Abstract
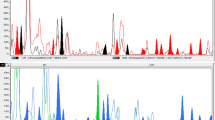
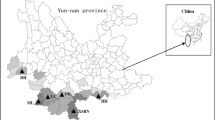
Wild banana Musa balbisiana Colla is one of the progenitors of cultivated bananas and plantains. It is native to Southeast Asia and the western Pacific. South China represents the northern limit of its distribution range. The genetic diversity of Musa balbisiana was assessed by the amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) fingerprinting in 15 populations of China. Four primer pairs produced 199 discernible loci. High levels of genetic diversity were detected, with P = 78.5%, H E = 0.241, and H pop = 0.3684 at population level, and P = 100%, H T = 0.3362 and H sp = 0.5048 at species level. Significant genetic differentiation among populations was detected based on Hickory’s analysis (27.6%), Shannon’s diversity index (27.0%) and AMOVA (27.1%). The AFLP results are discussed and compared with data obtained by microsatellites method. The estimates of genetic diversity and differentiation between each pair of populations computed with microsatellites and AFLP markers were not significantly correlated. Conservation strategies for Musa balbisiana in China are proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carreel F, Gonzalez de Leon D, Lagoda P, Lanaud C, Jenny C, Horry JP, Tezenas du Montcel H (2002) Ascertaining maternal and paternal lineage within Musa by chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA RFLP analysis. Genome 45:679–692
Cervera MT, Cabezas JA, Sancha JC, Martínez de Toda F, Martínez-Zapater JM (1998) Application of AFLPs to the characterization of grapevine Vitis vinifera L. genetic resources. A case study with accessions from Rioja (Spain). Theor Appl Genet 97:51–59
Compbell D, Duchesne P, Bernatchez L (2003) AFLP utility for population assignment studies: analytical investigation and empirical comparison with microsatellites. Mol Ecol 12:1979–1991
Creste S, Neto AT, Silva SDO, Figueira A (2003) Genetic characterization of banana cultivars (Musa spp.) from Brazil using microsatellite markers. Euphytica 132:259–268
Crouch JH, Crouch HK, Constandt H, Van Gysel A, Breyne P, Van Montagu M, Jarret RL, Ortiz R (1999) Comparison of PCR-based molecular marker analyses of Musa breeding populations. Mol Breed 5:233–244
Gaudeul M, Till-Bottraud I, Barjon F, Manel S (2004) Genetic diversity and differentiation in Eryngium alpinum L. (Apiaceae): comparison of AFLP and microsatellite markers. Heredity 92:508–518
Ge XJ, Liu MH, Wang WK, Schaal BA, Chiang TY (2005) Contrasting population structuring of wild banana, Musa balbisiana, in China based on evidence between microsatellite fingerprinting and cpDNA PCR-RFLP. Mol Ecol 14:933–944
Grapin A, Noyer JL, Carreel F, Dambier D, Baurens FC, Lanaud C, Lagoda PJL (1998) Diploid Musa acuminata genetic diversity assayed with sequence-tagged microsatellite sites. Electrophoresis 19:1374–1380
Hayward MD, Sackville Hamilton NR (1997) Genetic diversity-population structure and conservation. In: Callow JA, Ford-Lloyd BV, Newbury HJ (eds) Biotechnology and plant genetic resources: conservation and use. CAB INTERNATIONAL, New York, NY
Holsinger KE, Lewis PO, Dey DK (2002) A Bayesian approach to inferring population structure from dominant markers. Mol Ecol 11:1157–1164
Horry JP, Ortiz R, Arnaud E, Crouch JH, Ferris RSB, Johes DR, Mateo N, Picq C, Vuylsteke D (1997) Banana and Plantain. In: Fuccillo D, Sears L, Stapleton P (eds) Biodiversity in Trust. Conservation and use of plant genetic resources in CGIAR centres. Cambridge University Press, pp 67–81
Jarne P, Lagoda PJL (1996) Microsatellites, form molecules to populations and back. Trends Evol Ecol 11:424–429
Liu MH, Ge XJ, Wang WK, Hsu TW, Schaal BA, Chiang TY (2004) Pollen and seed dispersal of Musa balbisiana in South China. Conserv Quart 47:9–24
Loh JP, Kiew R, Set O, Gan LH, Gan YY (2000) Amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting of 16 banana cultivars (Musa cvs.) Mol Phylogenet Evol 17:360–366
Loveless MD, Hamrick JL (1984) Ecological determinants of genetic structure in plant populations. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 15:65–95
Maguire TL, Peakall R, Saenger P (2002) Comparative analysis of genetic diversity in the mangrove species Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. (Avicenniaceae) detected by AFLPs and SSRs. Theor Appl Genet 104:388–398
Mariette S, Le Corre V, Austerlitz F, Kremer A (2002) Sampling within the genome for measuring within-population diversity: trade-offs between markers. Mol Ecol 11:1145–1156
Miller MP (1997) Tools for population genetic analysis. Version 1.3. Department of Biological Sciences, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nwakanma DC, Pillay M, Okoli BE, Tenkouano A (2003) Sectional relationships in the genus Musa L. inferred from the PCR-RFLP of organelle DNA sequences Theor Appl Genet 107:850–856
Nybom H (2004) Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Mol Ecol 13:1143–1155
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) Arlequin: a software for population genetics data analysis, Version 2.000. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, Department of Anthropology, University of Geneva, Switzerland
Shim SI, Jørgensen RB (2000) Genetic structure in cultivated and wild carrots (Daucus carota L.) revealed by AFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 101:227–233
Sotto RC, Rabara RC (2000) Morphological diversity of Musa balbisiana Colla in the Philippines. InfoMusa 9:28–30
Start AN, Marshall AG (1976) Nectarivorous bats as pollinators of trees in west Malaysia. In: Burley J, Styles ST (eds) Tropical trees: variation, breeding and conservation. Academic Press, London, England, pp 141–150
Tautz D (1989) Hypervariability of simple sequence as a general source for polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6463–6471
Ude G, Pillay M, Nwakanma DC, Tenkouano A (2002a) Analysis of genetic iversity and sectional relationships in Musa using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1239–1245
Ude G, Pillay M, Nwakanma DC, Tenkouano A (2002b) Genetic diversity in Musa acuminata Colla and Musa balbisiana Colla and some of their natural hybrids using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1246–1252
Vuylsteke M, Mank R, Antonise R, Bastiaans E, Senior ML, Stuber CW, Melchinger AE, Lübberstedt T, Xia XC, Stam P, Zabeau M, Kuiper M (1999) Two high-density AFLP linkage maps of Zea mays L.: analysis of distribution of AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 99:921–935
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wong C, Kiew R, Loh JP, Gan HL, Set O, Lee SK, Lum S, Gan YY (2001) Genetic diversity of the wild banana Musa acuminata Colla in Malaysia as evidenced by AFLP. Ann Bot 88:1017–1025
Wright S (1951) The genetical structure of populations. Ann Eugen 15:323–354
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1999) POPGENE. Microsoft Windows-based freeware for population genetic analysis. Release 1.31. University of Alberta, Edmonton
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported through the receipt of an IPGRI sponsored capacity-building IFAR Fellowship 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XL., Chiang, TY., Roux, N. et al. Genetic diversity of wild banana (Musa balbisiana Colla) in China as revealed by AFLP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54, 1125–1132 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9004-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9004-9