Abstract
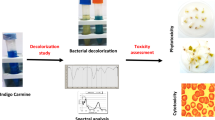
Fungi play an important role in dying wastewater treatment. In this work, the mycelia of Lactarius deliciosus exhibited an excellent capacity in decolorizing coomassie brilliant blue (CBB). The results demonstrated that the mycelia could treat CBB with high concentrations over a broad range of pH and temperature. The decolorization rate of 99.19% and the removal rate of 16.31 mg·L−1·h were realized. The mycelia could be recycled from decolorizing process for 19 times, indicating a good re-usability. It verified that the lignin peroxidase (121.65 U·L−1) and manganese peroxidase (36.77 U·L−1) were involved in the degradation and decolorization process of CBB. Toxicity assessments indicated the seed germination rate was up to 82.22% while inhibition to Escherichia coli decreased dramatically and no significant effect on Caenorhabditis elegans growth was found. The removal of CBB was a synergistic process accomplished by adsorption and biodegradation. The mycelia could be used for eco-friendly CBB treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mostafa A A, Elshikh M S, Al-Askar A A, Hadibarata T, Yuniarto A, Syafiuddin A. Decolorization and biotransformation pathway of textile dye by Cylindrocephalum aurelium. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 42(9): 1483–1494
Chakraborty S, Basak B, Dutta S, Bhunia B, Dey A. Decolorization and biodegradation of Congo red dye by a novel white rot fungus Alternaria alternata CMERI F6. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 147: 662–666
Hu MR, Chao Y P, Zhang G Q, Xue Z Q, Qian S. Laccase-mediator system in the decolorization of different types of recalcitrant dyes. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2009, 36(1): 45–51
Yang X, Zheng J, Lu Y, Jia R. Degradation and detoxification of the triphenylmethane dye malachite green catalyzed by crude manganese peroxidase from Irpex lacteus F17. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(10): 9585–9597
Chengalroyen M D, Dabbs E R. The microbial degradation of azo dyes: mini review. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2013, 29(3): 389–399
Saratale R G, Saratale G D, Chang J S, Govindwar S P. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: a review. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2011, 42(1): 138–157
Wang N, Chu Y, Wu F, Zhao Z, Xu X. Decolorization and degradation of Congo red by a newly isolated white rot fungus, Ceriporia lacerata, from decayed mulberry branches. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 117: 236–244
Shabbir S, Faheem M, Wu Y. Decolorization of high concentration crystal violet by periphyton bioreactors and potential of effluent reuse for agricultural purposes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 170: 425–436
Boonyakamol A, Imai T, Chairattanamanokorn P, Higuchi T, Sekine M. Key factors regarding decolorization of synthetic anthraquinone and azo dyes. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2009, 158(1): 180–191
Mueangtoom K, Kittl R, Mann O, Haltrich D, Ludwig R. Low pH dye decolorization with ascomycete Lamprospora wrightii laccase. Biotechnology Journal, 2010, 5(8): 857–870
Przystaś W, Zabłocka-Godlewska E, Grabińska-Sota E. Biological removal of azo and triphenylmethane dyes and toxicity of process by-products. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2012, 223(4): 1581–1592
Yang X, Wang J, Zhao X, Wang Q, Xue R. Increasing manganese peroxidase production and biodecolorization of triphenylmethane dyes by novel fungal consortium. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(22): 10535–10541
Kumar K V, Sivanesan S, Ramamurthi V. Adsorption of malachite green onto Pithophora sp., a fresh water algae: equilibrium and kinetic modelling. Process Biochemistry, 2005, 40(8): 2865–2872
He H, Yang S, Yu K, Ju Y, Sun C, Wang L. Microwave induced catalytic degradation of crystal violet in nano-nickel dioxide suspensions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173(1–3): 393–400
Ayed L, Mahdhi A, Cheref A, Bakhrouf A. Decolorization and degradation of azo dye methyl red by an isolated Sphingomonas paucimobilis: biotoxicity and metabolites characterization. Desalination, 2011, 274(1–3): 272–277
Verma P, Madamwar D. Decolourization of synthetic dyes by a newly isolated strain of Serratia marcescens. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2003, 19(6): 615–618
Ozdemir S, Cirik K, Akman D, Sahinkaya E, Cinar O. Treatment of azo dye-containing synthetic textile dye effluent using sulfidogenic anaerobic baffled reactor. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 146: 135–143
He X, Song C, Li Y, Wang N, Xu L, Han X, Wei D. Efficient degradation of azo dyes by a newly isolated fungus Trichoderma tomentosum under non-sterile conditions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 150: 232–239
Vajnhandl S, Le Marechal A M. Ultrasound in textile dyeing and the decolouration/mineralization of textile dyes. Dyes and Pigments, 2005, 65(2): 89–101
Veisi H, Razeghi S, Mohammadi P, Hemmati S. Silver nanoparticles decorated on thiol-modified magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4/SiO2-Pr-S-Ag) as a recyclable nanocatalyst for degradation of organic dyes. Materials Science & Engineering C—Materials for Biological Applications, 2019, 97: 624–631
Bankole P O, Adekunle A A, Govindwar S P. Biodegradation of a monochlorotriazine dye, cibacron brilliant red 3B-A in solid state fermentation by wood-rot fungal consortium, Daldinia concentrica and Xylaria polymorpha co-biomass decolorization of cibacron brilliant red 3B-A dye. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 120(A): 19–27
Salami F, Habibi Z, Yousefi M, Mohammadi M. Covalent immobilization of laccase by one pot three component reaction and its application in the decolorization of textile dyes. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 120(A): 144–151
Muthukumaran C, Sivakumar V M, Thirumarimurugan M. Adsorption isotherms and kinetic studies of crystal violet dye removal from aqueous solution using surfactant modified magnetic nanoadsorbent. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2016, 63: 354–362
Watharkar A D, Khandare R V, Kamble A A, Mulla A Y, Govindwar S P, Jadhav J P. Phytoremediation potential of Petunia grandiflora Juss., an ornamental plant to degrade a disperse, disulfonated triphenylmethane textile dye brilliant blue G. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2013, 20(2): 939–949
Salleh M A M, Mahmoud D K, Karim W A W A, Idris A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: a comprehensive review. Desalination, 2011, 280(1–3): 1–13
Gupta V K, Khamparia S, Tyagi I, Jaspal D, Malviya A. Decolorization of mixture of dyes: a critical review. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 1(1): 71–94
Bharagava R N, Mani S, Mulla S I, Saratale G D. Degradation and decolourization potential of an ligninolytic enzyme producing Aeromonas hydrophila for crystal violet dye and its phytotoxicity evaluation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 156: 166–175
van der Zee F P, Villaverde S. Combined anaerobic-aerobic treatment of azo dyes—a short review of bioreactor studies. Water Research, 2005, 39(8): 1425–1440
Anastasi A, Spina F, Romagnolo A, Tigini V, Prigione V, Varese G C. Integrated fungal biomass and activated sludge treatment for textile wastewaters bioremediation. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 123: 106–111
Zerva A, Zervakis G I, Christakopoulos P, Topakas E. Degradation of olive mill wastewater by the induced extracellular ligninolytic enzymes of two wood-rot fungi. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 203: 791–798
Rajesh R, Iyer S S, Ezhilan J, Kumar S S, Venkatesan R. Graphene oxide supported copper oxide nanoneedles: an efficient hybrid material for removal of toxic azo dyes. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2016, 166: 49–55
Saratale R G, Gandhi S S, Purankar M V, Kurade M B, Govindwar S P, Oh S E, Saratale G D. Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye C.I. Remazol Red and textile effluent by isolated Lysinibacillus sp. RGS. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2013, 115(6): 658–667
Ramsay J A, Mok W H W, Luu Y S, Savage M. Decoloration of textile dyes by alginate-immobilized Trametes versicolor. Chemo-sphere, 2005, 61(7): 956–964
Munck C, Thierry E, Gräßle S, Chen S H, Ting A S Y. Biofilm formation of filamentous fungi Coriolopsis sp. ion simple muslin cloth to enhance removal of triphenylmethane dyes. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 214: 261–266
Paz A, Carballo J, Pérez M J, Domínguez J M. Biological treatment of model dyes and textile wastewaters. Chemosphere, 2017, 181: 168–177
Janović B S, Mićić Vićovac M L, Vujčić ZM, Vujčić M T. Tailor-made biocatalysts based on scarcely studied acidic horseradish peroxidase for biodegradation of reactive dyes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(4): 3923–3933
Kulkarni A N, Watharkar A D, Rane N R, Jeon B, Govindwar S P. Decolorization and detoxification of dye mixture and textile effluent by lichen Dermatocarpon vellereceum in fixed bed upflow bioreactor with subsequent oxidative stress study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 148: 17–25
Pandey R K, Tewari S, Tewari L. Lignolytic mushroom Lenzites elegans WDP2: laccase production, characterization, and bioremediation of synthetic dyes. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 158: 50–58
Zhao W, Wei Z, Zhang L, Wu X, Wang X. Cr doped SnS2 nanoflowers: preparation, characterization and photocatalytic decolorization. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2018, 88: 173–180
Shabbir S, Faheem M, Ali N, Kerr P G, Wu Y. Periphyton biofilms: a novel and natural biological system for the effective removal of sulphonated azo dye methyl orange by synergistic mechanism. Chemosphere, 2017, 167: 236–246
Agrawal A, Chakraborty S. A kinetic study of pyrolysis and combustion of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris using thermo-gravimetric analysis. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 128: 72–80
Legerska B, Chmelova D, Ondrejovic M. Decolourization and detoxification of monoazo dyes by laccase from the white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 285: 84–90
Kumar R, Negi S, Sharma P, Prasher I B, Chaudhary S, Dhau J S, Umar A. Wastewater cleanup using Phlebia acerina fungi: an insight into mycoremediation. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 228: 130–139
Wang M, Zhang Q, Yao S. A novel biosorbent formed of marine-derived Penicillium janthinellum mycelial pellets for removing dyes from dye-containing wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 259: 837–844
Daâssi D, Mechichi T, Nasri M, Rodriguez-Couto S. Decolorization of the metal textile dye Lanaset Grey G by immobilized white-rot fungi. Journal of Environmental Management, 2013, 129: 324–332
Vitor V, Corso C R. Decolorization of textile dye by Candida albicans isolated from industrial effluents. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2008, 35(11): 1353–1357
Shabbir S, Faheem M, Ali N, Kerr P G, Wu Y. Evaluating role of immobilized periphyton in bioremediation of azo dye amaranth. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 225: 395–401
Dos Santos A B, Bisschops I A E, Cervantes F J, van Lier J B. Effect of different redox mediators during thermophilic azo dye reduction by anaerobic granular sludge and comparative study between mesophilic (30 °C) and thermophilic (55 °C) treatments for decolourisation of textile wastewaters. Chemosphere, 2004, 55(9): 1149–1157
Bedekar P A, Saratale R G, Saratale G D, Govindwar S P. Oxidative stress response in dye degrading bacterium Lysinibacillus sp. RGS exposed to reactive orange 16, degradation of RO16 and evaluation of toxicity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2014, 21(18): 11075–11085
Xu J Z, Zhang J L, Hu K H, Zhang W G. The relationship between lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase production capacities and cultivation periods of mushrooms. Microbial Biotechnology, 2013, 6(3SI): 241–247
Chen S H, Yien Ting A S. Biosorption and biodegradation potential of triphenylmethane dyes by newly discovered Penicillium simplicissimum isolated from indoor wastewater sample. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2015, 103: 1–7
Chen H, Guo S, Li H, Zhou D, Cao X, Wang C, Liu Y, Xiang M, Li L, Yu Y. Multi-generational effects and variations of stress response by hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) exposure in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 245: 216–222
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Anhui Provincial Program on Key Research and Development Project (Grant No. 202004a06020021), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21606002), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (CN) (Grant No. 1708085QC64) and the Undergraduate Research Training Programs for Innovation (Grant Nos. 201910357069, S201910357427).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
11705_2020_1952_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Biodegradation and detoxification of the triphenylmethane dye coomassie brilliant blue by the extracellular enzymes from mycelia of Lactarius deliciosus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Wu, QX., Cheng, XD. et al. Biodegradation and detoxification of the triphenylmethane dye coomassie brilliant blue by the extracellular enzymes from mycelia of Lactarius deliciosus. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15, 421–436 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1952-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1952-7