Abstract
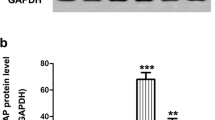
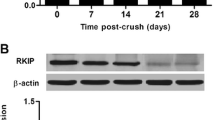
Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) apoptosis is considered an important pathological hallmark of glaucoma. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is a pleiotropic peptide with potent neuroprotective properties. In our previous study, we found that the expression of PACAP and its high-affinity receptor PACAP receptor type 1 (PAC1R) increased markedly after optic nerve crush (ONC), and occurred mainly in the ganglion cell layer of the retina. This suggests that the upregulation of PACAP may play a vital role in inhibiting RGC death after ONC. Therefore, in the present study, we investigate the specific effects and underlying mechanism of PACAP in RGC death after ONC. Vehicle (physiological saline) or PACAP (1 nM to 200 nM) solution was injected into the vitreous body. Seven days later, the retinas were harvested, and the surviving RGCs were retrogradely labeled with Fluoro-Gold (FG; Fluorochrome) at different concentrations of PACAP. Immunofluorescence double staining and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay were used to observe the effects of PACAP on RGC apoptosis. Our results showed that PACAP treatment inhibited caspase-3-mediated RGC apoptosis, promoted the phosphorylation of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), up-regulated the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), and ultimately improved RGC survival. These results suggest that PACAP may prevent RGC apoptosis after ONC via activation of CREB-mediated Bcl-2 transcription. The study thus contributes to a basic understanding of the mechanism by which PACAP decreased RGC apoptosis and provides a theoretical basis for future clinical application of PACAP in the treatment of glaucoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almasieh M, Wilson AM, Morquette B et al (2012) The molecular basis of retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res 31:152–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.11.002
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P et al (2010a) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in the retina: focus on the retinoprotective effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1200:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05512.x
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P et al (2010b) Evaluation of the protective effects of PACAP with cell-specific markers in ischemia-induced retinal degeneration. Brain Res Bull 81:497–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.09.004
Benito E, Barco A (2010) CREB’s control of intrinsic and synaptic plasticity: implications for CREB-dependent memory models. Trends Neurosci 33:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2010.02.001
Bonfanti L, Strettoi E, Chierzi S et al (1996) Protection of retinal ganglion cells from natural and axotomy-induced cell death in neonatal transgenic mice overexpressing bcl-2. J Neurosci 16:4186–4194. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.823.23
Cui L, He WJ, Xu F et al (2016) Alterations in the expression of Hs1-associated protein X-1 in the rat retina after optic nerve crush. Mol Med Rep 14:4761–4766. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5824
Dénes V, Czotter N, Lakk M et al (2014) PAC1-expressing structures of neural retina alter their PAC1 isoform splicing during postnatal development. Cell Tissue Res 355:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1761-0
Donegan RK, Lieberman RL (2016) Discovery of molecular therapeutics for Glaucoma: challenges, successes, and promising directions. J Med Chem 59:788–809. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00828
Doozandeh A, Yazdani S (2016) Neuroprotection in glaucoma. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 11:209–220. https://doi.org/10.4103/2008-322X.183923
Fabian E, Reglodi D, Mester L et al (2012) Effects of PACAP on intracellular signaling pathways in human retinal pigment epithelial cells exposed to oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci 48:493–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9812-7
Fukuchi M, Tabuchi A, Tsuda M (2005) Transcriptional regulation of neuronal genes and its effect on neural functions: cumulative mRNA expression of PACAP and BDNF genes controlled by calcium and cAMP signals in neurons. J Pharmacol Sci 98:212–218
Gillardon F, Hata R, Hossmann KA (1998) Delayed up-regulation of Zac1 and PACAP type I receptor after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Mol Brain Res 61:207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-328X(98)00202-2
Grosskreutz CL, Hänninen VA, Pantcheva MB et al (2005) FK506 blocks activation of the intrinsic caspase cascade after optic nerve crush. Exp Eye Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2004.11.017
Gusel’nikova VV, Korzhevskiy DE (2015) NeuN as a neuronal nuclear antigen and neuron differentiation marker. Acta Nat 7:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.28
Kellogg DL, Zhao JL, Wu Y, Johnson JM (2010) VIP/PACAP receptor mediation of cutaneous active vasodilation during heat stress in humans. J Appl Physiol 109:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01187.2009
Kido N, Tanihara H, Honjo M et al (2000) Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in eyes with NMDA-induced neuronal death. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02887-0
Lakk M, Denes V, Gabriel R (2015) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptors signal via phospholipase C pathway to block apoptosis in newborn rat retina. Neurochem Res 40:1402–1409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1607-0
Lambert HW, Weiss ER, Lauder JM (2001) Activation of 5-HT receptors that stimulate the adenylyl cyclase pathway positively regulates IGF-I in cultured craniofacial mesenchymal cells. Dev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1159/000048697
Lonze BE, Ginty DD (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35(4):605–623
Mester L, Kovacs K, Racz B et al (2011) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is protective against oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Mol Neurosci 43:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9427-9
Miura A, Kambe Y, Inoue K et al (2013) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type 1 receptor ( PAC1 ) gene is suppressed by transglutaminase 2 activation. J Biol Chem 288:32720–32730. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.452706
Prum BE (2014) Normal-tension glaucoma. In: Clinical glaucoma care: the essentials
Quigley HA (1996) Number of people with glaucoma worldwide. Br J Ophthalmol. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.80.5.389
Quigley HA (2011) Glaucoma. Lancet 377:1367–1377. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61423-7
Reichenstein M, Rehavi M, Pinhasov A (2008) Involvement of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) and its receptors in the mechanism of antidepressant action. J Mol Neurosci 36:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9116-0
Riccio A, Ahn S, Davenport CM, et al (1999) Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science (80- ). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5448.2358
Sakamoto K, Karelina K, Obrietan K (2011) CREB: a multifaceted regulator of neuronal plasticity and protection. J Neurochem 116:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07080.x
Seki T, Itoh H, Nakamachi T, Shioda S (2008) Suppression of ganglion cell death by PACAP following optic nerve transection in the rat. J Mol Neurosci 36:57–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9091-5
Shioda S, Ohtaki H, Nakamachi T et al (2006) Pleiotropic functions of PACAP in the CNS: neuroprotection and neurodevelopment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1070:550–560. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1317.080
Silveira MS, Costa MR, Bozza M, Linden R (2002) Pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide prevents induced cell death in retinal tissue through activation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 277:16075–16080. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110106200
Szabadfi K, Atlasz T, Kiss P et al (2012) Protective effects of the neuropeptide PACAP in diabetic retinopathy. Cell Tissue Res 348:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-012-1349-0
Szabadfi K, Szabo A, Kiss P et al (2014) PACAP promotes neuron survival in early experimental diabetic retinopathy. Neurochem Int 64:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.005
Szabo A, Danyadi B, Bognar E et al (2012) Effect of PACAP on MAP kinases, Akt and cytokine expressions in rat retinal hypoperfusion. Neurosci Lett 523:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.06.044
Tabuchi A, Sakaya H, Kisukeda T et al (2002) Involvement of an upstream stimulatory factor as well as cAMP-responsive element-binding protein in the activation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene promoter I. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204784200
Tang Z, Zhang S, Lee C et al (2011) An optic nerve crush injury murine model to study retinal ganglion cell survival. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/2685
Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY et al (2014) Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology
Uchida D, Arimura A, Somogyvári-Vigh A et al (1996) Prevention of ischemia-induced death of hippocampal neurons by pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide. Brain Res 736:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(96)00716-0
Vaudry D, Falluel-morel A, Bourgault S et al (2009) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors : 20 years after the discovery. Pept Res 61:283–357. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.109.001370.283
Weishaupt JH, Diem R, Kermer P et al (2003) Contribution of caspase-8 to apoptosis of axotomized rat retinal ganglion cells in vivo. Neurobiol Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-9961(03)00032-9
Werling D, Banks WA, Salameh TS et al (2017) Passage through the ocular barriers and beneficial effects in retinal ischemia of topical application of PACAP1-38 in rodents. Int J Mol Sci 18:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030675
Xu F, Huang H, Wu Y et al (2014a) Upregulation of gem relates to retinal ganglion cells apoptosis after optic nerve crush in adult rats. J Mol Histol 45:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9579-y
Xu Y, Yu S, Shu Q et al (2014b) Upregulation of CREM-1 relates to retinal ganglion cells apoptosis after light-induced damage in vivo. J Mol Neurosci 52:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0153-y
Xu Y, Yang B, Hu Y et al (2017) Secretion of down syndrome critical region 1 isoform 4 in ischemic retinal ganglion cells displays anti-Angiogenic properties via NFATc1-dependent pathway. Mol Neurobiol 54:6556–6571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0092-z
Xu J, Lu P, Dai M et al (2019) The relationship between binocular visual field loss and various stages of monocular visual field damage in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma 28:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.000000000000110
Yang C, Xu Y, Zhou H et al (2016) Tetramethylpyrazine protects CoCl2-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating the PHD2/HIF/1α-VEGF pathway. Mol Med Rep 13:1287–1296. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4679
Ye D, Yang Y, Lu X et al (2018) Spatiotemporal expression changes of PACAP and its receptors in retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve crush. J Mol Neurosci 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1203-2
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670850) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province in China (2018A030310144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were carried out according to the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals put forth by the US National Academy of Sciences, with the approval of the Administration Committee of Experimental Animals, Guangdong Province, China.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, D., Shi, Y., Xu, Y. et al. PACAP Attenuates Optic Nerve Crush-Induced Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis Via Activation of the CREB-Bcl-2 Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 68, 475–484 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01309-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01309-9