Abstract
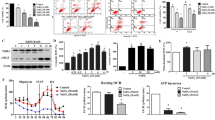
The integrity of retinal pigment epithelial cells is critical for photoreceptor survival and vision. Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) exerts retinoprotective effects against several types of injuries in vivo, including optic nerve transection, retinal ischemia, excitotoxic injuries, UVA-induced lesion, and diabetic retinopathy. In a recent study, we have proven that PACAP is also protective in oxidative stress-induced injury in human pigment epithelial cells (ARPE-19 cells). The aim of the present study was to investigate the possible mechanisms of this protection. ARPE cells were exposed to a 24-h hydrogen peroxide treatment. Expressions of kinases and apoptotic markers were studied by complex array kits and Western blot. Oxidative stress induced the activation of several apoptotic markers, including Bad, Bax, HIF-1α, several heat shock proteins, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, and Fas-associated protein with death domain, while PACAP treatment decreased them. The changes in the expression of MAP kinases showed that PACAP activated the protective ERK1/2 and downstream CREB, and decreased the activation of the pro-apoptotic p38MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase, an effect opposite to that observed with only oxidative stress. Furthermore, PACAP increased the activation of the protective Akt pathway. In addition, the effects of oxidative stress on several other signaling molecules were counteracted by PACAP treatment (Chk2, Yes, Lyn, paxillin, p53, PLC, STAT4, RSK). These play a role in cell death, cell cycle, inflammation, adhesion, differentiation and proliferation. In summary, PACAP, acting at several levels, influences the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic factors in favor of anti-apoptosis, thereby providing protection in oxidative stress-induced injury of human retinal pigment epithelial cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allais A, Burel D, Roy V et al (2010) Balanced effect of PACAP and FasL on granule cell death during cerebellar development: a morphological, functional and behavioural characterization. J Neurochem 113:329–340
Antonelli MC, Guillemin GJ, Raisman-Vozari R et al (2012) New strategies in neuroprotection and neurorepair. Neurotox Res 21:49–56
Atlasz T, Babai N, Kiss P et al (2007) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide is protective in bilateral carotid occlusion-induced retinal lesion in rats. Gen Comp Endocrinol 153:108–114
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P et al (2008) PACAP-mediated neuroprotection of neurochemically identified cell types in MSG-induced retinal degeneration. J Mol Neurosci 36:97–104
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Reglodi D et al (2009) Effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP1-38) and its fragments on retinal degeneration induced by neonatal MSG treatment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1163:348–352
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P et al (2010a) Evaluation of the protective effects of PACAP with cell-specific markers in ischemia-induced retinal degeneration. Brain Res Bull 81:497–504
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P et al (2010b) Review of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in the retina: focus on the retinoprotective effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1200:128–139
Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Kiss P et al (2011) Effects of PACAP in UV-A radiation-induced retinal degeneration models in rats. J Mol Neurosci 43:51–57
Aubert N, Vaudry D, Falluel-Morel A et al (2008) PACAP prevents toxicity induced by cisplatin in rat and primate neurons but not in proliferating ovary cells: involvement of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Neurobiol Dis 32:66–80
Babai N, Atlasz T, Tamas A, Reglodi D, Kiss P, Gabriel R (2005) Degree of damage compensation by various PACAP treatments in monosodium glutamate-induced retina degeneration. Neurotox Res 8:227–233
Babai N, Atlasz T, Tamas A et al (2006) Search for the optimal monosodium glutamate treatment schedule to study the neuroprotective effects of PACAP in the retina. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1070:149–155
Bazan NG (2008) Neurotrophins induce neuroprotective signaling in the retinal pigment epithelial cell by activating the synthesis of the anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic neuroprotectin D1. Adv Exp Med Biol 613:39–44
Bhave SV, Hoffman PL (2004) Phosphatidylinositol 3'-OH kinase and protein kinase A pathways mediate the anti-apoptotic effect of pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide in cultured cerebellar granule neurons: modulation by ethanol. J Neurochem 88:359–369
Brenneman DE, Hauser JM, Spong C, Phillips TM (2002) Chemokine release is associated with the protective action of PACAP-38 against HIV envelope protein neurotoxicity. Neuropeptides 36:271–280
Brenneman DE, Phillips TM, Hauser J, Hill JM, Spong CY, Gozes I (2003) Complex array of cytokines released by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Neuropeptides 37:111–119
Castorina A, Tiralongo A, Giunta S, Carnazza ML, Rasi G, D'Agata V (2008) PACAP and VIP prevent apoptosis in schwannoma cells. Brain Res 1241:29–35
Cheng JZ, Sharma R, Yang Y et al (2001) Accelerated metabolism and exclusion of 4-hydroxynonenal through induction of RLIP76 and hGST5.8 is an early adaptive response of cells to heat and oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 276:41213–41223
Dejda A, Jolivel V, Bourgault S et al (2008) Inhibitory effect of PACAP on caspase activity in neuronal apoptosis: a better understanding towards therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. J Mol Neurosci 36:26–37
Delgado M, Ganea D (2001) Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit expression of Fas ligand in activated T lymphocytes by regulating c-Myc, NF-kappa B, NF-AT, and early growth factors 2/3. J Immunol 166:1028–1040
Delgado M, Jonakait GM, Ganea D (2002) Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit chemokine production in activated microglia. Glia 39:148–161
Di Giovanni S, Rathore K (2012) p53-dependent pathways in neurite outgrowth and axonal regeneration. Cell Tissue Res in press
Endo K, Nakamachi T, Seki T et al (2011) Neuroprotective effect of PACAP against NMDA-induced retinal damage in the mouse. J Mol Neurosci 43:22–29
Glotin AL, Calipel A, Brossas JY, Faussat AM, Tréton J, Mascarelli F (2006) Sustained versus transient ERK1/2 signaling underlies the anti- and proapoptotic effects of oxidative stress in human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:4614–4623
Gringeri E, Carraro A, Tibaldi E et al (2009) Lyn-mediated mitochondrial tyrosine phosphorylation is required to preserve mitochondrial integrity in early liver regeneration. Biochem J 425:401–412
Horvath G, Racz B, Reglodi D et al (2010) Effects of PACAP on mitochondrial apoptotic pathways and cytokine expression in rats subjected to renal ischemia/reperfusion. J Mol Neurosci 42:411–418
Kalariya NM, Ramana KV, Srivastava SK, van Kuijk FJ (2008) Carotenoid derived aldehyde-induced oxidative stress causes apoptotic cell death in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 86:70–80
Kalonia H, Mishra J, Kumar A (2012) Targeting neuro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress by minocycline attenuates quinolinic-acid-induced Huntington's disease-like symptoms in rats. Neurotox Res. doi:10.1007/s12640-012-9315-x
Kook D, Wolf AH, Yu AL et al (2008) The protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress in the human RPE in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:1712–1720
Le SV, Yamaguchi DJ, McArdle CA, Tachiki K, Pisegna JR, Germano P (2002) PAC1 and PACAP expression, signaling, and effect on the growth of HCT8, human colonic tumor cells. Regul Pept 109:115–125
Lee H, Suk K (2004) Selective modulation of microglial signal transduction by PACAP. Neuroreport 15:1469–1474
Mester L, Kovacs K, Racz B et al (2011) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is protective against oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Mol Neurosci 43:35–43
Ohtaki H, Nakamachi T, Dohi K et al (2006) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) decreases ischemic neuronal cell death in association with IL-6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7488–7493
Onoue S, Hanato J, Yamada S (2008) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide attenuates streptozotocin-induced apoptotic death of RIN-m5F cells through regulation of Bcl-2 family protein mRNA expression. FEBS J 275:5542–5551
Racz B, Gallyas F Jr, Kiss P et al (2006a) The neuroprotective effects of PACAP in monosodium glutamate-induced retinal lesion involve inhibition of proapoptotic signaling pathways. Regul Pept 137:20–26
Racz B, Tamás A, Kiss P et al (2006b) Involvement of ERK and CREB signaling pathways in the protective effect of PACAP in monosodium glutamate-induced retinal lesion. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1070:507–511
Racz B, Gallyas F Jr, Kiss P et al (2007) Effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) on the PKA-Bad-14-3-3 signaling pathway in glutamate-induced retinal injury in neonatal rats. Neurotox Res 12:95–104
Racz B, Gasz B, Gallyas F Jr et al (2008) PKA-Bad-14-3-3 and Akt-Bad-14-3-3 signaling pathways are involved in the protective effects of PACAP against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Regul Pept 145:105–115
Racz B, Horvath G, Reglodi D et al (2010) PACAP ameliorates oxidative stress in the chicken inner ear: an in vitro study. Regul Pept 160:91–98
Rojas JC, John JM, Lee J, Gonzalez-Lima F (2009) Methylene blue provides behavioral and metabolic neuroprotection against optic neuropathy. Neurotox Res 15:260–273
Seaborn T, Masmoudi-Kouli O, Fournier A, Vaudry H, Vaudry D (2011) Protective effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) against apoptosis. Curr Pharm Des 17:204–214
Seki T, Itoh H, Nakamachi T, Shioda S (2008) Suppression of ganglion cell death by PACAP following optic nerve transection in the rat. J Mol Neurosci 36:57–60
Seki T, Itoh H, Nakamachi T et al (2011) Suppression of rat retinal ganglion cell death by PACAP following transient ischemia induced by high intraocular pressure. J Mol Neurosci 43:30–34
Somogyvari-Vigh A, Reglodi D (2004) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide: a potential neuroprotective peptide-review. Curr Pharm Des 10:2861–2889
Szabadfi K, Mester L, Reglodi D et al (2010) Novel neuroprotective strategies in ischemic retinal lesions. Int J Mol Sci 11:544–561
Szabadfi K, Atlasz T, Kiss P et al (2012a) Protective effects of the neuropeptide PACAP in diabetic retinopathy. Cell Tissue Res 348:37–46
Szabadfi K, Atlasz T, Kiss P et al (2012b) Mice deficient in pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) are more susceptible to retinal ischemic injury in vivo. Neurotox Res 21:41–48
Takadera T, Fujibayashi M, Koriyama Y, Kato S (2012) Apoptosis induced by Src-family tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cultured rat cortical cells. Neurotox Res 21:309–316
Tamas A, Gabriel R, Racz B et al (2004) Effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in retinal degeneration induced by monosodium-glutamate. Neurosci Lett 372:110–113
Tibaldi E, Brunati AM, Zonta F et al (2011) Lyn-mediated SHP-1 recruitment to CD5 contributes to resistance to apoptosis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 25:1768–1781
Turner CE, Glenney JR Jr, Burridge K (1990) Paxillin: a new vinculin-binding protein present in focal adhesions. J Cell Biol 111:1059–1068
Vaudry D, Pamantung TF, Basille M et al (2002) PACAP protects cerebellar granule neurons against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Eur J Neurosci 15:1451–1460
Vaudry D, Falluel-Morel A, Bourgault A et al (2009) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide and its receptors: 20 years after the discovery. Pharmacol Rev 61:283–357
Yang Y, Sharma A, Sharma R et al (2003) Cells preconditioned with mild, transient UVA irradiation acquire resistance to oxidative stress and UVA-induced apoptosis: role of 4-hydroxynonenal in UVA-mediated signaling for apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:41380–41388
Zhang XY, Hayasaka S, Chi ZL, Cui HS, Hayasaka Y (2005) Effect of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) on IL-6, and MCP-1 expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cell line. Curr Eye Res 30:1105–1111
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by SROP 4.1.2.B-10/2/KONV-20/0-0002, SROP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0029, OTKA K72592, 100144, CNK78480, Momentum-Program of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Bolyai Scholarship, Akira Arimura Foundation, and Richter Gedeon Centenary Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabian, E., Reglodi, D., Mester, L. et al. Effects of PACAP on Intracellular Signaling Pathways in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Exposed to Oxidative Stress. J Mol Neurosci 48, 493–500 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9812-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9812-7