 1239–1245.
Ude, G., Pillay, M., Nwakanma, A., & Tenkouano, A. (2002). Genetic diversity in Musa acuminata Colla and Musa balbisiana Colla and some of their natural hybrids using AFLP markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 104, 1246–1252.
Wang, X., Chiang, T., Roux, N., Hao, G., & Ge, X. (2006). Genetic diversity of wild banana (Musa balbisiana Colla) in China as revealed by AFLP markers. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 54, 1125–1132.
Bassam, B. J., Caetano-Anolle′s, G., & Gresshoff, P. M. (1991). Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry, 196, 80–83.
Jaccard, P. (1908). Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bulletin de la Societe Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles, 44, 223–270.
Bartoš, J., Alkhimova, O., Dolezelová, M., De Langhe, E., & Dolezel, J. (2005). Nuclear genome size and genomic distribution of ribosomal DNA in Musa and Ensete (Musaceae): Taxonomic implications. Cytogenetic and Genome Research, 109, 50–57.
Simmonds, N. W., & Weatherup, S. T. C. (1990). Numerical taxonomy of the wild bananas (Musa). The New Phytologist, 115, 567–571.
Shepherd, K. (1988) Observation on Musa taxonomy. In: Identification of genetic diversity in the genus Musa. (pp. 158–165) Proc Int Workshop, Los Banos, INIBAP, Montpellier, France.
Carreel, F., Faure, S., de Gonzalez Leon, D., Lagoda, P. J. L., & Perrier, X. (1994). Evaluation de la diversité génétique chez les bananiers diploides (Musa sp.). Genetics Selection Evolution, 26, 125–136.
Simmonds, N. W. (1956). Botanical results of the banana collecting expedition, 1954–5. Kew Bull, 11, 463–489.
Hotta, M. (1989). Identification list of Ensete and Musa (Musaceae) in SE Asia and West Malesia. In M. Hotta (Ed.), Diversity and plant-animal interaction in equatorial rainforests (pp. 67–75). Japan: Kagoshuma University.
Gawel, N. J., & Jarret, R. L. (1991). Chloroplast DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLPs) in Musa species. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 81, 783–786.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the contributions of MC. Roberto Ku-Cauich, MC. Margarita Aguilar, MC. Adriana Quiroz, IBQ. Jorge Itza and QFB. Miguel Keb for the technical support. This research was funded by the SAGARPA-CONACYT through the research grant 0048160 (RME) and scholarship 811.06.03-6371/07 for the senior author awarded by the government of Mexico through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssef, M., James, A.C., Rivera-Madrid, R. et al. Musa Genetic Diversity Revealed by SRAP and AFLP. Mol Biotechnol 47, 189–199 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9328-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9328-8