Abstract
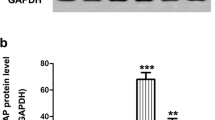
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is a neuropeptide that was first isolated from the ovine hypothalamus. PACAP has previously been shown in in vitro experiments to have neuroprotective effects, but its possible application in clinical situations must first be tested in vivo. We examined the protective effect of PACAP against retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death following optic nerve transection in the rat. Fourteen days after sectioning of the optic nerve, the number of RGCs in the vehicle control (untreated: vehicle 0.9% saline, volume 3 μl, injected into the vitreous body) group with axotomized optic nerve was decreased compared with that of intact animals. The number of RGCs in PACAP-treated animals (10 or 100 pM dose added to the vehicle) was significantly increased compared with the vehicle control group. These results indicate that PACAP suppresses ganglion cell death induced by optic nerve transection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura, A. (1998). Perspectives on pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) in the neuroendocrine, endocrine, and nervous systems. Japanese Journal of Physiology, 48, 301–331. doi:10.2170/jjphysiol.48.301.
Atluri, H., & Mitra, A. K. (2003). Disposition of short-chain aliphatic alcohols in rabbit vitreous by ocular microdialysis. Experimental Eye Research, 76(3), 315–320 (March).
Li, M., David, C., et al. (2005). Signaling cascades involved in neuroprotection by subpicomolar pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide 38. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 27(1), 91–105. doi:10.1385/JMN:27:1:091.
Mansour-Robaey, S., Clarke, D. B., Wang, Y. C., Bray, G. M., & Aguayo, A. J. (1994). Effects of ocular injury and administration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on survival and regrowth of axotomized retinal ganglion cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 91(5), 1632–1636. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.5.1632.
Miyata, A., Arimura, A., Dahl, R., et al. (1989). Isolation of a novel 38 residue-hypothalamic polypeptide which stimulates adenylate cyclase in pituitary cells. Biochemical And Biophysical Research Communications, 164(1), 567–574. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(89)91757-9.
Nakatani, M., Seki, T., Shinohara, Y., et al. (2006). Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) stimulates production of interleukin-6 in rat Muller cells. Peptides, 27(7), 1871–1876 (July).
Nilsson, S. F., De Neef, P., Robberecht, P., et al. (1994). Characterization of ocular receptors for pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) and their coupling to adenylate cyclase. Experimental Eye Research, 58(4), 459–467. doi:10.1006/exer.1994.1039.
Ohtaki, H., Nakamachi, T., Dohi, K., et al. (2006). Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) decreases ischemic neuronal cell death in association with IL-6. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(19), 7488–7493.
Quigley, H. A., Nickells, R. W., Kerrigan, L. A., et al. (1995). Retinal ganglion cell death in experimental glaucoma and after axotomy occurs by apoptosis. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 36(5), 774–786.
Reglodi, D., Tamás, A., et al. (2002). Effects of pretreatment with PACAP on the infarct size and functional outcome in rat permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Peptides, 23(12), 2227–2234 (December).
Seki, T., Izumi, S., Shioda, S., Arimura, A., et al. (2000). Electron microscopic observation of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)-containing in the rat retina. Peptides, 21, 109–113. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(99)00180-1.
Seki, T., Izumi, S., Zhou, C. -J., et al. (2000). Gene expression for PACAP receptor mRNA in the Rat Retina by in situ hybridization and in situ RT-PCR. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 921, 366–369.
Seki, T., Nakatani, M., Taki, C., et al. (2006). Neuroprotective effect of PACAP against kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rat retina. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1070, 531–534. doi:10.1196/annals.1317.074.
Seki, T., Shinohara, Y., Taki, C., Nakatani, M., et al. (2006). PACAP stimulates the release of interleukin-6 in cultured rat Müller cells. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1070, 535–539 (July).
Shioda, S., Ohtaki, H., Nakamachi, T., et al. (2006). Pleiotropic functions of PACAP in the CNS: neuroprotection and neurodevelopment. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1070, 550–560. doi:10.1196/annals.1317.080.
Shioda, S., Ozawa, H., Dohi, K., et al. (1998). PACAP protects hippocampal neurons against apoptosis: involvement of JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 865, 111–117. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb11169.x.
Xu, J., Heys, J. J., Barocas, V. H., et al. (2000). Permeability and diffusion in vitreous humor: implications for drug delivery. Pharmaceutical Research, 17(6), 664–669 (June).
Yoshitomi, T., Yamaji, K., Ishikawa, H., et al. (2002). Effect of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide on isolated rabbit iris sphincter and dilator muscles. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 43(3), 780–783.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seki, T., Itoh, H., Nakamachi, T. et al. Suppression of Ganglion Cell Death by PACAP Following Optic Nerve Transection in the Rat. J Mol Neurosci 36, 57–60 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9091-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9091-5