Abstract
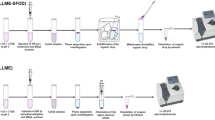
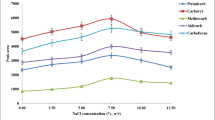
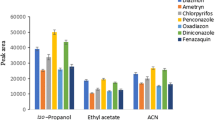
In this study, salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction (SALLE) method is coupled with reversed-phase dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (RP-DLLME) as a novel method for the determination of paraquat in various samples. Firstly, paraquat was extracted from the aqueous phase into the acetonitrile and then it pre-concentrated into the aqueous phase using the RP-DLLME method. Influential parameters of SALLE such as extracting solvent, volume of extracting solvent, sample pH, salt and its concentration were optimized. Also, effective parameters of RP-DLLME including immiscible solvent and its volume, and water volume as extracting solvent were investigated. Under the optimized conditions recoveries and relative standard deviations were in the range of 80.0–96.0 and 3.5–7.5, respectively. The limit of detection and limit of quantification of method were 0.02 and 0.09 µg/mL, respectively. The proposed method successfully was applied for the determination of paraquat in food and environmental samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.H. Jae, H.K. Kim, J.T. Kwon, S.H. Lee, S. Park, H.W. Gil, H.-Y. Song, S.-Y. Hong, Effect of MDR1 gene polymorphisms on mortality in paraquat intoxicated patients. Sci. Rep. 6, 31765 (2016)
T.R. Hawkes, Mechanisms of resistance to paraquat in plants. Pest Manag. Sci. 70, 1316–1323 (2014)
Y. Chen, Y.C. Nie, Y.L. Luo, F. Lin, Y.F. Zheng, G.H. Cheng, H. Wub, K.J. Zhang, W.W. Su, J.G. Shen, P.B. Li, Protective effects of naringin against paraquat-induced acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 58, 133–140 (2013)
F. Mohamed, N.A. Buckley, S. Jayamanne, J.W. Pickering, P. Peake, C. Palangasinghe, T. Wijerathna, I. Ratnayake, F. Shihana, Z.H. Endre, Kidney damage biomarkers detect acute kidney injury but only functional markers predict mortality after paraquat ingestion. Toxicol. Lett. 237, 140–150 (2015)
H.W. Gil, J.R. Hong, S.H. Jang, S.Y. Hong, Diagnostic and therapeutic approach for acute paraquat intoxication. J. Korean Med. Sci. 29, 1441–1449 (2014)
P. Chuntib, J. Jakmunee, Simple flow injection colorimetric system for determination of paraquat in natural water. Talanta 144, 432–438 (2015)
K. Tyszczuk-Rotko, I. Bęczkowska, A. Nosal-Wiercińska, Simple, selective and sensitive voltammetric method for the determination of herbicide (paraquat) using a bare boron-doped diamond electrode. Diam. Relat. Mater. 50, 86–90 (2014)
A. Gevaerd, P.R. de Oliveira, A.S. Mangrich, M.F. Bergamini, L.H. Marcolino-Junior, Evaluation of antimony microparticles supported on biochar for application in the voltammetric determination of paraquat. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 26, 123–129 (2016)
C. Kalinke, A.S. Mangrich, L.H. Marcolino-Junior, M.F. Bergamini, Carbon paste electrode modified with biochar for sensitive electrochemical determination of paraquat. Electroanalysis 28, 764–769 (2016)
W. Siangproh, T. Somboonsuk, O. Chailapakul, K. Songsrirote, Novel colorimetric assay for paraquat detection on-silica bead using negatively charged silver nanoparticles. Talanta 174, 448–453 (2017)
I.R. Pizzutti, G.M.E. Vela, A. de Kok, J.M. Scholten, J.V. Dias, C.D. Cardoso, G. Concenço, R. Vivian, Determination of paraquat and diquat: LC-MS method optimization and validation. Food Chem. 209, 248–255 (2016)
R. Lanaro, J.L. Costa, S.O.S. Cazenave, L.A. Zanolli-Filho, M.F.M. Tavares, A.A.M. Chasin, Determination of herbicides paraquat, glyphosate, and aminomethylphosphonic acid in marijuana samples by capillary electrophoresis. J. Forensic Sci. 60, 241–247 (2015)
S. Jafarinejad, Recent advances in determination of herbicide paraquat in environmental waters and its removal from aqueous solutions: a review. Int. Res. J. Appl. Basic Sci. 9, 1758–1774 (2015)
M. Trojanowicz, K. Kołacińska, Recent advances in flow injection analysis. Analyst 141, 2085–2139 (2016)
S. Hara, N. Sasaki, D. Takase, S. Shiotsuka, K. Ogata, K. Futagami, K. Tamura, Rapid and sensitive HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of paraquat and diquat in human serum. Anal. Sci. 23, 523–526 (2007)
Y.C. Tsao, Y.C. Lai, H.C. Liu, R.H. Liu, D.L. Lin, Simultaneous determination and quantitation of paraquat, diquat, glufosinate and glyphosate in postmortem blood and urine by LC–MS–MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 40, 427–436 (2016)
O. Núñez, J.B. Kim, E. Moyano, M.T. Galceran, S. Terabe, Analysis of the herbicides paraquat, diquat and difenzoquat in drinking water by micellar electrokinetic chromatography using sweeping and cation selective exhaustive injection. J. Chromatogr. A 961, 65–75 (2002)
W.T. Tsai, A review on environmental exposure and health risks of herbicide paraquat. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2, 197–206 (2013)
R. Heydari, M. Hosseini, R. Rezaeepour, Semi-automated salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography to determine three aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 14, 1691–1698 (2017)
R. Rezaeepour, R. Heydari, A. Ismaili, Ultrasound and salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction as an efficient method for natural product extraction. Anal. Methods 7, 3253–3259 (2015)
R. Heydari, S. Zarabi, Development of combined salt- and air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction as a novel sample preparation technique. Anal. Methods 6, 8469–8475 (2014)
M. Hosseini, R. Heydari, M. Alimoradi, Vortex and air assisted liquid-liquid microextraction as a sample preparation method for high-performed liquid chromatography determinations. Talanta 130, 171–176 (2014)
Y.Q. Tang, N. Weng, Salting-out assisted liquid–liquid extraction for bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 5, 1583–1598 (2013)
R. Salimikia, F. Heydari, Yazdankhah, Polyaniline/graphene oxide nanocomposite as a sorbent for extraction and determination of nicotine using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–flame. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 15, 1593–1601 (2018)
M. Mohebbi, R. Heydari, M. Ramezani, Solvent-vapor-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction: a novel method for the determination of phthalate esters in aqueous samples using GC–MS. J. Sep. Sci. 40, 4394–4402 (2017)
M. Rashidipour, R. Heydari, A. Feizbakhsh, P. Hashemi, Rapid monitoring of carvacrol in plants and herbal medicines using matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography flame ionisation detector. Nat. Prod. Res. 29, 621–627 (2015)
M. Rashidipour, R. Heydari, A. Feizbakhsh, P. Hashemi, Rapid screening of oleuropein from olive leaves using matrix solid-phase dispersion and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 97, 1109–1113 (2014)
Z. Pourghobadi, R. Heydari, R. Pourghobadi, M. Rashidipour, Determination of gabapentin in human plasma using simultaneous cloud point extraction and precolumn derivatization by HPLC. Monatsh. Chem. 144, 773–779 (2013)
R. Heydari, Residual solvents determination in pharmaceuticals by static headspace-gas chromatography and headspace liquid-phase microextraction gas chromatography. Anal. Lett. 45, 1875–1884 (2012)
P. Salehi, A.R. Fakhari, S. Nejad Ebrahimi, R. Heydari, Rapid essential oil screening of Rosmarinus officinalis L. by hydrodistillation–headspace solvent microextraction. Flavour Fragr. J. 22, 280–285 (2007)
M.P. Godoy-Caballero, M.I. Acedo-Valenzuela, T. Galeano-Díaz, New reversed phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the determination of phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil by rapid resolution liquid chromatography with UV-visible and mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1313, 291–301 (2013)
M. Hosseini, R. Heydari, M. Alimoradi, Reversed-phase vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction: a new sample preparation method for the determination of amygdalin in oil and kernel samples. J. Sep. Sci. 38, 663–669 (2015)
R. Heydari, M. Rashidipour, N. Naleini, Determination of efavirenz in plasma by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. Curr. Anal. Chem. 10, 280–287 (2014)
M. Mohebbi, R. Heydari, M. Ramezani, Determination of Cu, Cd, Ni, Pb and Zn in edible oils using reversed-phase ultrasonic assisted liquid–liquid microextraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 73, 30–35 (2018)
P. Hashemi, F. Raeisi, A.R. Ghiasvand, A. Rahimi, Reversed-phase dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with central composite design optimization for preconcentration and HPLC determination of oleuropein. Talanta 80, 1926–1931 (2010)
D.I.S. Kolberg, D. Mack, M. Anastassiades, M.T. Hetmanski, R.J. Fussell, T. Meijer, H.G.J. Mol, Development and independent laboratory validation of a simple method for the determination of paraquat and diquat in potato, cereals and pulses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 404, 2465–2474 (2012)
H.S. Lee, K. Kim, J.H. Kim, K.S. Do, S.K. Lee, On-line sample preparation of paraquat in human serum samples using high-performance liquid chromatography with column switching. J. Chromatogr. B 716, 371–374 (1998)
R. Gill, S.C. Qua, A.C. Moffat, High-performance liquid chromatography of paraquat and diquat in urine with rapid sample preparation involving ion-pair extraction on disposable cartridges of octadecylsilica. J. Chromatogr. 255, 483–490 (1983)
S. Ito, T. Nagata, K. Kudo, K. Kimura, T. Imamura, Simultaneous determination of paraquat and diquat in human tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 617, 119–123 (1993)
X.P. Lee, T. Kumazawa, M. Fujishiro, C. Hasegawa, T. Arinobu, H. Seno, A. Ishii, K. Sato, Determination of paraquat and diquat in human body fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 39, 1147–1152 (2004)
B. Winnik, D.B. Barr, M. Thiruchelvam, M.A. Montesano, E.K. Richfield, B. Buckley, Quantification of paraquat, MPTP, and MPP + in brain tissue using microwave-assisted solvent extraction (MASE) and high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 395, 195–201 (2009)
M.R. Brunetto, A.R. Morales, M. Gallignani, J.L. Burguera, M. Burguera, Determination of paraquat in human blood plasma using reversedphase ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with direct sample injection. Talanta 59, 913–921 (2003)
R.D. Whitehead, M.A. Montesano, N.K. Jayatilaka, B. Buckley, B. Winnik, L.L. Needham, D.B. Barr, Method for measurement of the quaternary amine compounds paraquat and diquat in human urine using high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 878, 2548–2553 (2010)
C. Fuke, T. Arao, Y. Morinaga, H. Takaesu, K. Ameno, T. Miyazaki, Analysis of paraquat, diquat and two diquat metabolites in biological materials by high-performance liquid chromatography. Leg. Med. 4, 156–163 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Environmental Health Research Center of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences (grant number: IR.MUK.1395.73) and Razi Herbal Medicines Research Center of Lorestan University of Medical Sciences (grant number: 1980). Also, this study was financially supported by the Biotechnology Development Council of the Islamic Republic of Iran (grant No: 970503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashidipour, M., Heydari, R., Maleki, A. et al. Salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction coupled with reversed-phase dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for sensitive HPLC determination of paraquat in environmental and food samples. Food Measure 13, 269–276 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9941-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9941-y