Abstract
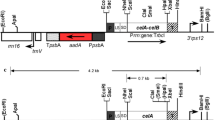
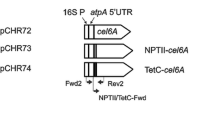
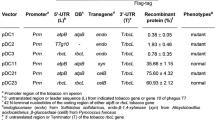
Production of enzymes for lignocellulose hydrolysis in planta has been proposed as a lower-cost alternative to microbial production, with plastid transformation as a preferred method due to high foreign protein yields. An important regulator of chloroplast protein production is the downstream box (DB) region, located immediately downstream of the start codon. Protein accumulation can vary over several orders of magnitude by altering the DB region. Experiments in bacteria have suggested that these differences in protein accumulation may result from changes in translation efficiency, though the precise mechanism of DB function is not known. In this study, three DB regions were fused to the bglC ORF encoding a β-glucosidase from the thermophilic bacterium Thermobifida fusca and inserted into the tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plastid genome. More than a two order of magnitude of difference in BglC protein accumulation was observed, dependent on the identity of the DB fusion. Differential transcript accumulation explained some the observed differences in protein accumulation, but in addition, less 3′ degradation of bglC transcripts was observed in transgenic plants that accumulated the most BglC enzyme. Chloroplast-produced BglC was active against both pure cellobiose and against tobacco lignocellulose. These experiments demonstrate the potential utility of transplastomic plants as a vehicle for heterologous β-glucosidase production for the cellulosic ethanol industry.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apel W, Schulze WX, Bock R (2010) Identification of protein stability determinants in chloroplasts. Plant J 63:636–650
Barkan A (1988) Proteins encoded by a complex chloroplast transcription unit are each translated from both monocistronic and polycistronic mRNAs. EMBO J 7:2637–2644
Farran I, McCarthy-Suárez I, Río-Manterola F, Mansilla C, Lasarte JJ, Mingo-Castel AM (2010) The vaccine adjuvant extra domain a from fibronectin retains its proinflammatory properties when expressed in tobacco chloroplasts. Planta 231:977–990
Gonzalez de Valdivia EI, Isaksson LA (2005) Abortive translation caused by peptidyl-tRNA drop-off at NGG codons in the early coding region of mRNA. FEBS J 272:5306–5316
Gray BN, Ahner BA, Hanson MR (2009) High-level bacterial cellulase accumulation in chloroplast-transformed tobacco mediated by downstream box fusions. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1045–1054
Hayes R, Kudla J, Gruissem W (1999) Degrading chloroplast mRNA: the role of polyadenylation. Trends Biochem Sci 24:199–202
Juhász T, Egyházi A, Réczey K (2005) β-glucosidase production by Trichoderma reesei. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 121–124:243–254
Jung S, Suyeon K, Bae H, Lim H-S, Bae H-J (2010) Expression of thermostable bacterial β-glucosidase (BglB) in transgenic tobacco plants. Bioresource Technol 101:7144–7150
Kuroda H, Maliga P (2001a) Complementarity of the 16S rRNA penultimate stem with sequences downstream of the AUG destabilizes the plastid mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 29:970–975
Kuroda H, Maliga P (2001b) Sequences downstream of the translation initiation codon are important determinants of translation efficiency in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 125:430–436
Lamed R, Kenig R, Morgenstern E, Calzada JF, De Micheo F, Bayer EA (1991) Efficient cellulose solubilization by a combined cellulosome-β-glucosidase system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 27:173–183
Lenzi P, Scotti N, Alagna F, Tornesello ML, Pompa A, Vitale A, De Stradis A, Monti L, Grillo S, Buonaguro FM, Maliga P, Cardi T (2008) Translational fusion of chloroplast-expressed human papillomavirus type 16 L1 capsid protein enhances antigen accumulation in transplastomic tobacco. Transgenic Res 17:1091–1102
Maliga P (2003) Progress towards commercialization of plastid transformation technology. Trends Biotechnol 21:20–28
Monde RA, Schuster G, Stern DB (2000) Processing and degradation of chloroplast mRNA. Biochimie 82:573–582
Nilsson G, Belasco JG, Cohen SN, von Gabain A (1987) Effect of premature termination of translation on mRNA stability depends on the site of ribosome release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4890–4894
Oey M, Lohse M, Kreikemeyer B, Bock R (2009) Exhaustion of the chloroplast protein synthesis capacity by massive expression of a highly stable protein antibiotic. Plant J 57:436–445
Quesada-Vargas T, Ruiz ON, Daniell H (2005) Characterization of heterologous multigene operons in transgenic chloroplasts. Transcription, processing, and translation. Plant Physiol 138:1746–1762
Rapaport LR, Mackie GA (1994) Influence of translational efficiency on the stability of the mRNA for ribosomal protein S20 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 176:992–998
Schell DJ, Hinman ND, Wyman CE, Werdene PJ (1990) Whole broth cellulase production for use in simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 24–25:287–297
Spindler DD, Wyman CE, Grohmann K, Mohagheghi A (1989) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of pretreated wheat straw to ethanol with selected yeast strains and β-glucosidase supplementation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 20–21:529–540
Spiridonov NA, Wilson DB (2001) Cloning and biochemical characterization of BglC, a beta-glucosidase from the cellulolytic actinomycete Thermobifida fusca. Curr Microbiol 42:295–301
Svab Z, Maliga P (1993) High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:913–917
Tregoning JS, Nixon P, Kuroda H, Svab Z, Clare S, Bowe F, Fairweather N, Ytterberg J, van Wijk KJ, Dougan G, Maliga P (2003) Expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in tobacco chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res 31:1174–1179
Twyman RM, Stoger E, Schillberg S, Christou P, Fischer R (2003) Molecular farming in plants: host systems and expression technology. Trends Biotechnol 21:570–578
Verma D, Kanagaraj A, Jin S, Singh ND, Kolattukudy PE, Daniell H (2010) Chloroplast-derived enzyme cocktails hydrolyse lignocellulosic biomass and release fermentable sugars. Plant Biotechnol J 8:332–350
Wei S, Marton I, Dekel M, Shalitin D, Lewinsohn E, Bravdo B-A, Shoseyov O (2004) Manipulating volatile emission in tobacco leaves by expressing Aspergillus niger beta-glucosidase in different subcellular compartments. Plant Biotechnol J 2:341–350
Ye GN, Hajdukiewicz PT, Broyles D, Rodriguez D, Xu CW, Nehra N, Staub JM (2001) Plastid-expressed 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase genes provide high level glyphosate tolerance in tobacco. Plant J 25:261–270
Zhang Y-HP, Lynd LR (2004) Toward an aggregated understanding of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose: Noncomplexed cellulase systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:797–824
Zhou F, Karcher D, Bock R (2007) Identification of a plastid intercistronic expression element (IEE) facilitating the expression of stable translatable monocistronic mRNAs from operons. Plant J 52:961–972
Ziegelhoffer T, Raasch JA, Austin-Phillips S (2009) Expression of Acidothermus cellulolyticus E1 endo-beta-1, 4-glucanase catalytic domain in transplastomic tobacco. Plant Biotechnol J 7:527–536
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Acknowledgments
We thank David Wilson and Diana Irwin for their kind donation of anti-BglC antibodies and the pNS6 plasmid for cloning the bglC gene, and Deborah Sills for her kindly donated Spezyme CP for tobacco hydrolysis. BNG was the recipient of an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship. This work was supported by a USDA Grant (USDA NRI 2007-02133) to BAA and MRH. This research was also supported in part by the Cornell University Agricultural Experiment Station federal formula funds, Project No. NYC-165425 received from Cooperative State Research, Education and Extension Service, US Department of Agriculture. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the view of the US Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, B.N., Yang, H., Ahner, B.A. et al. An efficient downstream box fusion allows high-level accumulation of active bacterial beta-glucosidase in tobacco chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 76, 345–355 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9743-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9743-7