Abstract
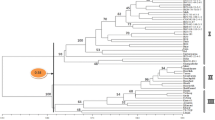
Fifteen AFLP primer pairs (EcoRI+3 and MseI+3) and 60 10-mer RAPD primers were used to detect polymorphisms and assess genetic relationships in a sample of 25 plantains from diverse parts of Western and Central Africa. The discriminatory power of the AFLP technique was greater than that of the RAPD technique, since the former produced markers with greater polymorphic information content (PIC) than the latter. Hence, AFLP analysis appeared to be a more-powerful approach for identifying genetic differences among plantain accessions. In this regard, significant genetic diversity within the plantains was shown by the unweighted pair-group method of arithmetic averages (UPGMA) and the multidimensional principal coordinate (PCO) analyses. The AFLP-derived clusters indicated closer relationships between similar inflorescence types than the RAPD-derived clusters. A small group of cultivars from Cameroon were separated from the bulk of other plantains, suggesting that Cameroon may harbour accessions with useful or rare genes for widening the genetic base of breeding populations derived from the plantains. A greater effort should be directed at collecting and characterizing plantain cultivars from Cameroon.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat KV, Jarret RL (1995) Random amplified polymorphic DNA and genetic diversity in Indian Musa germplasm. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42:107–118
Brown-Guedira GL, Thompson JA, Nelson RL, Warburton ML (2000) Evaluation of genetic diversity of soybean introductions and North American ancestors using RAPD and SSR markers. Crop Sci 40:815–823
Crouch JH, Crouch HK, Constandt H, Van Gysel A, Breyne P, Van Montagu M, Jarret RL Ortiz R (2000) Comparison of PCR-based molecular marker analyses of Musa breeding populations. Theor Appl Genet 101:1056–1065
De Langhe E (1961) La taxonomic du bananier plantain en Afrique Equatoriale. J d'Agric Tropicale et de Botanique Appliquee (Brussels) 8:419–449
De Langhe E (1964a) The origin of variation in the plantain banana. State Agric Univ Ghent 39:45–80
De Langhe E (1964b) Influence de la parthenocarpie sur la degenerence florale chez le bananier. Fruits 19:311–322
Engelborghs I, Swennen R (1999) Fluorescent AFLP detection of dwarf types in banana (Musa spp.) at early growth stage. Med Fac Landbouww Univ Gent 64/5b
Howell E, Newbury HJ, Swennen RL, Withers LA, Ford-Lloyd BV (1994) The use of RAPD for identifying and classifying Musa germplasm. Genome 37:328–332
Kaemmer D, Fischer D, Jarret RL, Baurens F-C, Grapin A, Dambier D, Noyer JL, Lanaud C, Kahl G, Lagoda PJL (1997) Molecular breeding in the genus Musa: a strong case for STMS marker technology. Euphytica 96:49–63
Lebot V, Johnston ED, Zheng QY, McKern D, McKenna DJ (1999) Morphological, phytochemical, and genetic variation in Hawaiian cultivars of 'Awa Kawa' (Piper methysticum, Piperaceae). Econ Bot 53:407–418
Lin JJ, Kuo J, Ma J, Saunders JA, Beard HS, Macdonald MH, Kenworthy W, Ude GN, Matthews BF (1996) Identification of molecular markers in soybean comparing RFLP, RAPD and AFLP DNA mapping techniques. Plant Mol Biol Rep 14:156–169
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Newbury HJ, Howell EC, Crouch JH, Ford-Lloyd BV (2000) Natural and culture-induced genetic variation in plantains (Musa spp. AAB group). Aust J Bot 48:493–500
O'Neill NR, van Berkum P, Lin JJ, Kuo J, Ude GN, Kenworthy W, Saunders JA (1997) Application of amplified restriction fragment length polymorphism for genetic characterization of Colletotrichum pathogens of Alfalfa. Phytopathology 87:745–750
Ortiz R (1995) Musa genetics. In: Gowen S (ed) Bananas and plantains. Chapman and Hall, London
Ortiz R (1997) Morphological variation in Musa germplasm. Genet Resour Crop Evol 44:393–404
Ortiz R, Madsen S, Vuylsteke D (1998) Classification of African plantain landraces and banana cultivars using a phenotypic distance index of quantitative descriptors. Theor Appl Genet 96:904–911
Pillay M, Nwakanma DC, Tenkouano A (2000) Identification of RAPD markers linked to A and B genome sequences in Musa. Genome 43:763–767
Pillay M, Ogundiwin E, Nwakanma DC, Ude G, Tenkouano A (2001) Analysis of genetic diversity and relationships in east African banana germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 102:965–970
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.02f. Exter Software, Setauket, New York, USA
Rossel G (1998) Taxonomic-linguistic study of plantain in Africa. PhD thesis, Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Schut JW, Qi X, Stam P (1997) Association between relationship measures based on AFLP markers, pedigree data and morphological traits in barley. Theor Appl Genet 95:1161–1168
Simmonds NW (1995) Bananas: Musa (Musaceae). In: Smartt J, Simmonds NW (eds) Evolution of Crop Plants, 2nd edn. Longman Scientific and Technical: Harlow, UK
Swennen R, Rosales F (1994) Bananas. Encylopedia of agricultural science, vol 1:215–232
Swennen R, Vuylsteke D (1987) Morphological taxonomy of plantains (Musa cultivars AAB) in West Africa. In: Persley GJ, De Langhe EA (eds) Banana and plantain breeding strategies pp 165–171. Proc Wkshp held at Cairns, Australia, Oct 1986. ACIAR Proceedings No 21, pp 13–17
Ude GN, Devine TE, Kuykendall LD, Mathews BF, Saunders JA, Kenworthy W, Lin JJ (1999) Molecular mapping of the soybean nodulation gene, Rj4. Symbiosis 26:101–110
Ude G, Pillay M, Nwakanma D, Tenkouano A (2002) Analysis of genetic diversity and sectional relationships in Musa using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1239–1245
Virk PS, Zhu J, Newbury HJ, Bryan GJ, Jackson MT, Ford-Lloyd BV (2000) Effectiveness of different classes of molecular markers for classifying and revealing variation in rice (Oryza sativa) germplasm. Euphytica 112:275–284
Vuylsteke D, Swennen R, De Langhe E (1991) Somaclonal variation in plantains (Musa spp. AAB group) derived from shoot-tip culture. Fruits 46:429–439
Vuylsteke DR, Swennen RL, Ortiz R (1993) Development and performance of black sigatoka-resistant tetraploid hybrids of plantain (Musa spp. AAB group). Euphytica 65:33–42
Weir B (1990) Genetic data analysis: methods for discrete population genetic data. Sinauer Assoc, Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Zabeau M, Vos P (1993) Selective restriction fragment amplification: a general method for DNA fingerprinting. European Patent Application, Publication No: EP 0534858-AL, No 92402629.7
Acknowledgements
This study was partly funded by the Directorate General for International Cooperation (DGIC), Belgium. This manuscript is no. IITA/62/JA/45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ude, G., Pillay, M., Ogundiwin, E. et al. Genetic diversity in an African plantain core collection using AFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 107, 248–255 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1246-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1246-8