Abstract
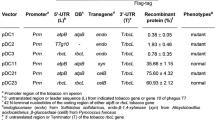
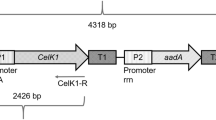
The high capacity of the chloroplast genome to integrate and express transgenes at high levels makes transplastomic technology a good option for overexpressing proteins of interest. This report presents the stable expression of β-glucosidase (bgl1 gene) from Aspergillus niger and two cellulases (celA and celB genes) from Thermotoga neapolitana into the chloroplast genome of tobacco. The pES6, pHM4, pHM5 and pHM6 vectors were derived from the pES4 plasmid containing bgl1, celA-celB, celA and celB synthetic genes, respectively. All of the genes were flanked by a synthetic rrn16 promoter and the 3′UTR from rbcL gene. The integration of the genes into intergenic regions rrn16 and 3′rps12 of the inverted repeats was confirmed by Southern blot analysis. Stable expression and processing of monocistronic mRNA were confirmed by Northern blot analysis, and protein functionality was analysed via enzymatic activity assay. The recombinant enzymes exhibited high enzymatic activity at pH 5 (β-glucosidase: 30.45 U mg−1 of TSP, celA-celB 58 U mg−1 of TSP, celA 49.10 U mg−1 of TSP and celB 48.72 U mg−1 of TSP). In addition, β-glucosidase exhibited high activity at 40 °C, whereas cellulases type A (celA) and type B (celB) showed high activity at 65 °C. NtpES6, NtpHM5 and NtpHM6 plants showed a similar phenotype compared with the wild type plants; however, NtpHM4 plants presented an abnormal phenotype with variegated leaves. This study, demonstrated that hydrolytic genes such as bgl1, celA and celB could be integrated and expressed correctly in the chloroplast genome. This work provides new information on methods and strategies for the expression of hydrolytic enzymes that are potentially useful for biotechnological applications using transplastomic plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barras F, van Gijsegem F, Chatterjee AK (1994) Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu Rev Phytopathol 32:201–234. doi:10.1146/annurev.py.32.090194.001221
Beguin P, Aubert JP (1994) The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:25–58. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00033.x
Berghem LE, Pettersson LG (1973) The mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation. Eur J Biochem 37:21–30. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4960
Bock R (2001) Transgenic plastids in basic research and plant biotechnology. J Mol Biol 312:425–438. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4960
Bock R (2007) Plastid biotechnology: prospects for herbicide and insect resistance, metabolic engineering and molecular farming. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:100–106. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2006.12.001
Bok JD, Yernool DA, Eveleigh DE (1998) Purification, characterization, and molecular analysis of thermostable cellulases CelA and CelB from Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl Environ Microb 64:4774–4781
Cosgrove DJ (1993) How do plant cell walls extend? Plant Physiol 102:1–6. doi:10.1104/pp.102.1.1
Dai Z, Hooker B, Quesenberry R, Gao J (1999) Expression of Trichoderma reesei exo-cellobiohydrolase I in transgenic tobacco leaves and calli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 79:689–699. doi:10.1385/ABAB:79:1-3:689
Dan S, Marton I, Dekel M, Bravdo BA, He S, Withers SG, Shoseyov O (2000) Cloning, expression, characterization, and nucleophile identification of family 3, Aspergillus niger beta-glucosidase. J Biol Chem 275:4973–4980. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.7.4973
Daniell H, Ruiz ON, Dhingra A (2005) Chloroplast genetic engineering to improve agronomic traits. Methods Mol Biol 286:111–138. doi:10.1385/1-59259-827-7:111
Davarpanah S, Ahn J-W, Ko S, Jung S, Park Y-I, Liu J, Jeong W (2012) Stable expression of a fungal laccase protein using transplastomic tobacco. Plant Biotechnol Rep 6:305–312. doi:10.1007/s11816-012-0225-4
Derepas A, Dulieu H (1992) Inheritance of the capacity to transfer plastids by the pollen parent in Petunia hybrida. Hort J Hered 83:6–10
Diers L (1971) Übertragung von Plastiden durch den Pollen bei Antirrhinum majus. Mol Gen Genet MGG 113:150–153. doi:10.1007/BF00333187
Doyle J (1991) DNA protocols for plants. In: Mol Tech Tax. Springer, pp 283–293. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-83962-7_18
Dufourmantel N, Pelissier B, Garcon F, Peltier G, Ferullo JM, Tissot G (2004) Generation of fertile transplastomic soybean. Plant Mol Biol 55:479–489. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-0192-4
Espinoza-Sánchez EA, Torres-Castillo J, Rascón-Cruz Q, Gutiérrez-Díez A, Zavala-García F, Sinagawa-García SR (2015) Stable expression and characterization of a fungal pectinase and bacterial peroxidase genes in tobacco chloroplast. Electron J Biotechnol 18(3):161–168. doi:10.1016/j.ejbt.2015.03.002
Goyal AK, Eveleigh DE (1996) Cloning, sequencing and analysis of the ggh-A gene encoding a 1,4-β-d-glucan glucohydrolase from Microbispora bispora. Gene 172:93–98. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(96)00076-5
Gray B, Yang H, Ahner B, Hanson M (2011) An efficient downstream box fusion allows high-level accumulation of active bacterial beta-glucosidase in tobacco chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 76:345–355. doi:10.1007/s11103-011-9743-7
Hoondal GS, Tiwari RP, Tewari R, Dahiya N, Beg QK (2002) Microbial alkaline pectinases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biot 59:409–418. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1061-1
Jabbour D, Klippel B, Antranikian G (2012) A novel thermostable and glucose-tolerant β-glucosidase from Fervidobacterium islandicum. Appl Microbiol Biot 93:1947–1956. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3406-0
Jin S, Kanagaraj A, Verma D, Lange T, Daniell H (2011) Release of hormones from conjugates: chloroplast expression of beta-glucosidase results in elevated phytohormone levels associated with significant increase in biomass and protection from aphids or whiteflies conferred by sucrose esters. Plant Physiol 155:222–235. doi:10.1104/pp.110.160754
Jung S, Kim S, Bae H, Lim H-S, Bae H-J (2010) Expression of thermostable bacterial β-glucosidase (BglB) in transgenic tobacco plants. Bioresour Technol 101:7144–7150. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.140
Jung S, Lee D-S, Kim Y-O, Joshi C, Bae H-J (2013) Improved recombinant cellulase expression in chloroplast of tobacco through promoter engineering and 5′ amplification promoting sequence. Plant Mol Biol 83:317–328. doi:10.1007/s11103-013-0088-2
Juturu V, Wu JC (2014) Microbial cellulases: engineering, production and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 33:188–203. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.077
Kanamoto H, Yamashita A, Asao H, Okumura S, Takase H, Hattori M, Yokota A, Tomizawa K (2006) Efficient and stable transformation of Lactuca sativa L. cv. Cisco (lettuce) plastids. Transgenic Res 15:205–217. doi:10.1007/s11248-005-3997-2
Kleczkowski K, Schell J, Bandur R (1995) Phytohormone conjugates: nature and function. Crit Rev Plant Sci 14:283–298. doi:10.1080/07352689509382361
Kolotilin I, Kaldis A, Pereira EO, Laberge S, Menassa R (2013) Optimization of transplastomic production of hemicellulases in tobacco: effects of expression cassette configuration and tobacco cultivar used as production platform on recombinant protein yields. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:65. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-6-65
Kurniasih SD, Alfi A, Natalia D, Radjasa OK, Nurachman Z (2014) Construction of individual, fused, and co-expressed proteins of endoglucanase and β-glucosidase for hydrolyzing sugarcane bagasse. Microbiol Res 169:725–732. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2014.02.002
Kuroda H, Maliga P (2001) Sequences downstream of the translation initiation codon are important determinants of translation efficiency in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 125:430–436. doi:10.1104/pp.125.1.430
Leelavathi S, Gupta N, Maiti S, Ghosh A, Siva Reddy V (2003) Overproduction of an alkali- and thermo-stable xylanase in tobacco chloroplasts and efficient recovery of the enzyme. Mol Breed 11(1):59–67. doi:10.1023/A:1022168321380
Lelivelt CL, McCabe MS, Newell CA, Desnoo CB, van Dun KM, Birch-Machin I, Gray JC, Mills KH, Nugent JM (2005) Stable plastid transformation in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 58:763–774. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-7704-8
Li Q, Li P, Sun L, Wang Y, Ji K, Sun Y, Dai S, Chen P, Duan C, Leng P (2012) Expression analysis of β-glucosidase genes that regulate abscisic acid homeostasis during watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) development and under stress conditions. J Plant Physiol 169:78–85. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2011.08.005
Lutz KA, Maliga P (2008) Plastid genomes in a regenerating tobacco shoot derive from a small number of copies selected through a stochastic process. Plant J 56:975–983. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03655.x
Lutz KA, Svab Z, Maliga P (2006) Construction of marker-free transplastomic tobacco using the Cre-loxP site-specific recombination system. Nat Protoc 1:900–910. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.118
Maliga P (2002) Engineering the plastid genome of higher plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:164–172. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00248-0
Maliga P (2004) Plastid transformation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:289–313. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141633
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. doi:10.1021/ac60147a030
Nascimento C, Souza F, Masui D, Leone F, Peralta R, Jorge J, Furriel R (2010) Purification and biochemical properties of a glucose-stimulated β-d-glucosidase produced by Humicola grisea var. thermoidea grown on sugarcane bagasse. J Microbiol 48:53–62. doi:10.1007/s12275-009-0159-x
Nugent GD, Coyne S, Nguyen TT, Kavanagh TA, Dix PJ (2006) Nuclear and plastid transformation of Brassica oleracea var. botrytis (cauliflower) using PEG-mediated uptake of DNA into protoplasts. Plant Sci 170:135–142. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.08.020
Pei J, Pang Q, Zhao L, Fan S, Shi H (2012) Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum β-glucosidase: a glucose-tolerant enzyme with high specific activity for cellobiose. Biotechnol Biof 5:1–10. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-5-31
Pérez-Pons JA, Rebordosa X, Querol E (1995) Properties of a novel glucose-enhanced β-glucosidase purified from Streptomyces sp. (ATCC 11238). Biochim Biophys Acta 1251:145–153. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(95)00074-5
Petersen K, Bock R (2011) High-level expression of a suite of thermostable cell wall-degrading enzymes from the chloroplast genome. Plant Mol Biol 76:311–321. doi:10.1007/s11103-011-9742-8
Quesada-Vargas T, Ruiz ON, Daniell H (2005) Characterization of heterologous multigene operons in transgenic chloroplasts: transcription, processing, and translation. Plant Physiol 138:1746–1762. doi:10.1104/pp.105.063040
Ragauskas AJ, Williams CK, Davison BH, Britovsek G, Cairney J, Eckert CA, Frederick WJ, Hallett JP, Leak DJ, Liotta CL (2006) The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311:484–489. doi:10.1126/science.1114736
Rixon JE, Ferreira LM, Durrant AJ, Laurie JI, Hazlewood GP, Gilbert HJ (1992) Characterization of the gene celD and its encoded product 1,4-beta-d-glucan glucohydrolase D from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. Cellulosa. Biochem J 285(Pt 3):947–955
Ruf S, Hermann M, Berger IJ, Carrer H, Bock R (2001) Stable genetic transformation of tomato plastids and expression of a foreign protein in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:870–875. doi:10.1038/nbt0901-870
Ruf S, Karcher D, Bock R (2007) Determining the transgene containment level provided by chloroplast transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6998–7002. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700008104
Saha BC, Bothast RJ (1996) Production, purification, and characterization of a highly glucose-tolerant novel beta-glucosidase from Candida peltata. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3165–3170
Sidorov VA, Kasten D, Pang SZ, Hajdukiewicz PT, Staub JM, Nehra NS (1999) Technical advance: stable chloroplast transformation in potato: use of green fluorescent protein as a plastid marker. Plant J 19:209–216. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00508.x
Sinagawa-Garcia SR, Tungsuchat-Huang T, Paredes-Lopez O, Maliga P (2009) Next generation synthetic vectors for transformation of the plastid genome of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 70:487–498. doi:10.1007/s11103-009-9486-x
Smith SE (1989) Influence of parental genotype on plastid inheritance in Medicago sativa. J Hered 80:214–217
Sørensen I, Domozych D, Willats WGT (2010) How have plant cell walls evolved? Plant Physiol 153:366–372. doi:10.1104/pp.110.154427
Soriano M, Diaz P, Pastor FIJ (2006) Pectate lyase C from Bacillus subtilis: a novel endo-cleaving enzyme with activity on highly methylated pectin. Microbiology 152:617–625. doi:10.1099/mic.0.28562-0
Souza FHM, Meleiro LP, Machado CB, Zimbardi ALRL, Maldonado RF, Souza TACB, Masui DC, Murakami MT, Jorge JA, Ward RJ, Furriel RPM (2014) Gene cloning, expression and biochemical characterization of a glucose- and xylose-stimulated β-glucosidase from Humicola insolens RP86. J Mol Cat B Enzym 106:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.04.007
Stiekema WJ, Heidekamp F, Dirkse WG, van Beckum J, de Haan P, Bosch CT, Louwerse JD (1988) Molecular cloning and analysis of four potato tuber mRNAs. Plant Mol Biol 11:255–269. doi:10.1007/bf00027383
Svab Z, Maliga P (1993) High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:913–917. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.3.913
Svab Z, Hajdukiewicz P, Maliga P (1990) Stable transformation of plastids in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8526–8530. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.21.8526
Teeri TT (1997) Crystalline cellulose degradation: new insight into the function of cellobiohydrolases. Trends Biotechnol 15:160–167. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(97)01032-9
Uchima C, Tokuda G, Watanabe H, Kitamoto K, Arioka M (2011) Heterologous expression and characterization of a glucose-stimulated β-glucosidase from the termite Neotermes koshunensis in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biot 89:1761–1771. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2963-y
Verma D, Kanagaraj A, Jin S, Singh ND, Kolattukudy PE, Daniell H (2010) Chloroplast-derived enzyme cocktails hydrolyse lignocellulosic biomass and release fermentable sugars. Plant Biotechnol J 8:332–350. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009.00486.x
Wakuta S, Hamada S, Ito H, Matsuura H, Nabeta K, Matsui H (2010) Identification of a β-glucosidase hydrolyzing tuberonic acid glucoside in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Phytochemistry 71:1280–1288. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.04.025
Watson J, Koya V, Leppla SH, Daniell H (2004) Expression of Bacillus anthracis protective antigen in transgenic chloroplasts of tobacco, a non-food/feed crop. Vaccine 22:4374–4384. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.01.069
Wegener CB, Olsen O (2004) Heterologous pectate lyase isoenzymes are not different in their effects on soft rot resistance in transgenic potatoes. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 65:59–66. doi:10.1016/j.pmpp.2004.12.004
Wei H, Xu Q, Taylor Ii LE, Baker JO, Tucker MP, Ding S-Y (2009) Natural paradigms of plant cell wall degradation. Curr Opin Biotech 20:330–338. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2009.05.008
Wilson DB (2009) Cellulases and biofuels. Curr Opin Biotech 20:295–299. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2009.05.007
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulase activities. In: Willis A, Wood STK (eds) Method Enzymol, vol 160. Academic Press, pp 87–112. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(88)60109-1
Yan T-R, Lin C-L (1997) Purification and characterization of a glucose-tolerant β-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger CCRC 31494. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:965–970. doi:10.1271/bbb.61.965
Yu L, Gray B, Rutzke C, Walker L, Wilson D, Hanson M (2007) Expression of thermostable microbial cellulases in the chloroplasts of nicotine-free tobacco. J Biotechnol 131:362–369. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.07.942
Zanoelo FF, Polizeli MdLTdM, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA (2004) β-glucosidase activity from the thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum is stimulated by glucose and xylose. FEMS Microbiol Lett 240:137–143. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.09.021
Zhang Q, Zhang W, Lin C, Xu X, Shen Z (2012) Expression of an Acidothermus cellulolyticus endoglucanase in transgenic rice seeds. Protein Expres Purif 82:279–283. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2012.01.011
Ziegelhoffer T, Raasch J, Austin-Phillips S (2001) Dramatic effects of truncation and sub-cellular targeting on the accumulation of recombinant microbial cellulase in tobacco. Mol Breed 8:147–158. doi:10.1023/A:1013338312948
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología for financial support of this work (CB-2012-179794) and are grateful to Dr. Pal Maliga, Waksman Institute, Rutgers University, USA for providing pPRV111 plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espinoza-Sánchez, E.A., Torres-Castillo, J.A., Rascón-Cruz, Q. et al. Production and characterization of fungal β-glucosidase and bacterial cellulases by tobacco chloroplast transformation. Plant Biotechnol Rep 10, 61–73 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-016-0386-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-016-0386-7