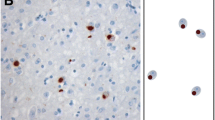
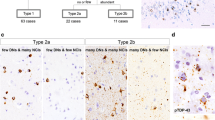
Abstract
Recently, TDP-43, a 43 kDa nuclear TAR DNA-binding protein, was identified as the major disease protein in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitinated inclusions (FTLD-U), FTLD-U with motor neuron disease (FTLD–MND), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. To date, TDP-43 pathology in sporadic FTLD–MND has been reported only in select central nervous system areas. However, this distribution of lesions is insufficient to explain all clinical signs of FTLD–MND and the extent of TDP-43 pathology, throughout the brain, remains unknown. Therefore, as a pilot study, we performed an immunohistochemical whole brain scan of two cases diagnosed clinically as FTLD–MND and two control subjects. We found evidence of both neuronal and glial TDP-43 pathology in multiple brain areas including the nigro-striatal system, neo- and allocortical brain areas, with varying frequency, morphology, and degree, and nowhere in control tissue. The finding of a distinct cytopathological profile consisting of a cell nucleus devoid of endogenous TDP-43 staining coupled with diffuse/granular cytoplasmic staining (“pre-inclusion”) was prominent in a couple of brain areas. These pre-inclusions were not or only weakly ubiquitin-immunoreactive. While the findings of severe involvement of extracortical or extrapyramidal areas are strongly suggestive for FTLD–MND being a TDP-43 multisystem proteinopathy rather than a disease predominantly affecting the cortex and spinal cord, more detailed clinicopathological studies of larger cohorts are needed to fully elucidate the distribution and severity of pathological TDP-43 in this disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador-Ortiz C, Lin WL, Ahmed Z, Personett D, Davies P, Duara R, Graff-Radford NR, Hutton ML, Dickson DW (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 61:435–445
Buratti E, Baralle FE (2001) Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem 276:36337–36343
Cairns NJ, Bigio EH, Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Lee VM-Y, Hatanpaa KJ, White CL III, Schneider JA, Grinberg LT, Halliday G, Duyckaerts C, Lowe JS, Holm IE, Tolnay M, Okamoto K, Yokoo H, Murayama S, Woulfe J, Munoz DG, Dickson DW, Ince PG, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DM (2007) Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 114:5–22
Cairns NJ, Neumann M, Bigio EH, Holm IE, Troost D, Hatanpaa KJ, Foong C, White CL III, Schneider JA, Kretzschmar HA, Carter D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Paulsmeyer K, Strider J, Gitcho M, Goate AM, Morris JC, Mishra M, Kwong LK, Stieber A, Xu Y, Forman MS, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Mackenzie IR (2007) TDP-43 in familial and sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin inclusions. Am J Pathol 171:227–240
Croisier E, Graeber MB (2006) Glial degeneration and reactive gliosis in alpha-synucleinopathies: the emerging concept of primary gliodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol 112:517–530
Davidson Y, Kelley T, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown S, Du PD, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2007) Ubiquitinated pathological lesions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration contain the TAR DNA-binding protein, TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol 113:521–533
Deymeer F, Smith TW, DeGirolami U, Drachman DA (1989) Thalamic dementia and motor neuron disease. Neurology 39:58–61
Dickson DW, Josephs KA, Amador-Ortiz C (2007) TDP-43 in differential diagnosis of motor neuron disorders. Acta Neuropathol 114:71–79
Forman MS, Farmer J, Johnson JK, Clark CM, Arnold SE, Coslett HB, Chatterjee A, Hurtig HI, Karlawish JH, Rosen HJ, Van Deerlin V, Lee VM-Y, Miller BL, Trojanowski JQ, Grossman M (2006) Frontotemporal dementia: clinicopathological correlations. Ann Neurol 59:952–962
Geser F, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Frontotemporal dementias. In: Rosenberg RN, DiMauro S, Paulson H, Ptacek L, Nestler E (eds) The molecular and genetic basis of neurological and psychiatric disease. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 330–338
Geser F, Winton MJ, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Xie SX, Igaz LM, Garruto RM, Perl DP, Galasko D, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Pathological TDP-43 in parkinsonism–dementia complex and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of Guam. Acta Neuropathol. 10.1007/s00401-007-0257-y
Higashi S, Iseki E, Yamamoto R, Minegishi M, Hino H, Fujisawa K, Togo T, Katsuse O, Uchikado H, Furukawa Y, Kosaka K, Arai H (2007) Appearance pattern of TDP-43 in Japanese frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions. Neurosci Lett 419:213–218
Kim JS (2002) Post-stroke emotional incontinence after small lenticulocapsular stroke: correlation with lesion location. J Neurol 249:805–810
Kwong LK, Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) TDP-43 proteinopathy: the neuropathology underlying major forms of sporadic and familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration and motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol 114:63–70
Leverenz JB, Yu CE, Montine TJ, Steinbart E, Bekris LM, Zabetian C, Kwong LK, Lee VM, Schellenberg GD, Bird TD (2007) A novel progranulin mutation associated with variable clinical presentation and tau, TDP43 and alpha-synuclein pathology. Brain 130:1360–1374
Mackenzie IR, Bigio EH, Ince PG, Geser F, Neumann M, Cairns NJ, Kwong LK, Forman MS, Ravits J, Stewart H, Eisen A, McClusky L, Kretzschmar HA, Monoranu CM, Highley JR, Kirby J, Siddique T, Shaw PJ, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann Neurol 61:427–434
Mackenzie IR, Feldman HH (2005) Ubiquitin immunohistochemistry suggests classic motor neuron disease, motor neuron disease with dementia, and frontotemporal dementia of the motor neuron disease type represent a clinicopathologic spectrum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:730–739
Nakashima-Yasuda H, Uryu K, Robinson J, Xie SX, Hurtig H, Duda JE, Arnold SE, Siderowf A, Grossman M, Leverenz JB, Woltjer R, Lopez OL, Hamilton R, Tsuang DW, Galasko D, Masliah E, Kaye J, Clark CM, Montine TJ, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Co-morbidity of TDP-43 proteinopathy in Lewy body related diseases. Acta Neuropathol 114:221–229
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Vanmassenhove B, Kretzschmar HA, Van Deerlin VM, Clark CM, Grossman M, Miller BL, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2007) TDP-43-positive white matter pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:177–183
Neumann M, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Boyer PJ, Markesbery WR, Smith CD, Taylor JP, Kretzschmar HA, Kimonis VE, Forman MS (2007) TDP-43 in the ubiquitin pathology of frontotemporal dementia with VCP gene mutations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:152–157
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Ou SH, Wu F, Harrich D, Garcia-Martinez LF, Gaynor RB (1995) Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J Virol 69:3584–3596
Sampathu DM, Neumann M, Kwong LK, Chou TT, Micsenyi M, Truax A, Bruce J, Grossman M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2006) Pathological heterogeneity of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions delineated by ubiquitin immunohistochemistry and novel monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol 169:1343–1352
Schiffer R, Pope LE (2005) Review of pseudobulbar affect including a novel and potential therapy. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 17:447–454
Seelaar H, Jurgen SH, Azmani A, Kusters B, Rosso S, Majoor-Krakauer D, de Rijik MC, Rizzu P, Brummelhuis MT, van Doorn PA, Kamphorst W, Willemsen R, van Swieten JC (2007) TDP-43 pathology in familial frontotemporal dementia and motor neuron disease without Progranulin mutations. Brain 130:1375–1385
Snowden J, Neary D, Mann D (2007) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: clinical and pathological relationships. Acta Neuropathol 114:31–38
Tan CF, Eguchi H, Tagawa A, Onodera O, Iwasaki T, Tsujino A, Nishizawa M, Kakita A, Takahashi H (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in neuronal inclusions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with or without SOD1 gene mutation. Acta Neuropathol 113:535–542
Wang HY, Wang IF, Bose J, Shen CK (2004) Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics 83:130–139
Zhang H, Tan CF, Mori F, Tanji K, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2007) TDP-43-immunoreactive neuronal and glial inclusions in the neostriatum in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with and without dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 10.1007/s00401-007-0285-7
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank T. Schuck, J. Robinson, and M. Getahun for their expert technical assistance and M. Martinez-Lage for critical comments on the discussion. Further, they thank their patients and families who made this research possible. This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (AG10124, AG17586, and HL071483).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nicholas J. Brandmeir and Felix Geser contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandmeir, N.J., Geser, F., Kwong, L.K. et al. Severe subcortical TDP-43 pathology in sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol 115, 123–131 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0315-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0315-5