Abstract
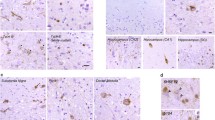
It has been only 5 years since the identification of TDP-43 as the major protein component of the ubiquitinated inclusions in FTLD-U. At that time, there were approximately a dozen papers about TDP-43; today, a “TDP-43” search reveals almost 600 papers. It is now clear that the majority of FTLD cases containing tau- and alpha-synuclein-negative, ubiquitin-positive inclusions (FTLD-U) are FTLD-TDP. The spectrum of TDP-43 proteinopathies includes FTLD-TDP with or without ALS, with or without mutations in GRN, VCP, or TARDBP, with or without chromosome 9p linkage, and sporadic and non-SOD1 familial ALS with or without FTLD-TDP. There are four sub-types of FTLD-TDP, and these correlate with specific clinical and genetic profiles. Sub-types are determined by the presence, predominance, and distribution of the various TDP-43 immunopositive insoluble aggregates—neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions, neuronal intranuclear inclusions, and dystrophic neurites. In this paper, FTLD-TDP pathologic sub-types will be described, and examples of each sub-type will be shown, and implications for future research will be discussed.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador-Ortiz C, Lin W-L, Ahmed Z, Personett D, Davies P, Duara R, Graff-Radford NR, Hutton ML, Dickson DW (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 61:435–445
Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Oda T (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:602–611
Armstrong RA, Ellis W, Hamilton RL, Mackenzie IRA, Hedreen J, Gearing M, Montine T, Vonsattel J-P, Head E, Lieberman AP, Cairns NJ (2010) Neuropathological heterogeneity in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 proteinopathy: a quantitative study of 94 cases using principal components analysis. J Neural Transm 117:227–239
Baker M, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown SM, Gass J, Rademakers R, Lindholm C, Snowden J, Adamson J, Sadovnick D, Rollinson S, Cannon A, Dwosh E, Neary D, Melquist S, Richardson A, Dickson D, Berger Z, Eriksen J, Robinson T, Zehr C, Dickey CA, Crook R, McGowan E, Mann D, Boeve B, Feldman H, Hutton M (2006) Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 442:916–919
Borroni B, Bonvicini C, Alberici A, Buratti E, Agosti C, Archetti S, Papetti A, Stuani C, Di Luca M, Gennarelli M, Padovani A (2009) Mutation within TARDBP leads to frontotemporal dementia without motor neuron disease. Human Mutat 30:E974–E983
Borroni B, Archetti S, Del Bo R, Papetti A, Buratti E, Bonvicini C, Agosti C, Cosseddu M, Turla M, Di Lorenzo D, Pietro Comi G, Gennarelli M, Padovani A (2010) TARDBP mutations in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: frequency, clinical features, and disease course. Rejuvenation Res 13:509–517
Boxer AL, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Baker M, Seeley WW, Crook R, Feldman H, Hsiung G-YR, Rutherford N, Laluz V, Whitwell J, Foti D, McDade E, Molano J, Karydas A, Wojtas A, Goldman J, Mirsky J, Sengdy P, DeArmond S, Miller BL, Rademakers R (2010) Clinical, neuroimaging and neuropathological features of a new chromosome 9p-linked FTD-ALS family. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:196–203
Brandmeir NJ, Geser F, Kwong LK, Zimmerman E, Qian J, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2008) Severe subcortical TDP-43 pathology in sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol 115:123–131
Cairns NJ, Neumann M, Bigio EH, Holm IE, Troost D, Hatanpaa KJ, Foong C, White CL III, Schneider JA, Kretzschmar H, Carter D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Paulsmeyer K, Strider J, Gitcho M, Goate AM, Morris JC, Mishra M, Kwong LK, Stieber A, Xu Y, Forman MS, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ, Mackenzie IR (2007a) TDP-43 in familial and sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin inclusions. Am J Pathol 171:227–240
Cairns NJ, Bigio EH, Mackenzie IRA, Neumann M, Lee VM-Y, Hatanpaa KJ, White CL III, Schneider JA, Grinberg LT, Halliday G, Cuyckaerts C, Lowe JS, Holm IE, Tolnay M, Okamoto K, Yokoo H, Murayama S, Woulfe J, Munoz DG, Dickson DW, Ince PG, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DMA (2007b) Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 114:5–22
Cruts M, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J, Engelborghs S, Wils H, Pirici D, Rademakers R, Vandenberghe R, Dermaut B, Martin J-J, van Duijn C, Peeters K, Sciot R, Santens P, De Pooter T, Mattheijssens M, Van den Broeck M, Cuijt I, Vennekens K, De Deyn PP, Kumar-Singh S, Van Broeckhoven C (2006) Null mutations in progranulin cause ubiquitin positive frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17q21. Nature 442:920–924
Davidson Y, Kelley T, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown S, Du PD, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2007) Ubiquitinated pathological lesions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration contain the TAR DNA-binding protein, TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol 113:521–533
Davion S, Johnson N, Weintraub S, Mesulam M-M, Engberg A, Mishra M, Baker M, Adamson J, Hutton M, Rademakers R, Bigio EH (2007) Clinicopathologic correlations in PGRN mutations. Neurology 69:1113–1121
Forman MS, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Swanson E, Boyer PJ, Drachman DA, Jhaveri BS, Karlawish JH, Pestronk A, Smith TW, Tu P-H, Watts GDJ, Markesbery WR, Smith CH, Kimonis VE (2006) Novel ubiquitin neuropathology in frontotemporal dementia with Valosin-Containing Protein gene mutations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:571–581
Gitcho MA, Bigio EH, Mishra M, Johnson N, Weintraub S, Mesulam M, Rademakers R, Chakraverty S, Cruchaga C, Morris JC, Goate AM, Cairns NJ (2009) TARDBP 3’ UTR variant in autopsy-confirmed frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 proteinopathy. Acta Neuropathol 118:633–645
Guinto JB, Ritson GP, Taylor JP, Forman MS (2007) Valosin-containing protein and the pathogenesis of frontotemporal dementia associated with inclusion body myopathy. Acta Neuropathol 114:55–61
Hasegawa M, Arai T, Nonaka T, Kametani F, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Beach TG, Buratti E, Baralle F, Morita M, Nakano I, Oda T, Tsuchiya K, Akiyama H (2008) Phosphorylated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 64:60–70
Hatanpaa KJ, Blass DM, Pletnikova O, Crain BJ, Bigio EH, Hedreen JC, White CL III, Troncoso JC (2004) Most cases of dementia with hippocampal sclerosis may represent frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 63:538–542
Hatanpaa KJ, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Womack KB, Weintraub S, Morris JC, Foong C, Xiao G, Hladik C, Mantanona TY, White CLIII (2008) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 immunohistochemistry reveals extensive neuritic pathology in FTLD-U: a midwest-southwest consortium for FTLD study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:271–279
Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Truax AC, Uryu K, Neumann M, Clark CM, Elman LB, Miller BL, Grossman M, McCluskey LF, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2008) Enrichment of C-terminal fragments in TAR DNA-binding protein-43 cytoplasmic inclusions in brain but not in spinal cord of frontotemporal lobar degeneration anad amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am M Pathol 173:182–194
Josephs KA, Stroh A, Dugger B, Dickson DW (2009) Evaluation of subcortical pathology and clinical correlations in FTLD-U subtypes. Acta Neuropathol 118:349–358
Kovari E, Gold G, Giannakopolous P, Bouras D (2004) Cortical ubiquitin-positive inclusions in frontotemporal dementia without motor neuron disease: a quantitative immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol 108:207–212
Kwong LK, Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2007) TDP-43 proteinopathy: the neuropathology underlying major forms of sporadic and familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration and motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol 114:63–70
LeBer I, Camuzat A, Berger E, Hannequin D, Laquerriere A, Golfier V, Seilhean D, Viennet G, Couratier P, Verpillat P, Heath S, Camu W, Martinaud O, Lacomblez I, Vercelletto M, Salachas F, Sellal F, Didic M, Thomas-Anterion C, Puel M, Michel B-F, Besse C, Duyckaerts C, Meininger V, Campion D, Dubois B, Brice A (2009) Chromosome 9p-linked families with frontotemporal dementia associated with motor neuron disease. Neurology 72:1669–1676
Luty AA, Kwok JBJ, Thompson EM, Blumbergs P, Brooks WS, Loy CT, Dobson-Stone C, Panegyres PK, Hecker J, Nicholson GA, Halliday GM, Schofield PR (2008) Pedigree with frontotemporal lobar degeneration-motor neuron disease and Tar DNA binding protein-43 positive neuropathology: genetic linkage to chromosome 9. BMC Neurol 8:1–11
Mackenzie IR, Baborie A, Pickering-Brown S, Plessis DD, Jaros E, Perry RH, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2006) Heterogeneity of ubiquitin pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: classification and relation to clinical phenotype. Acta Neuropathol 112:539–549
Mackenzie IR, Bigio EH, Ince PG et al (2007) Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann Neurol 61:427–434
Mackenzie IRA, Foti D, Woulfe J, Hurwitz TA (2008) Atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive, TDP-43-negative neuronal inclusions. Brain 131:1282–1293
Mackenzie IRA, Neumann M, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Alafuzoff I, Kril J, Kovacs GG, Ghetti B, Halliday G, Holm IE, Ince PG, Kamphorst W, Revesz T, Rozemuller AJM, Kumar-Singh S, Akiyama H, Baborie A, Spina S, Dickson DW, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DMA (2010) Nomenclature and nosology for neuropathologic subtypes of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: an update. Acta Neuropathol 119:1–4
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Neumann M, Rademakers R, Roeber S, Baker M, Kretzschmar HA, Mackenzie IRA (2009a) A new subtype of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with FUS pathology. Brain 132:2922–2931
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Lee EB, Kremmer E, Flatley A, Xu Y, Forman MS, Troost D, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2009b) Phosphorylation of S409/410 of TDP-43 is a consistent feature in all sporadic and familial forms of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Acta Neuropathol 117:137–149
Nishimura AL, Zupunski V, Troakes C, Kathe C, Fratta P, Howell M, Gallo J-M, Hortobagyi T, Shaw CE, Rogelj B (2010) Nuclear import impairment causes cytoplasmic trans-activation response DNA-binding protein accumulation and is associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Brain 133:1763–1771
Ou SH, Wu F, Harrich D, Garcia-Martinez LF, Gaynor RB (1995) Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J Virol 69:3584–3596
Probst A, Taylor KI, Tolnay M (2007) Hippocampal sclerosis dementia: a reappraisal. Acta Neuropathol 114:335–345
Roeber S, Mackenzie IR, Kretzschmar HA, Neumann M (2008) TDP-43-negative FTLD-U is a significant new clinico-pathological subtype of FTLD. Acta Neuropathol 116:147–157
Sampathu DM, Neumann M, Kwong LK, Chou TT, Micsenyi M, Truax A, Bruce J, Grossman M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Pathological heterogeneity of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions delineated by ubiquitin immunohistochemistry and novel monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol 169:1343–1352
Wang I-F, Wu L-S, Chang H-Y, Shen C-K J (2008) TDP-43, the signature protein of FTLD-U, is a neuronal activity-responsive factor. J Neurochem 105:797–806. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05190.x
Acknowledgments
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the NU CNADC directed by Dr. M-Marcel Mesulam, the NU Lois Insolia ALS Center directed by Dr. Teepu Siddique, Manjari Mishra, and Katherine Gasho for histological and immunohistochemical expertise, the UT Southwestern ADC for the FTLD-TDP type 4 case, and, most importantly, the generous patients and families without whom these studies would not be possible. This study is supported in part by NIH grant AG13854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented at the 7th International FTD Conference in Indianapolis, IN, USA on October 6, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bigio, E.H. TDP-43 Variants of Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. J Mol Neurosci 45, 390–401 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9545-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9545-z