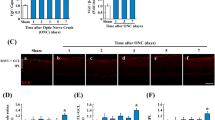
Abstract
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) has been demonstrated to play a crucial part in protecting retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) from apoptosis in various retinal injury animal models. PACAP has two basic groups of receptors: PACAP receptor type 1 (PAC1R) and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide/PACAP receptors (VPAC1R and VPAC2R). However, few studies illustrated the spatial and temporal expression changes of endogenous PACAP and its receptors in a rodent optic nerve crush (ONC) model. In this study, a significant upregulation of PACAP and PAC1R in the retina after ONC was observed in both protein and RNA levels. The peak level of PACAP and PAC1R expression could be found on the fifth day following ONC. In addition, immunofluorescent labeling indicated that PACAP and PAC1R were localized mainly in RGCs. On the contrary, VPAC1R and VPAC2R were hardly detected in the retina. Collectively, the spatiotemporal expression of PACAP and its high-affinity receptor PAC1R were remarkably changed after ONC, and mainly expressed in the ganglion cell layer of the retina. This suggested that the upregulation of PACAP and PAC1R may play a vital role in RGC death after ONC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asghar MS, Hansen AE, Amin FM, van der Geest RJ, Koning, Larsson HBW, Olesen J, Ashina M (2011) Evidence for a vascular factor in migraine. Ann Neurol 69:635–645
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P, Tamas A, Toth G, Reglodi D, Gabriel R (2010) Evaluation of the protective effects of PACAP with cell-specific markers in ischemia-induced retinal degeneration. Brain Res Bull 81:497–504
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P, Marton Z, Griecs M, Hamza L, Gaal V, Biro Z, Tamas A, Hild G, Nyitrai M, Toth G, Reglodi D, Gabriel R (2011) Effects of PACAP in UV-A radiation-induced retinal degeneration models in rats. J Mol Neurosci 43:51–57
Banks WA, Uchida D, Arimura A et al (1996) Transport of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide across the blood-brain barrier and the prevention of ischemia-induced death of hippocampal neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci 805:270–279
Basille M, Vaudry D, Coulouarn Y, Jegou S, Lihrmann I, Fournier A, Vaudry H, Gonzalez B (2000) Comparative distribution of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) binding sites and PACAP receptor mRNAs in the rat brain during development. J Comp Neurol 425:495–509
Birk S, Sitarz JT, Petersen KA, Oturai PS, Kruuse C, Fahrenkrug J, Olesen J (2007) The effect of intravenous PACAP38 on cerebral hemodynamics in healthy volunteers. Regul Pept 140:185–191
Boni L, Ploug K, Olesen J et al (2009) The in vivo effect of VIP, PACAP-38 and PACAP-27 and mRNA expression of their receptors in rat middle meningeal artery. Cephalalgia 29:837–847
D’Agata V, Cavallaro S (1998) Functional and molecular expression of PACAP/VIP receptors in the rat retina. Mol Brain Res 54:161–164
Drago F, Valzelli S, Emmi I, Marino A, Scalia CC, Marino V (2001) Latanoprost exerts neuroprotective activity in vitro and in vivo. Exp Eye Res 72:479–486
Fabian E, Reglodi D, Mester L, Szabo A, Szabadfi K, Tamas A, Toth G, Kovacs K (2012) Effects of PACAP on intracellular signaling pathways in human retinal pigment epithelial cells exposed to oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci 48:493–500
Han X, Ran Y, Su M et al (2017) Chronic changes in pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and related receptors in response to repeated chemical dural stimulation in rats. Mol Pain 13:1–10
Huang R, Lan Q, Chen L, Zhong H, Cui L, Jiang L, Huang H, Li L, Zeng S, Li M, Zhao X, Xu F (2018) CD200Fc attenuates retinal glial responses and RGCs apoptosis after optic nerve crush by modulating CD200/CD200R1 interaction. J Mol Neurosci 64:200–210
Jaworski DM (2000) Expression of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) and the PACAP-selective receptor in cultured rat astrocytes, human brain tumors, and in response to acute intracranial injury. Cell Tissue Res 300:219–230
Jonas JB, Aung T, Bourne RR, Bron AM, Ritch R, Panda-Jonas S (2017) Glaucoma. Lancet 390:2183–2193
Lakk M, Denes V, Gabriel R (2015) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptors signal via phospholipase C pathway to block apoptosis in newborn rat retina. Neurochem Res 40:1402–1409
Lam SY, Liu Y, Liong EC et al (2012) Upregulation of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide and its receptor expression in the rat carotid body in chronic and intermittent hypoxia. Adv Exp Med Biol 758:301–306
Lauenstein HD, Quarcoo D, Plappert L, Schleh C, Nassimi M, Pilzner C, Rochlitzer S, Brabet P, Welte T, Hoymann HG, Krug N, Müller M, Lerner EA, Braun A, Groneberg DA (2011) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide receptor 1 mediates anti-inflammatory effects in allergic airway inflammation in mice. Clin Exp Allergy 41:592–601
Miyata A, Arimura A, Dahl RR, Minamino N, Uehara A, Jiang L, Culler MD, Coy DH (1989) Isolation of a novel 38 residue-hypothalamic polypeptide which stimulates adenylate cyclase in pituitary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 164:567–574
Morikawa K, Dohi K, Yofu S, Mihara Y, Nakamachi T, Ohtaki H, Shioda S, Aruga T (2009) Expression and localization of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) specific receptor (PAC1R) after traumatic brain injury in mice. In: Shioda S, Homma I, Kato N (eds) Transmitters and modulators in health and disease. Springer Japan, Tokyo, pp 207–210
Nakamachi T, Matkovits A, Seki T, Shioda S (2012a) Distribution and protective function of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide in the retina. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 3:1–10
Nakamachi T, Tsuchida M, Kagami N, Yofu S, Wada Y, Hori M, Tsuchikawa D, Yoshikawa A, Imai N, Nakamura K, Arata S, Shioda S (2012b) IL-6 and PACAP receptor expression and localization after global brain ischemia in mice. J Mol Neurosci 48:518–525
Nakamachi T, Farkas J, Kagami N, Wada Y, Hori M, Tsuchikawa D, Tsuchida M, Yoshikawa A, Imai N, Hosono T, Atrata S, Shioda S (2013) Expression and distribution of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptor in reactive astrocytes induced by global brain ischemia in mice Tomoya. Acta Neurochir Suppl 118:55–59
Quigley HA (2011) Glaucoma. Lancet 377:1367–1377
Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya’ale D et al (2004) Global data on visual impairment in the year 2002. Bull World Health Organ 82:844–851
Sakamoto K, Kuno K, Takemoto M, He P, Ishikawa T, Onishi S, Ishibashi R, Okabe E, Shoji M, Hattori A, Yamaga M, Kobayashi K, Kawamura H, Tokuyama H, Maezawa Y, Yokote K (2015) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide protects glomerular podocytes from inflammatory injuries. J Diabetes Res 2015:1–10
Seki T, Shioda S, Ogino D, Nakai Y, Arimura A, Koide R (1997) Distribution and ultrastructural localization of a receptor for pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide and its mRNA in the rat retina. Neurosci Lett 238:127–130
Seki T, Shioda S, Izumi S, Arimura A, Koide R (2000) Electron microscopic observation of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)-containing neurons in the rat retina. Peptides 21:109–113
Seki T, Itoh H, Nakamachi T, Shioda S (2008) Suppression of ganglion cell death by PACAP following optic nerve transection in the rat. J Mol Neurosci 36:57–60
Shioda S, Nakamachi T (2015) PACAP as a neuroprotective factor in ischemic neuronal injuries. Peptides 72:202–207
Shioda S, Ohtaki H, Nakamachi T et al (2006) Pleiotropic functions of PACAP in the CNS: neuroprotection and neurodevelopment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1070:550–560
Shioda S, Takenoya F, Wada N, Hirabayashi T, Seki T, Nakamachi T (2016) Pleiotropic and retinoprotective functions of PACAP. Anat Sci Int 91:313–324
Shoge K, Mishima HK, Saitoh T, Ishihara K, Tamura Y, Shiomi H, Sasa M (1999) Attenuation by PACAP of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in cultured retinal neurons. Brain Res 839:66–73
Shu Q, Xu Y, Zhuang H, Fan J, Sun Z, Zhang M, Xu G (2014) Ras homolog enriched in the brain is linked to retinal ganglion cell apoptosis after light injury in rats. J Mol Neurosci 54:243–251
Szabadfi K, Reglodi D, Szabo A, Szalontai B, Valasek A, Setalo G, Kiss P, Tamas A, Wilhelm M, Gabriel R (2016) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide, a potential therapeutic agent for diabetic retinopathy in rats: focus on the vertical information processing pathway. Neurotox Res 29:432–446
Vaczy A, Reglodi D, Somoskeoy T, Kovacs K, Lokos E, Szabo E, Tamas A, Atlasz T (2016) The protective role of PAC1-receptor agonist Maxadilan in BCCAO-induced retinal degeneration. J Mol Neurosci 60:186–194
Varga B, Szabadfi K, Kiss P, Fabian E, Tamas A, Griecs M, Gabriel R, Reglodi D, Kemeny-Beke A, Pamer Z, Biro Z, Tosaki A, Atlasz T, Juhasz B (2011) PACAP improves functional outcome in excitotoxic retinal lesion: an electroretinographic study. J Mol Neurosci 43:44–50
Vaudry D, Falluel-morel A, Bourgault S et al (2009) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors : 20 years after the discovery. Pept Res 61:283–357
Werling D, Banks WA, Salameh TS et al (2017) Passage through the ocular barriers and beneficial effects in retinal ischemia of topical application of PACAP1-38 in rodents. Int J Mol Sci 18:1–12
Xu Y, Chen C, Jin N, Zhu J, Kang L, Zhou T, Wang J, Sheng A, Shi J, Gu Z, Sang A (2013) Müller glia cells activation in rat retina after optic nerve injury: spatiotemporal correlation with transcription initiation factor IIB. J Mol Neurosci 51:37–46
Xu Y, Yu S, Shu Q, Yang L, Yang C, Wang J, Xu F, Ji M, Liang X (2014) Upregulation of CREM-1 relates to retinal ganglion cells apoptosis after light-induced damage in vivo. J Mol Neurosci 52:331–338
Xu F, Chen L, Zhao X, Zhong H, Cui L, Jiang L, Huang H, Li L, Zeng S, Li M (2017a) Interaction of Wip1 and NF-κB regulates neuroinflammatory response in astrocytes. Inflamm Res 66:1011–1019
Xu Y, Yang B, Hu Y, Lu L, Lu X, Wang J, Shu Q, Cheng Q, Yu S, Xu F, Huang J, Liang X (2017b) Secretion of down syndrome critical region 1 isoform 4 in ischemic retinal ganglion cells displays anti-angiogenic properties via NFATc1-dependent pathway. Mol Neurobiol 54:6556–6571
Xu Y, Lu X, Hu Y et al (2018) Melatonin attenuated retinal neovascularization and neuroglial dysfunction by inhibition of HIF-1α-VEGF pathway in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice. J Pineal Res 64:1–17
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670850) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province in China (2015A030313052, 2018A030310144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All animals involved in the experiments were carried out according to the US National Institute of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals evolved by the US National Academy of Sciences, with the approval of the Administration Committee of Experimental Animals, Guangdong Province, China.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, D., Yang, Y., Lu, X. et al. Spatiotemporal Expression Changes of PACAP and Its Receptors in Retinal Ganglion Cells After Optic Nerve Crush. J Mol Neurosci 68, 465–474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1203-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1203-2